ISO standards
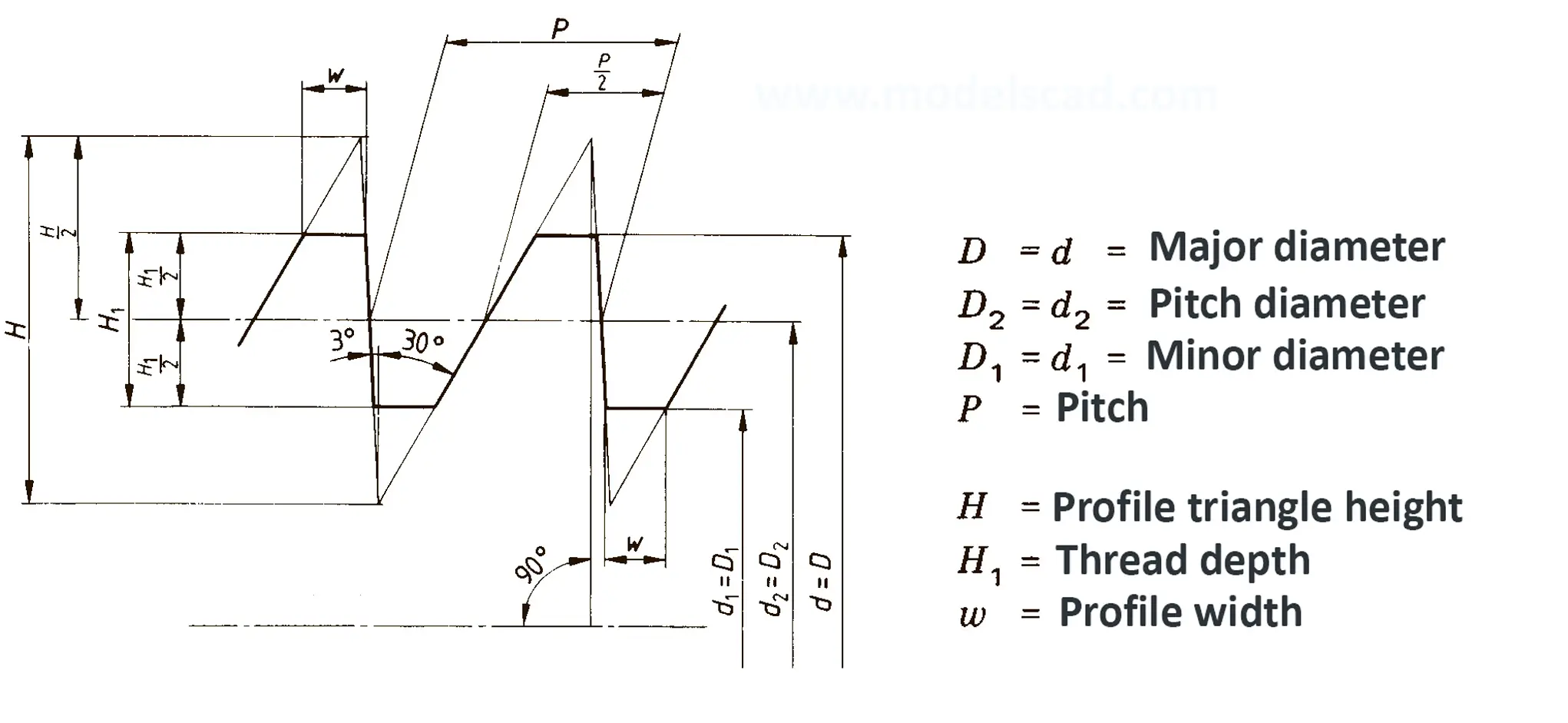
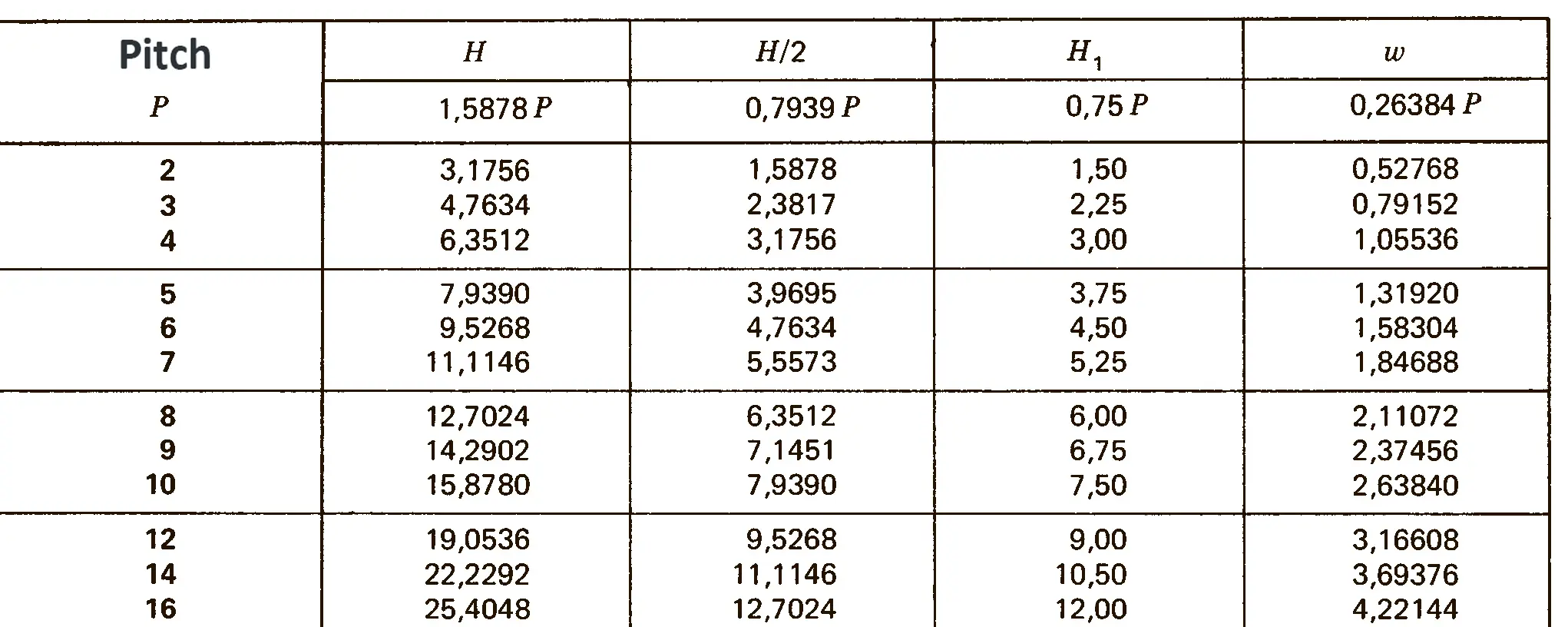
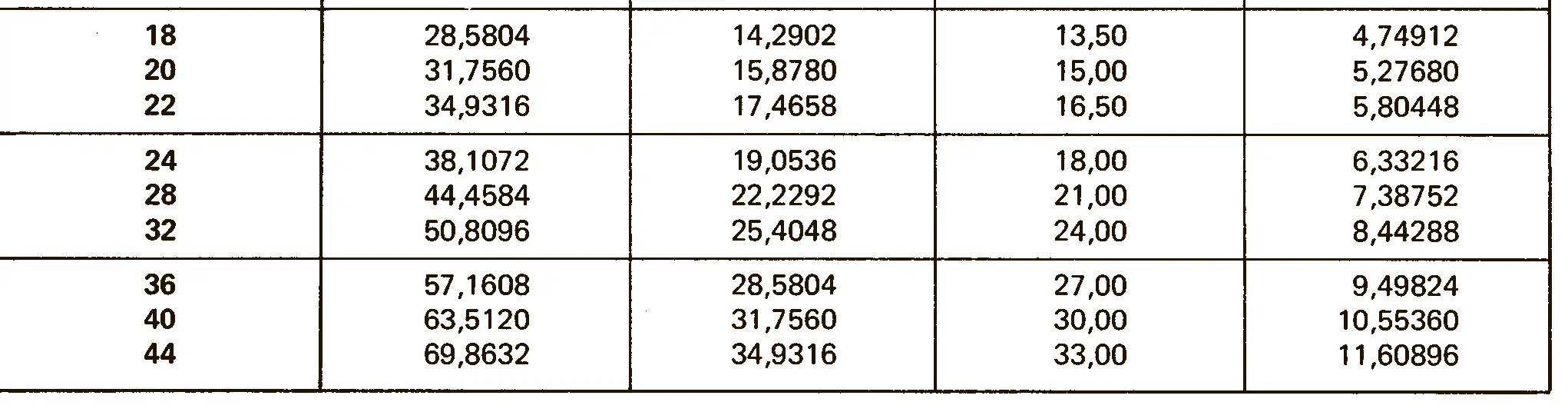
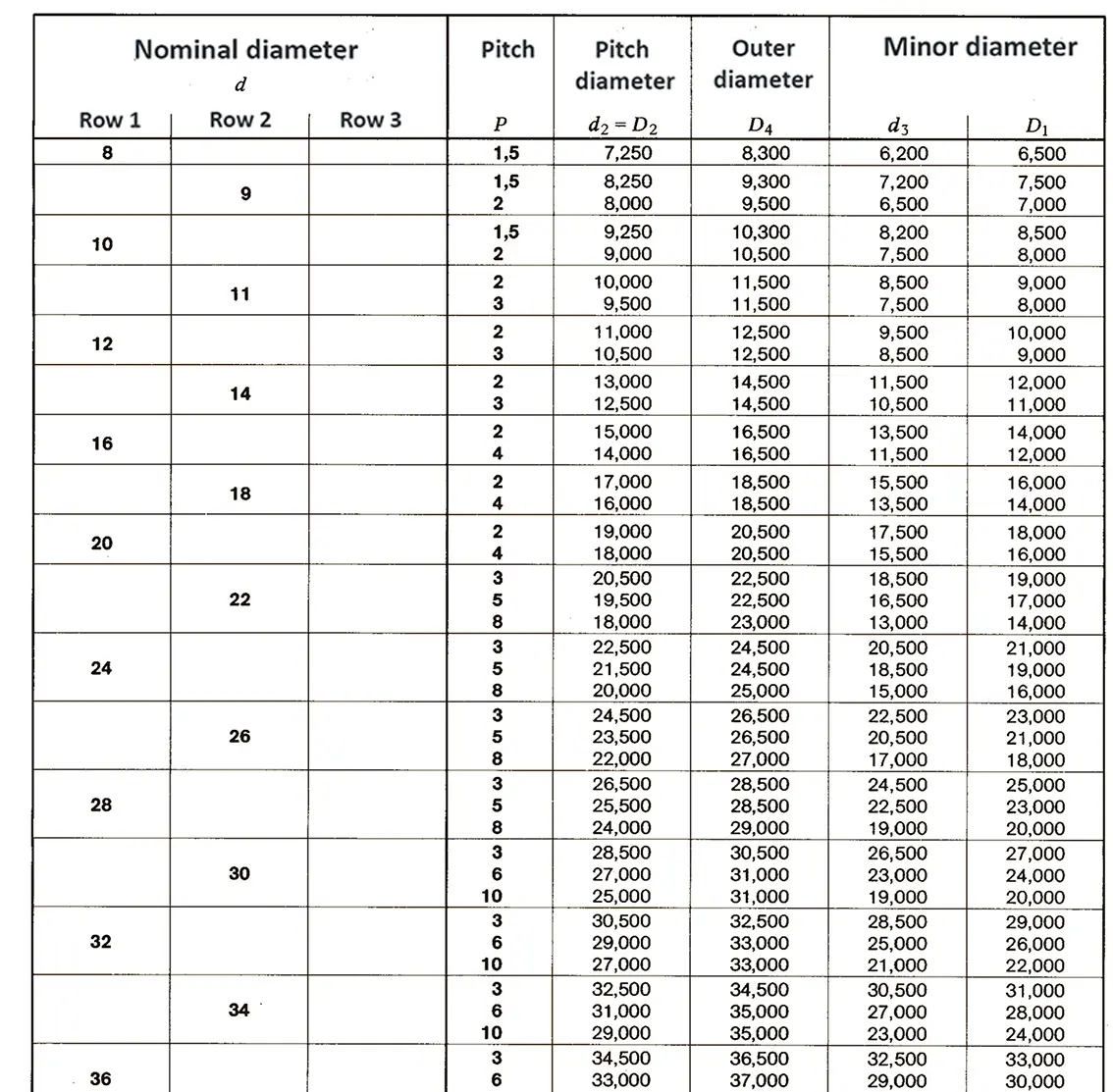
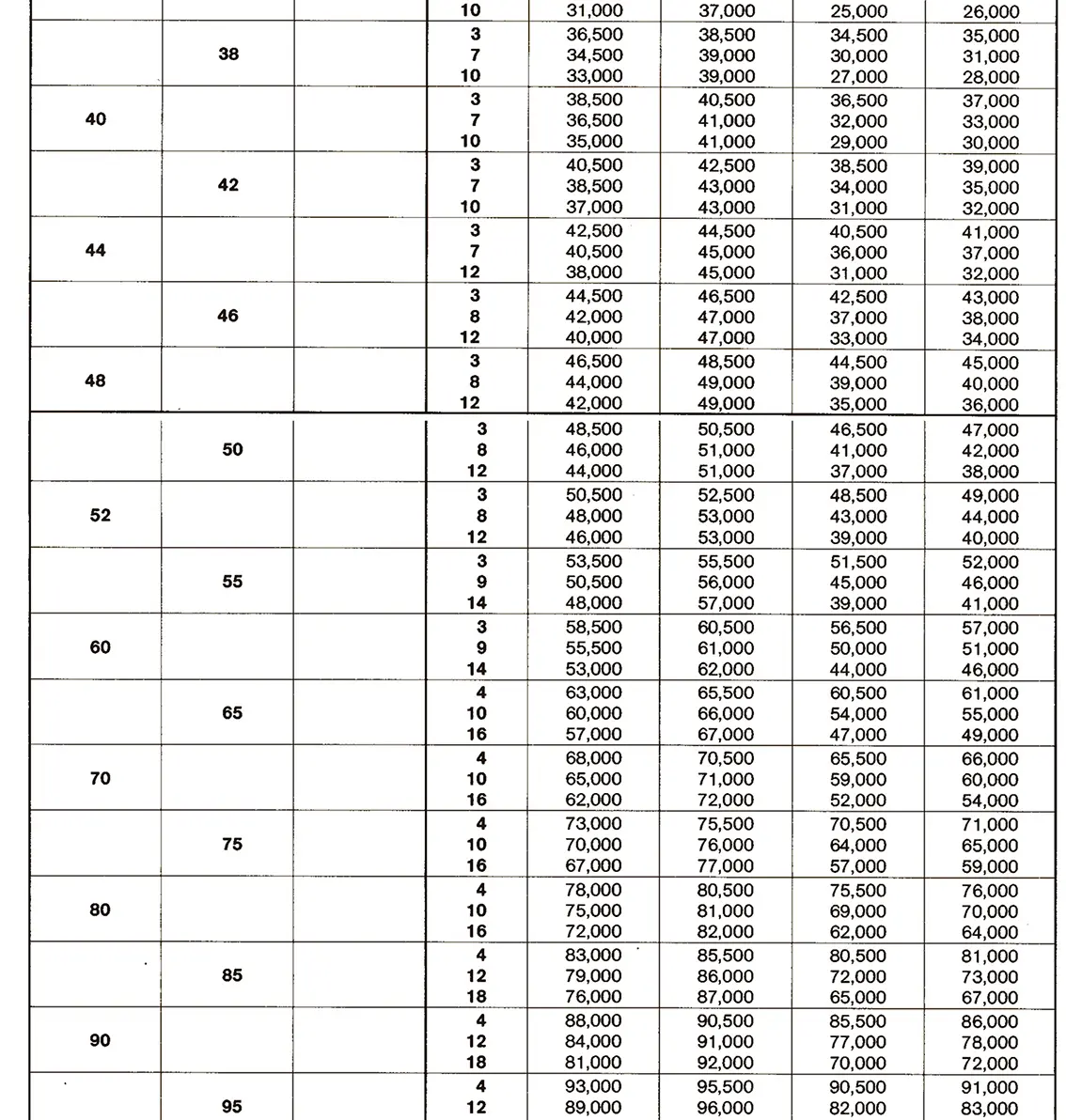
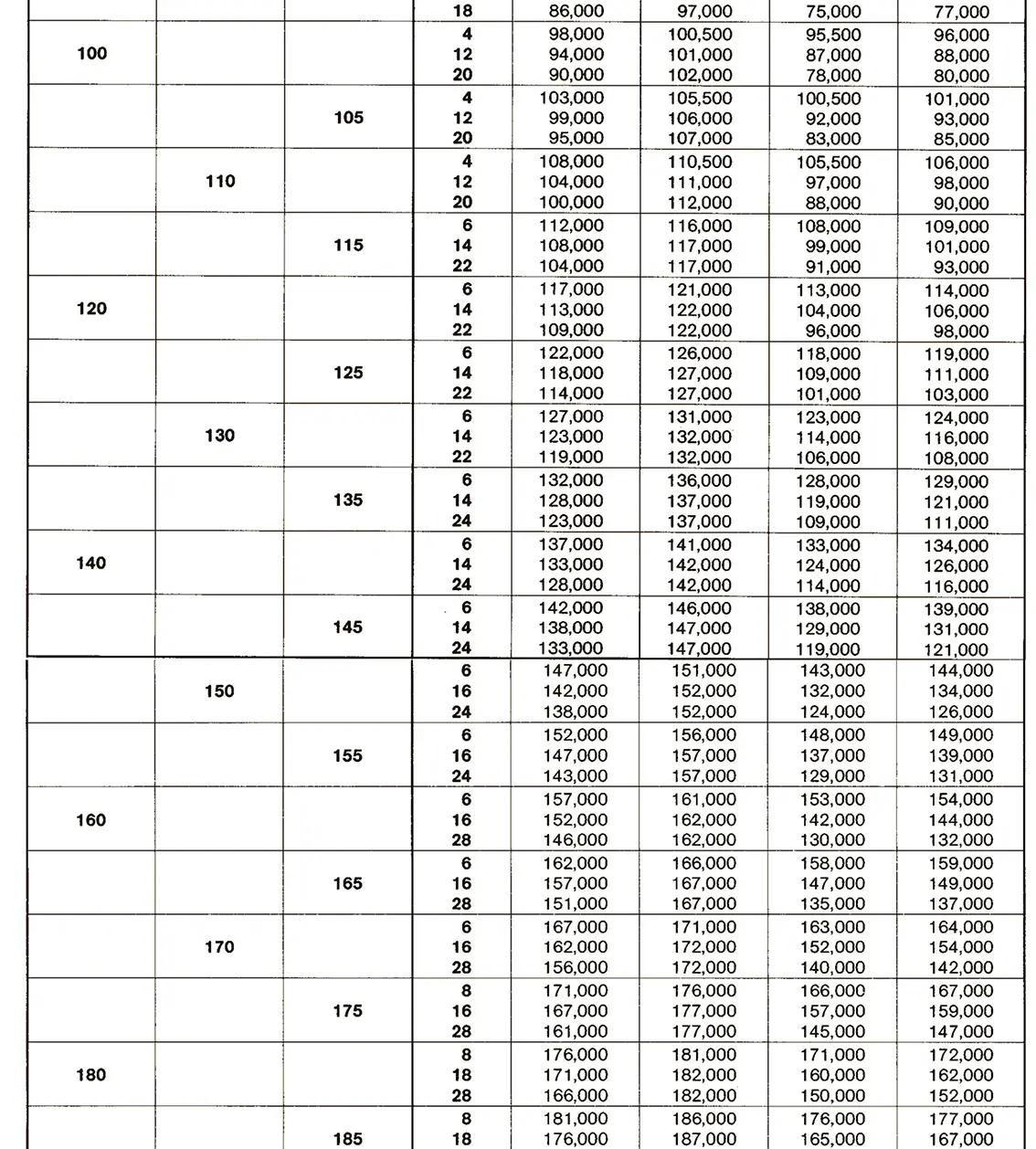
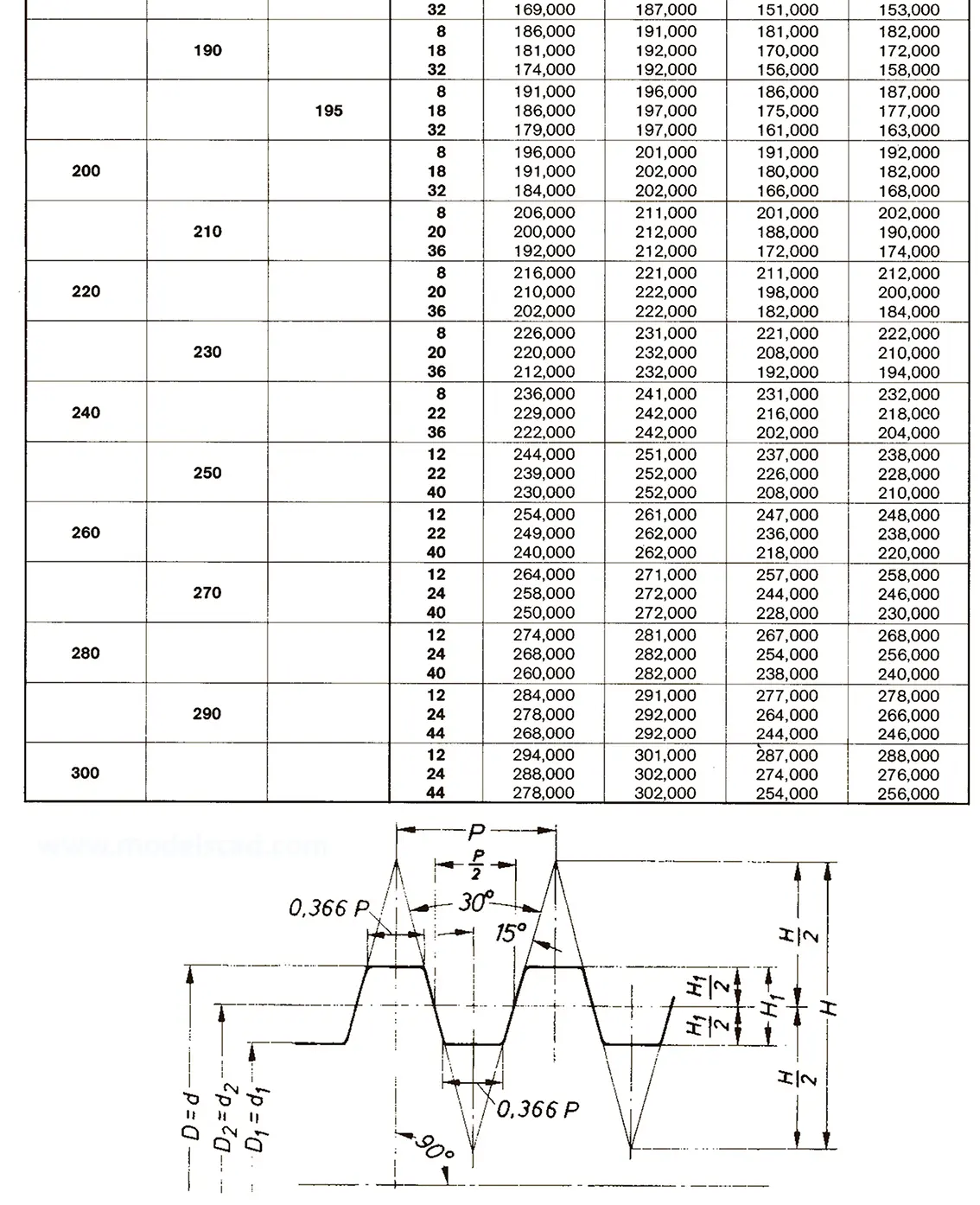
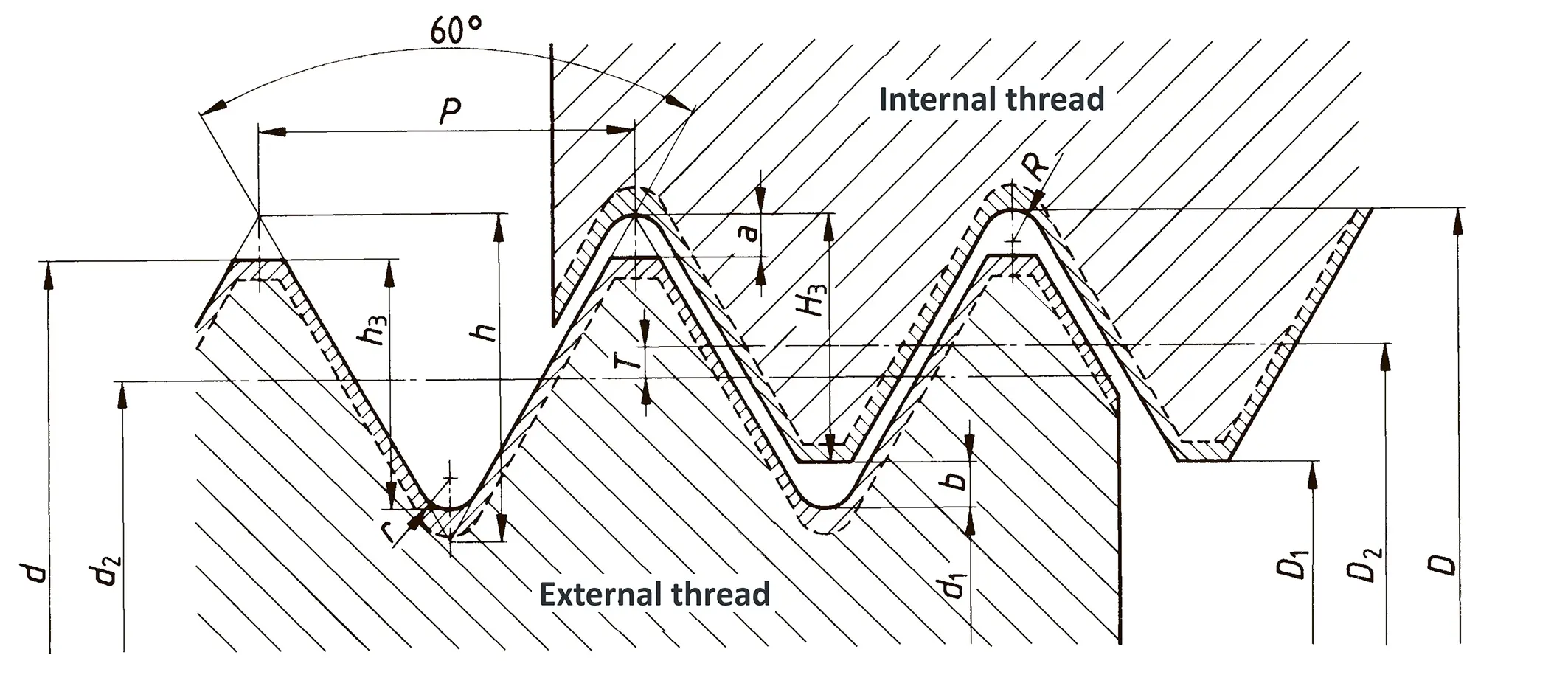
Standardized thread that replaces the old metric and most inch threads. It is designated by the letter M (metric), followed by a number indicating the nominal diameter, the angle of inclination of the profile is 60°.
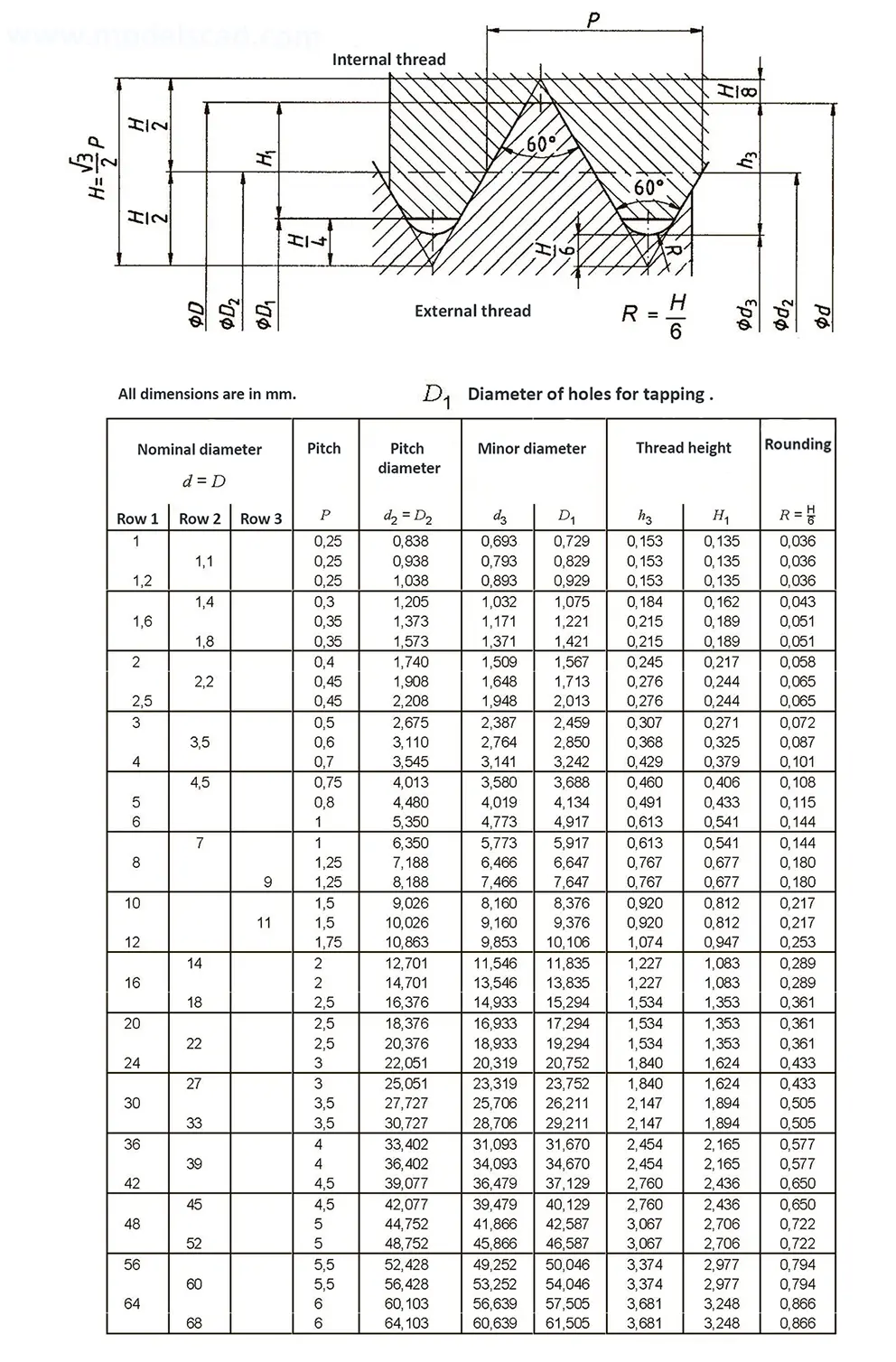
The fine thread ISO DIN 13-2 has a smaller pitch than the coarse thread, which increases its elasticity. This thread is used, for example, for adjusting screws in measuring instruments, which allows for more precise settings. The designation consists of the letter M, nominal diameter and pitch, angle of inclination 60°. Pitches 0.2 mm, 0.25 mm, 0.35 mm.
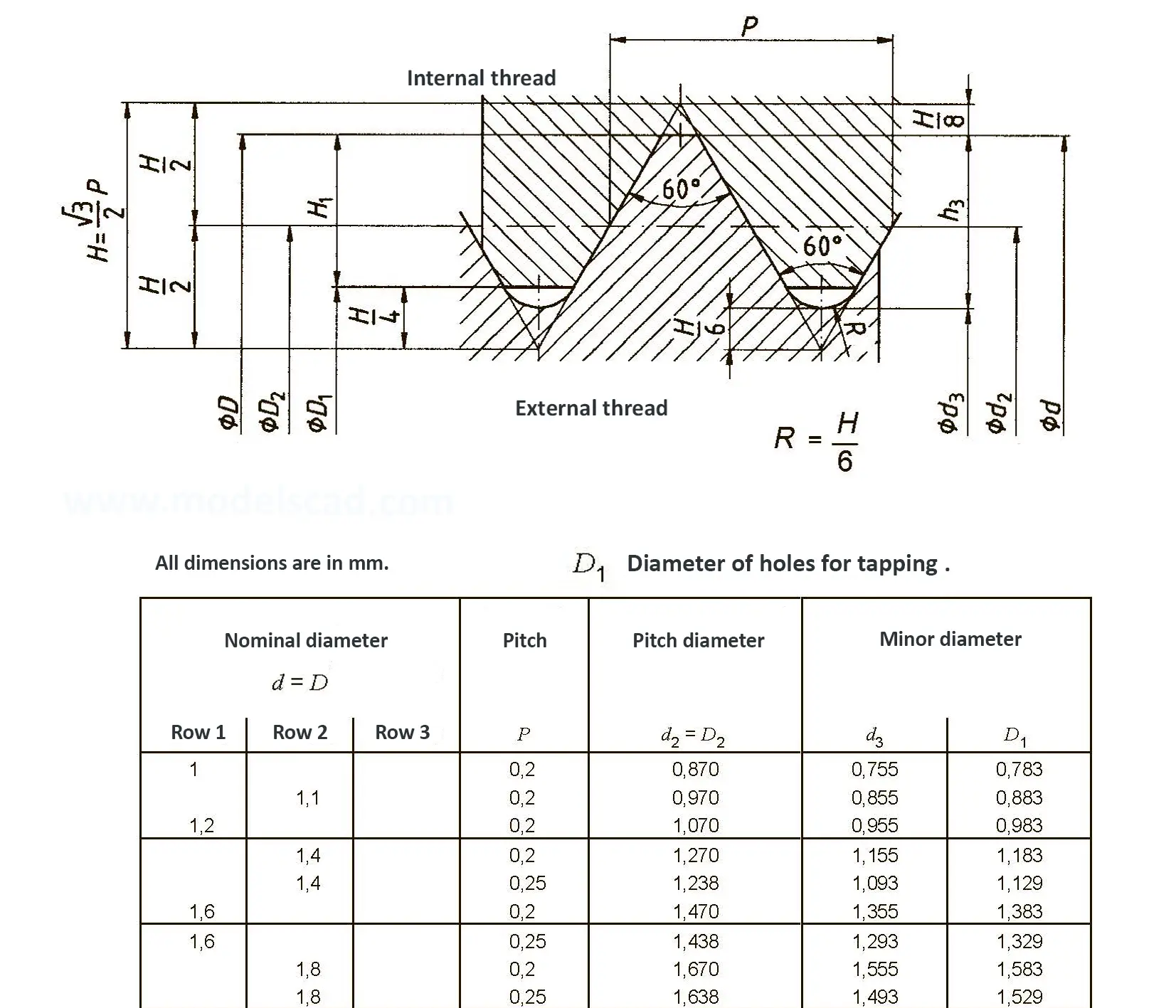
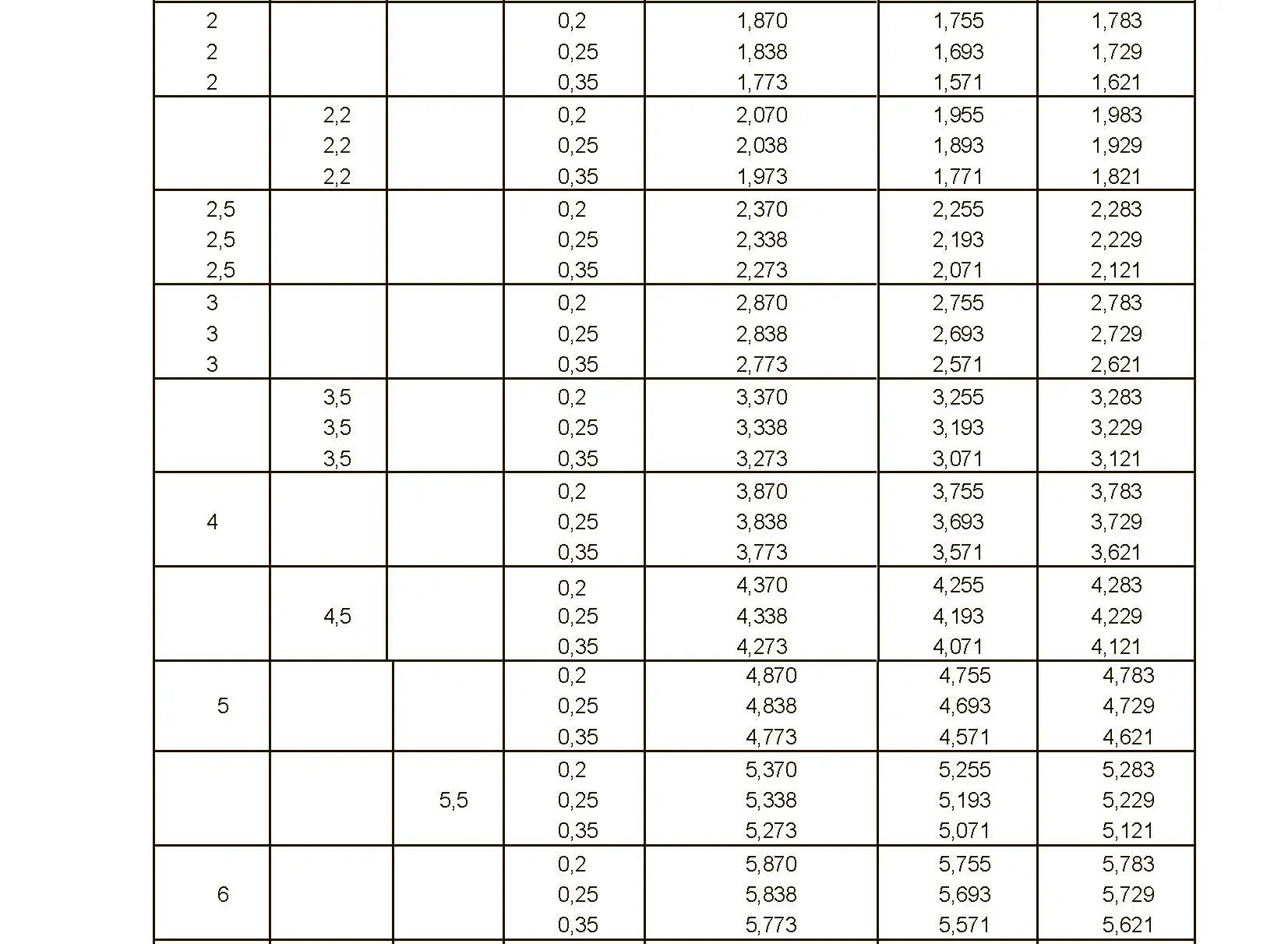
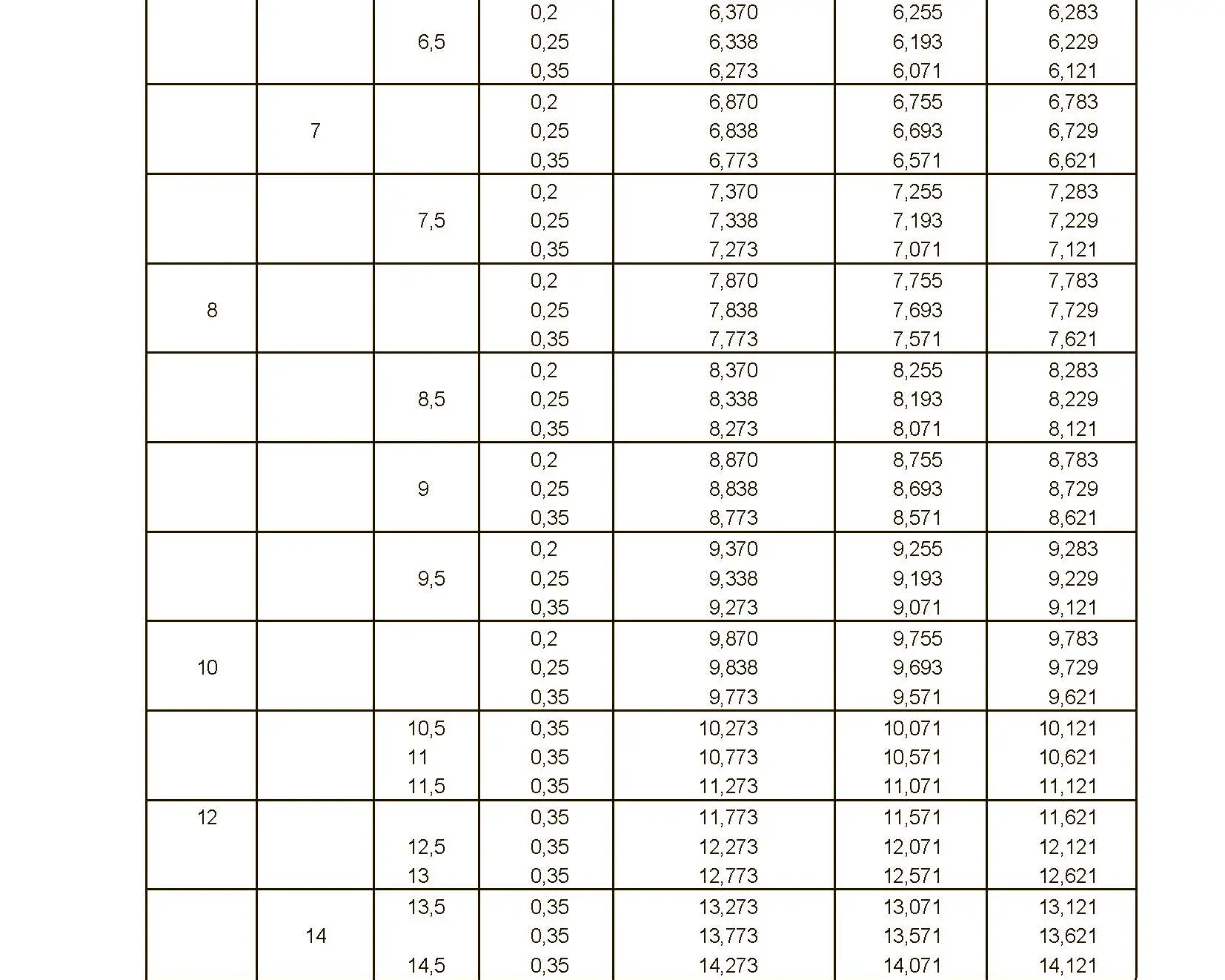
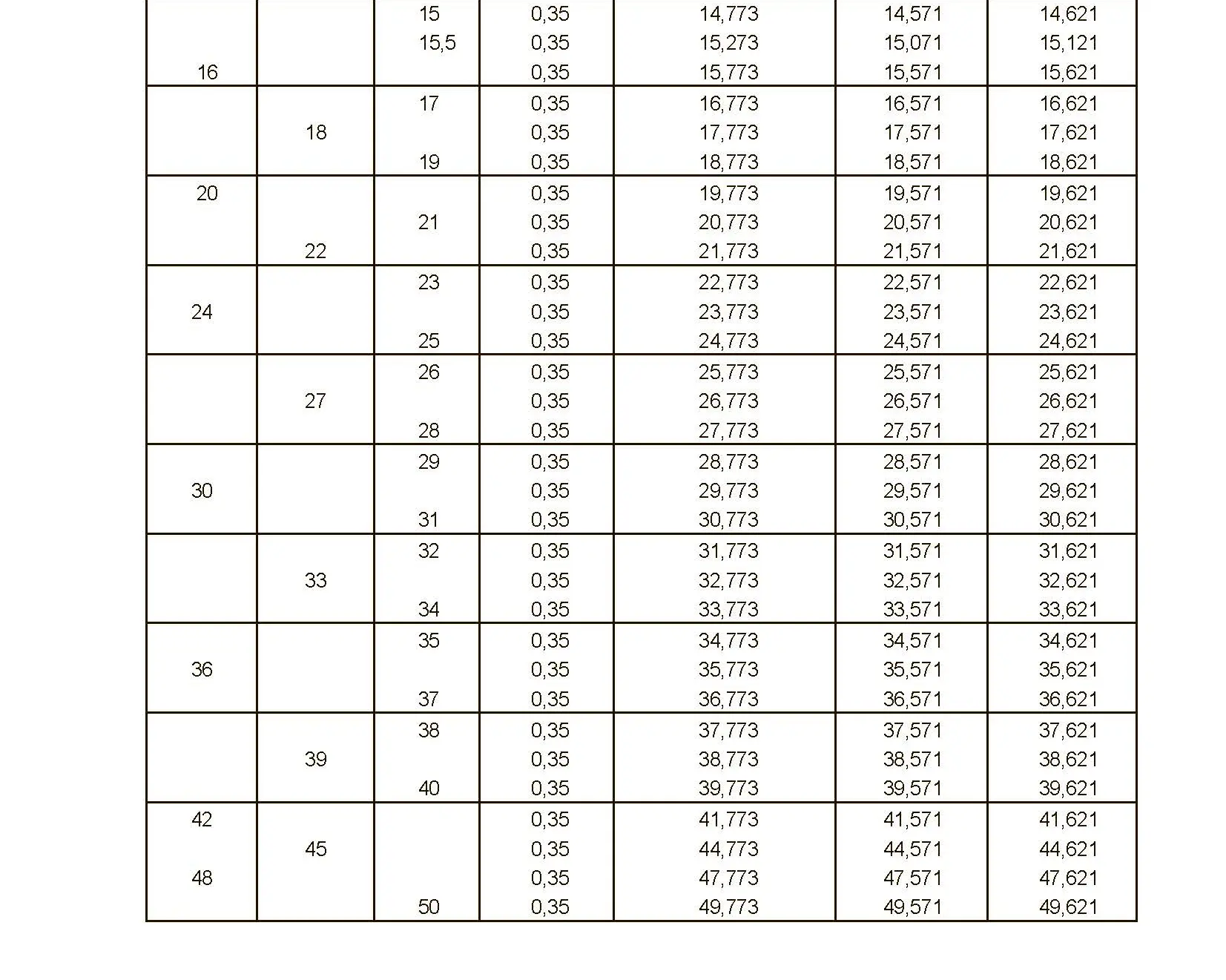
The fine thread ISO DIN 13-3 has a smaller pitch than the coarse thread, which increases its elasticity. This thread is used, for example, for adjusting screws in measuring instruments, which allows for more precise settings. The designation consists of the letter M, nominal diameter and pitch, angle of inclination 60°. Pitch 0.5 mm.
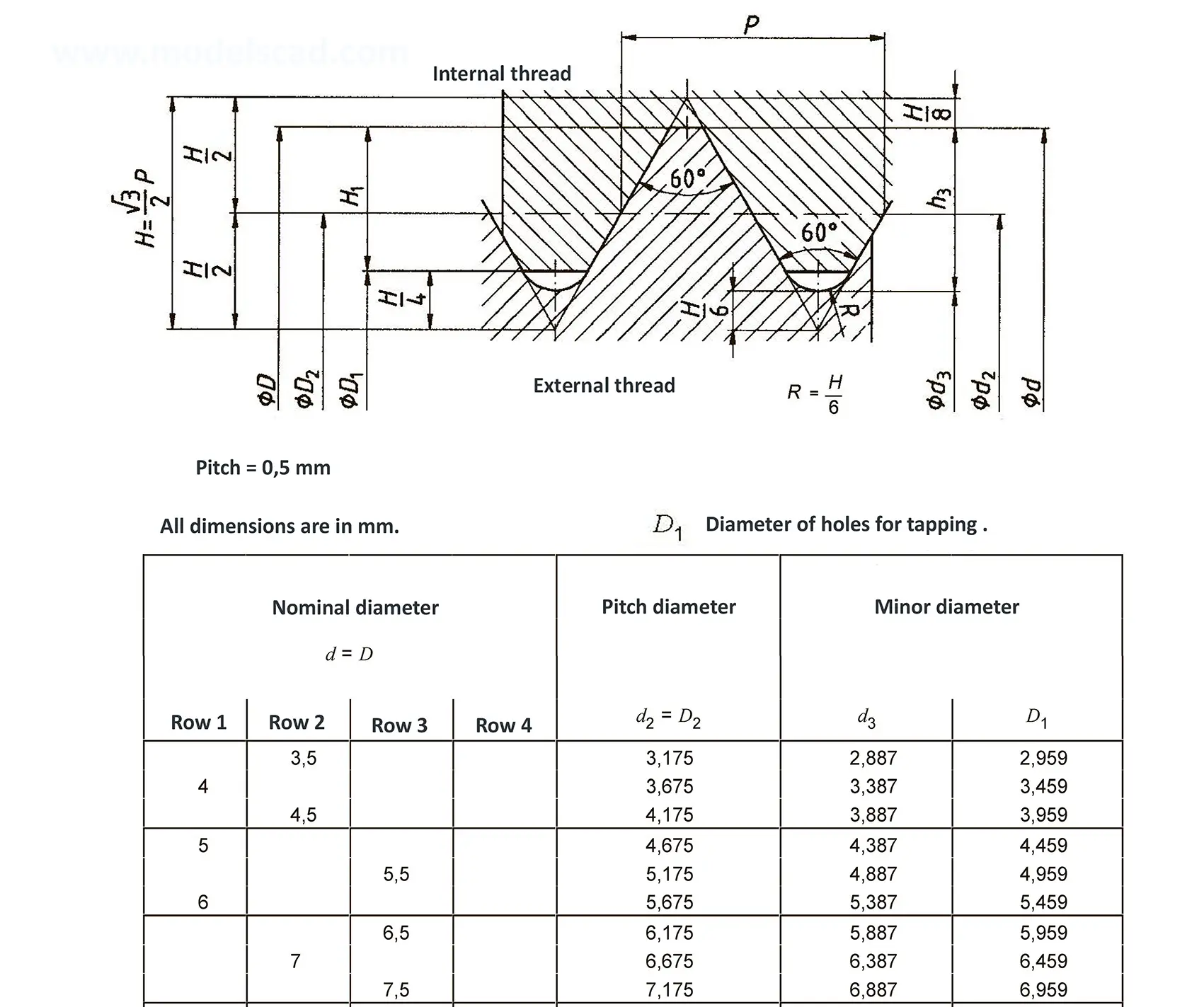
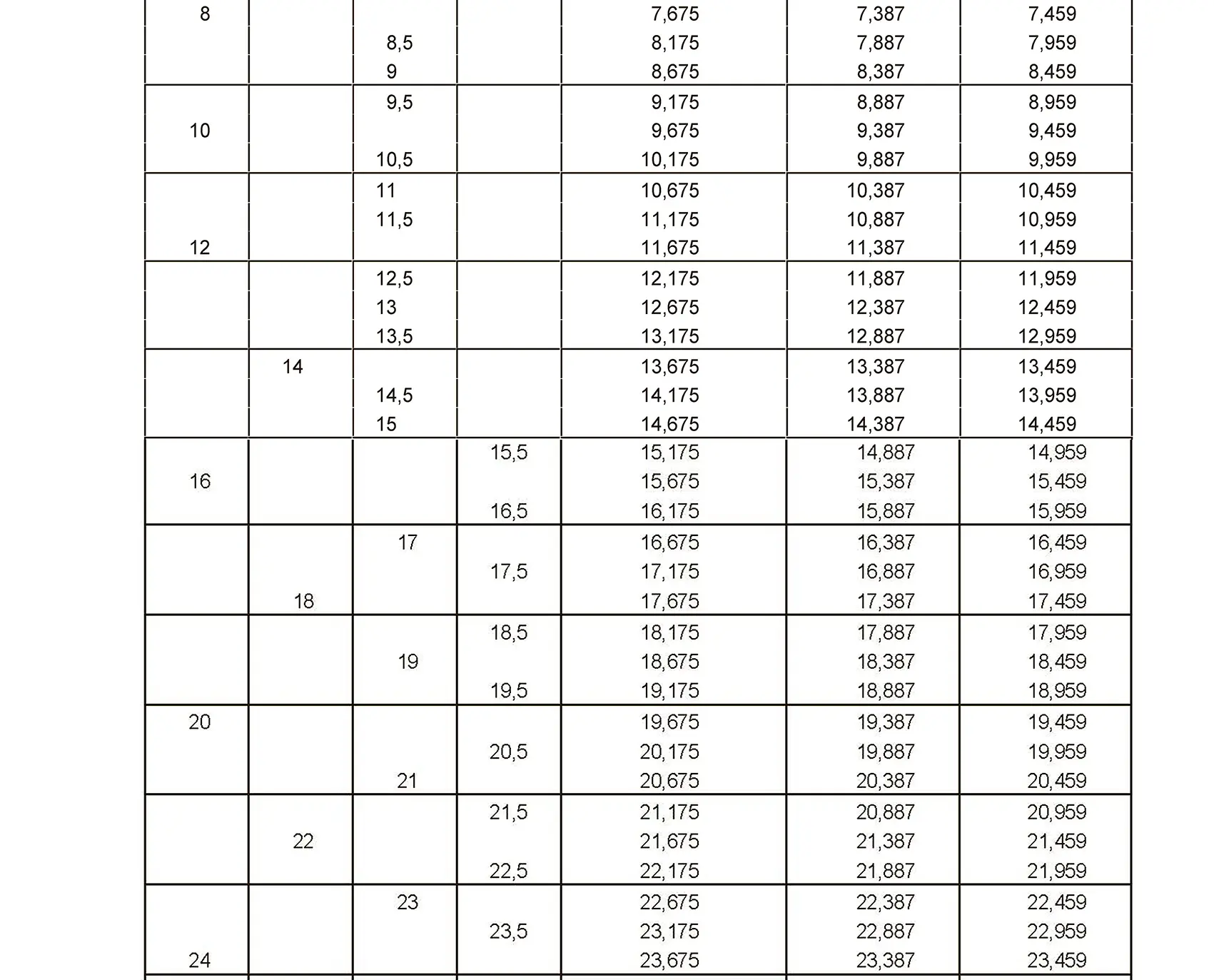
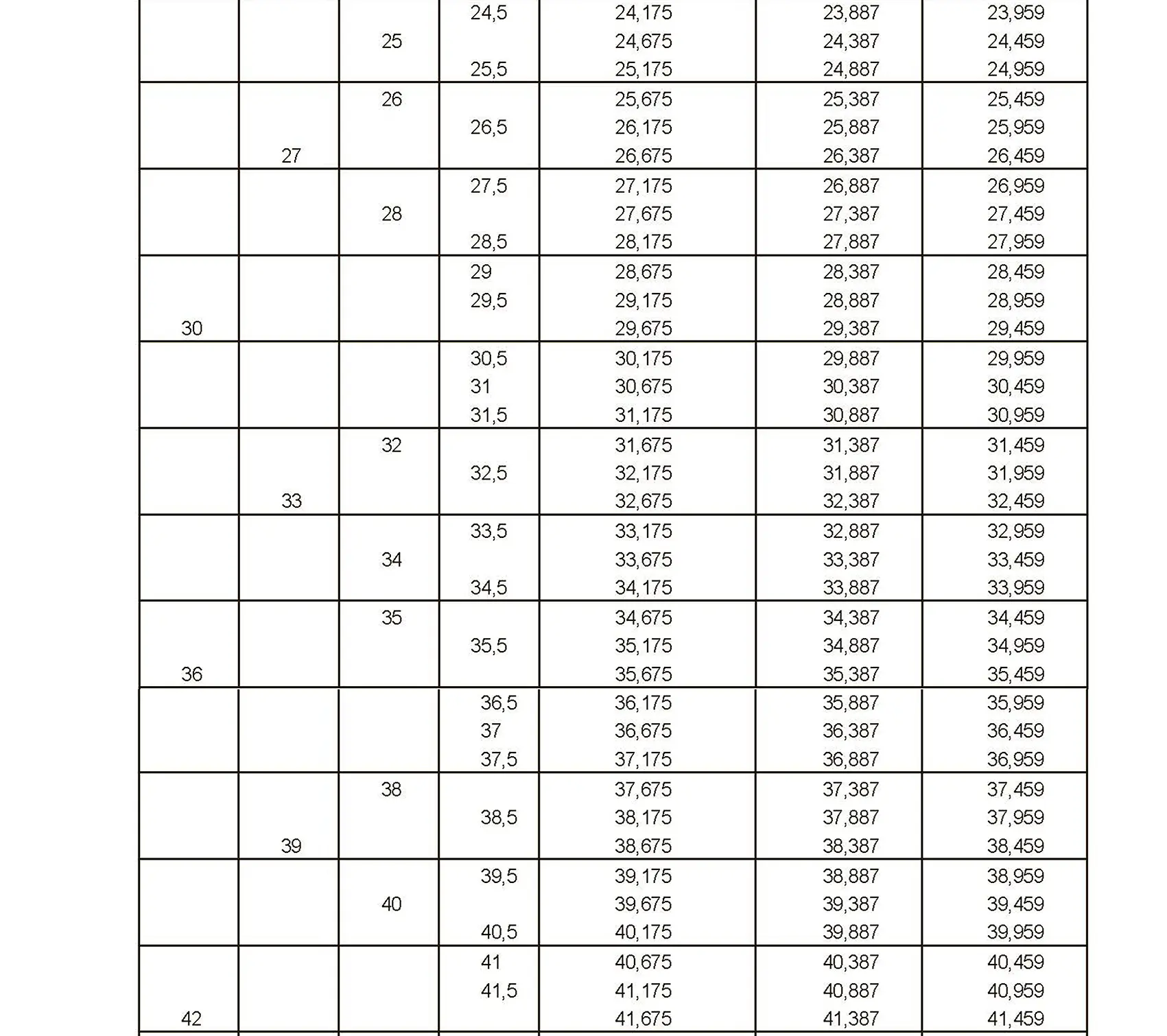
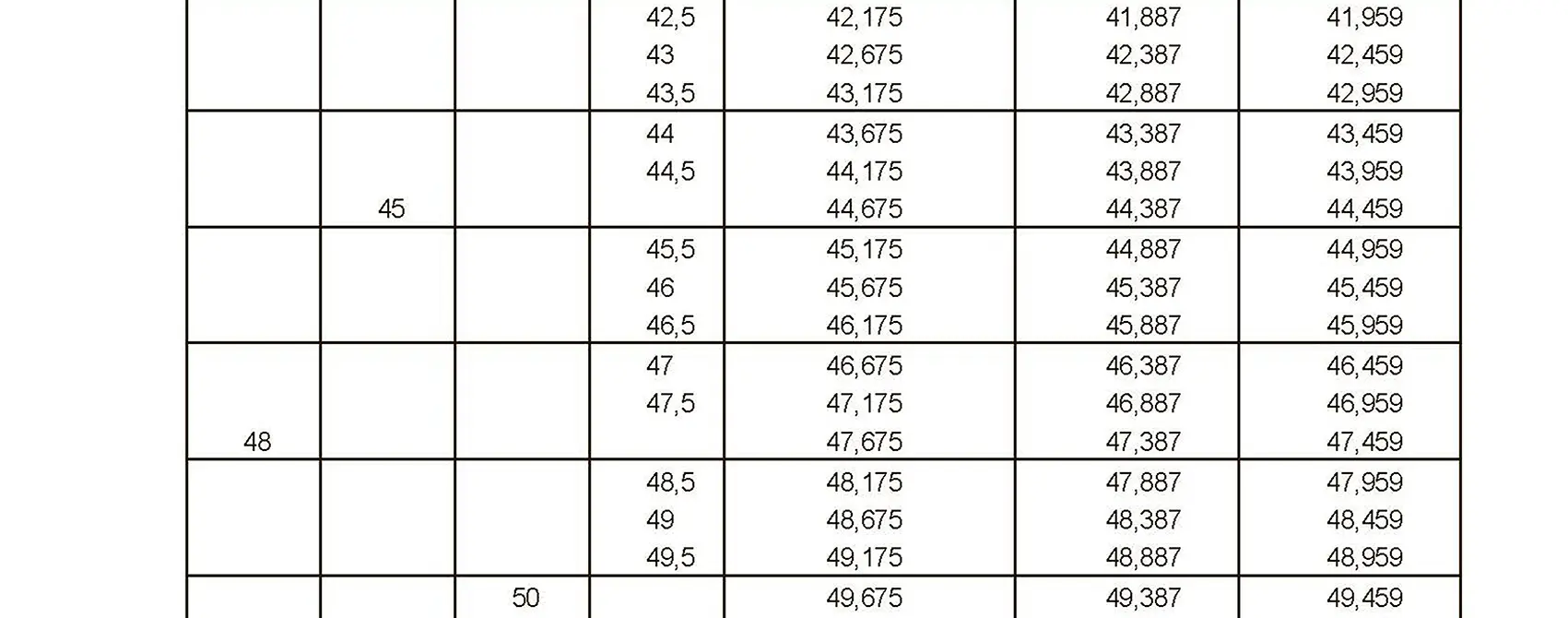
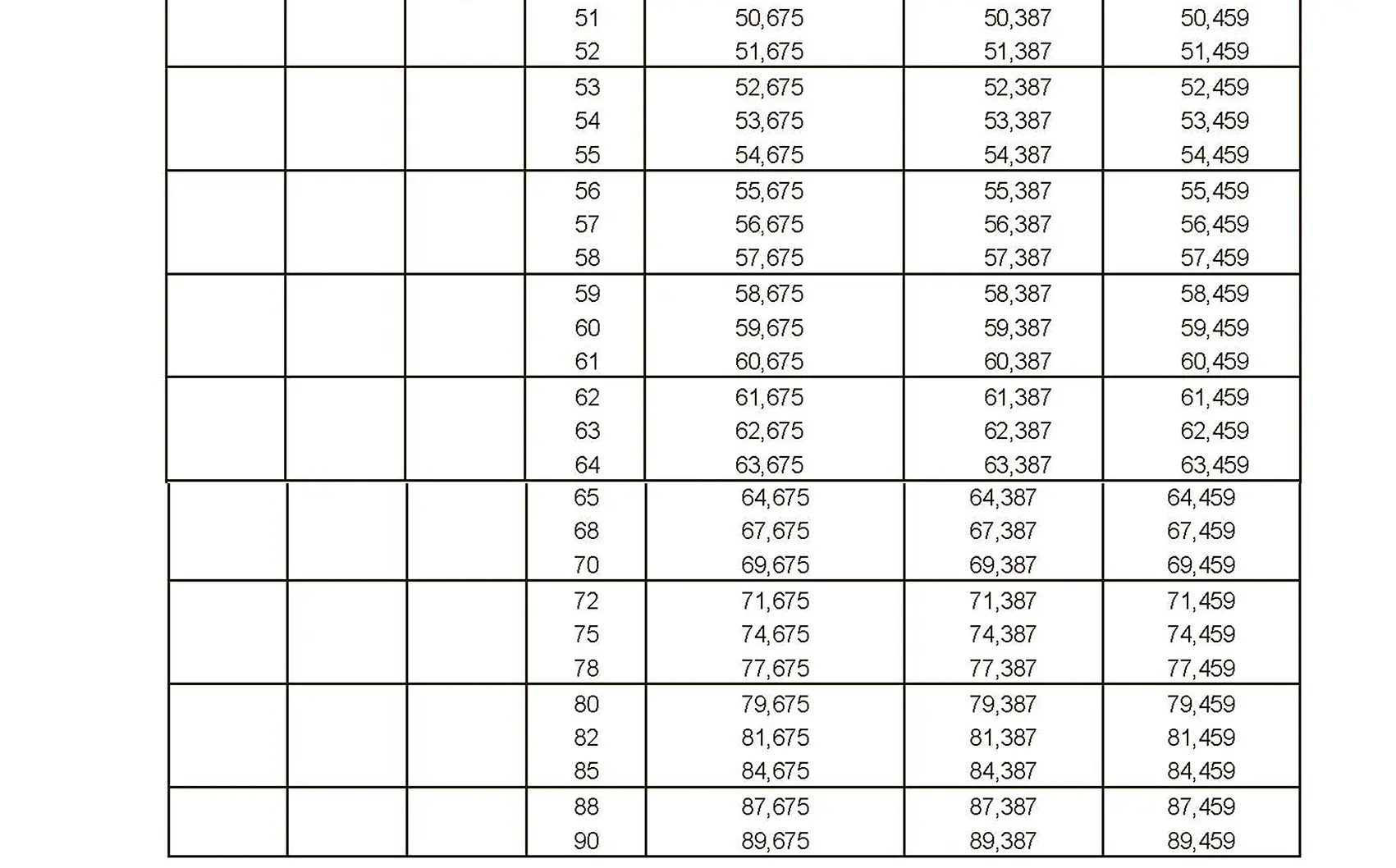
The fine thread ISO DIN 13-4 has a smaller pitch than the coarse thread, which increases its elasticity. This thread is used, for example, for adjusting screws in measuring instruments, which allows for more precise settings. The designation consists of the letter M, nominal diameter and pitch, angle of inclination 60°. Pitch 0.75 mm.
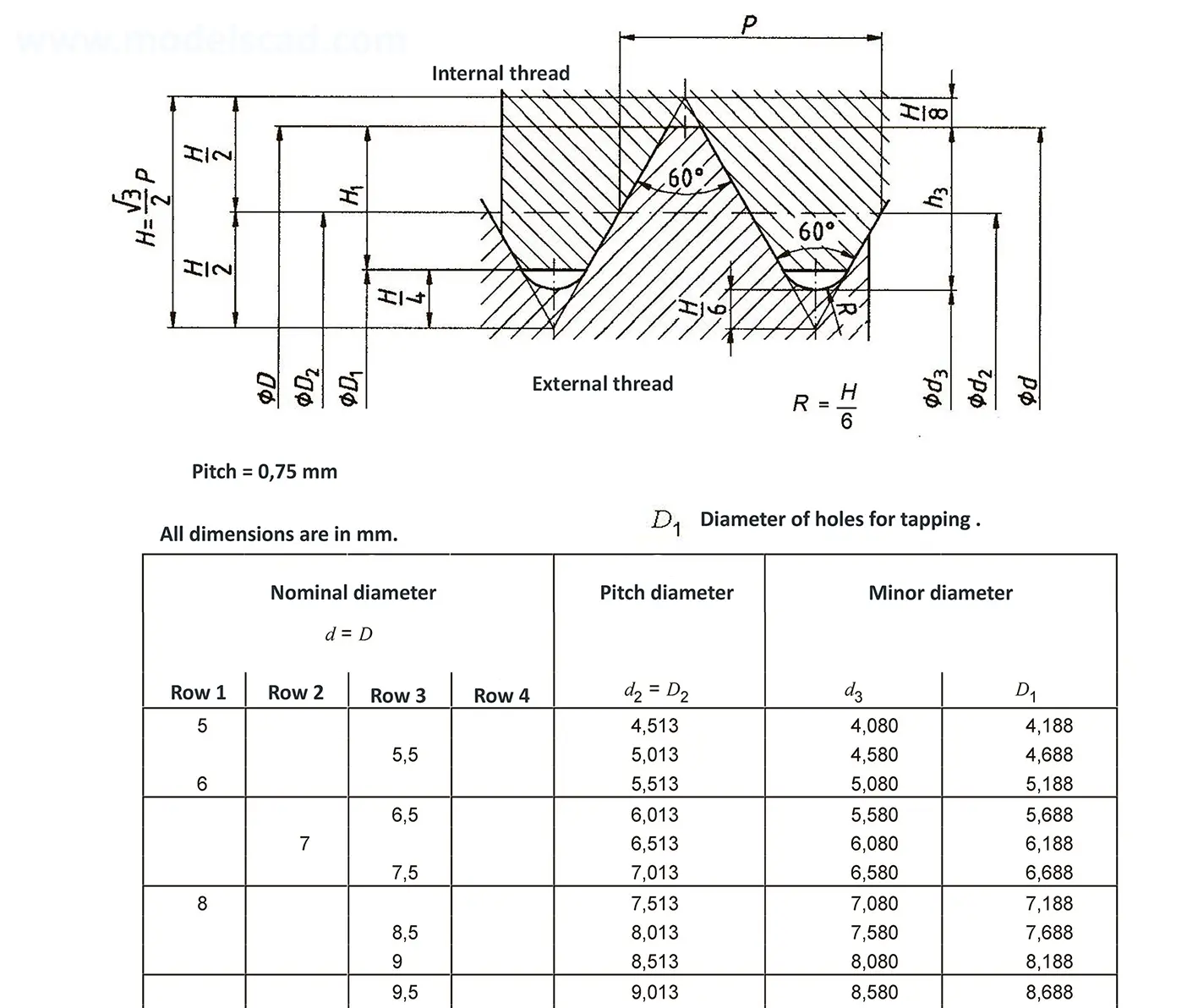
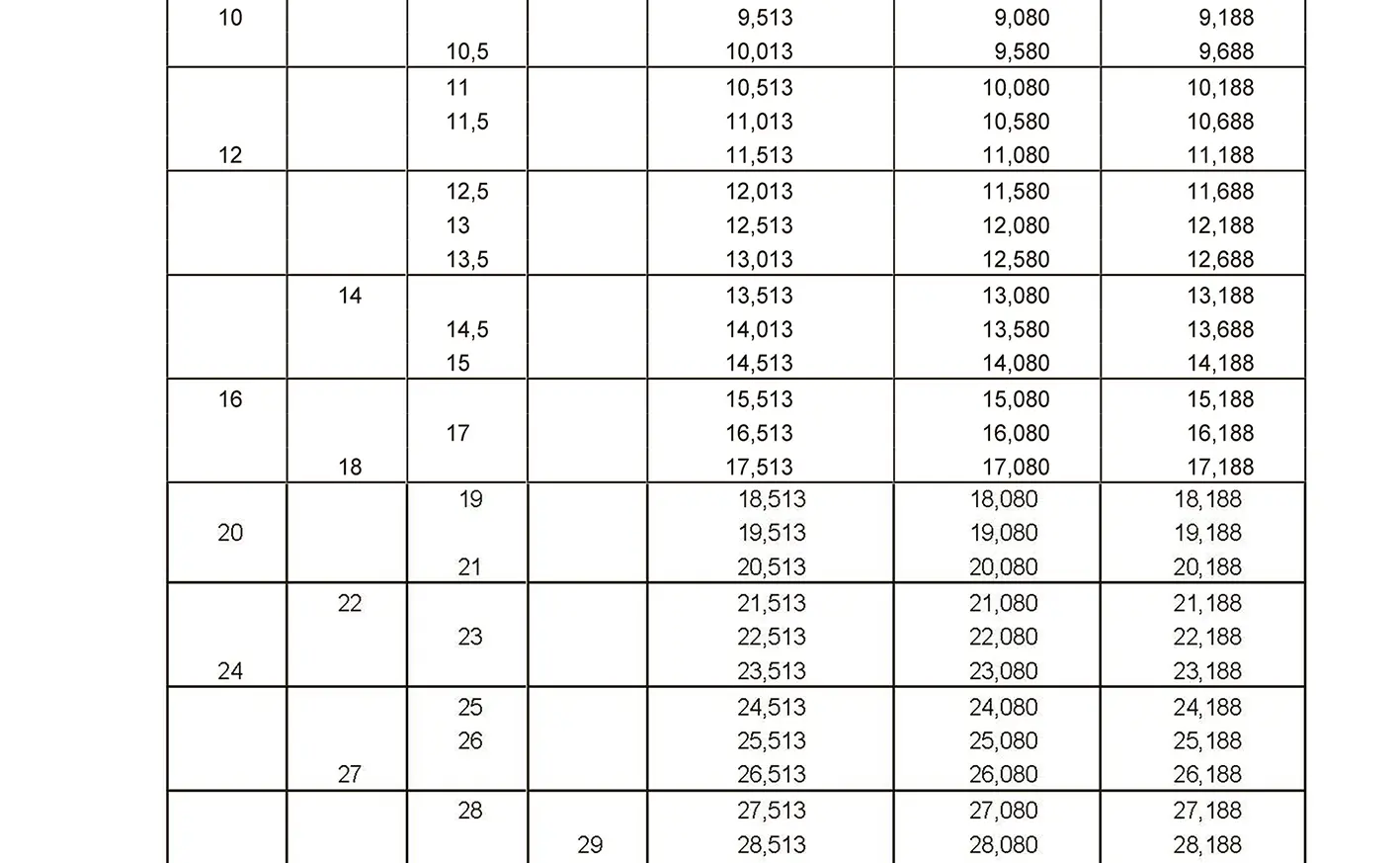
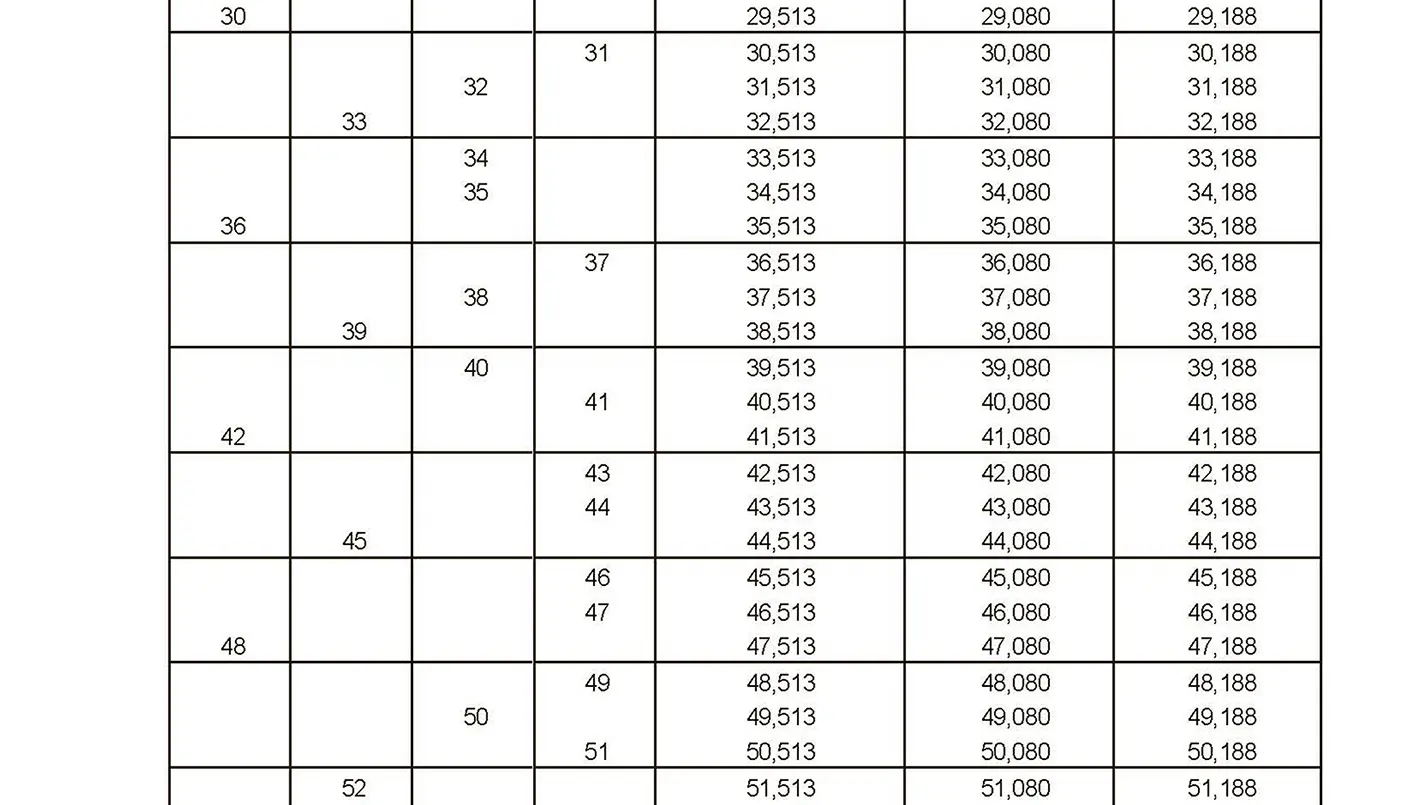
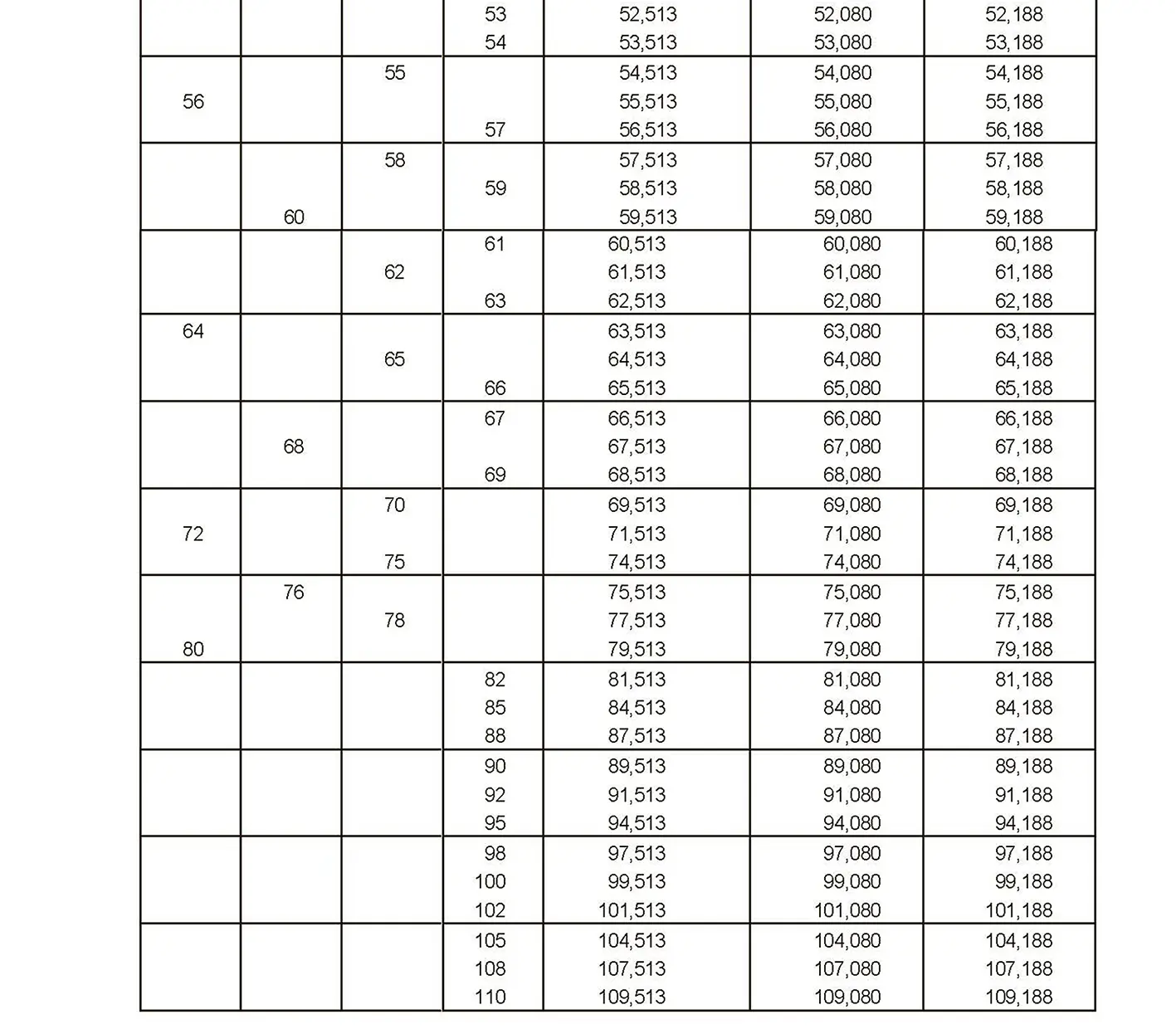
The fine thread ISO DIN 13-5 has a smaller pitch than the coarse thread, which increases its elasticity. This thread is used, for example, for adjusting screws in measuring instruments, which allows for more precise settings. The designation consists of the letter M, nominal diameter and pitch, angle of inclination 60°. Pitch 1 mm, 1.25 mm.
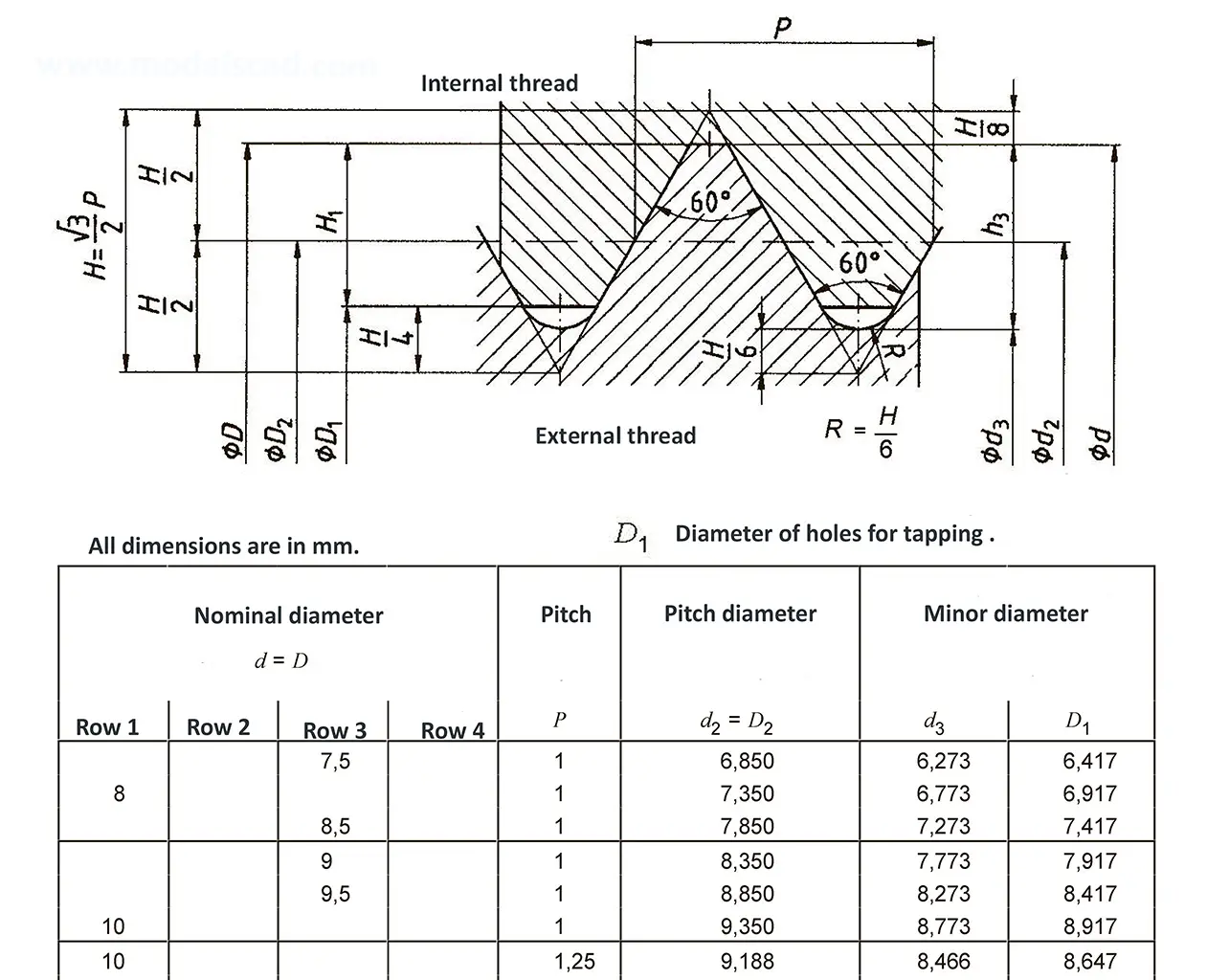
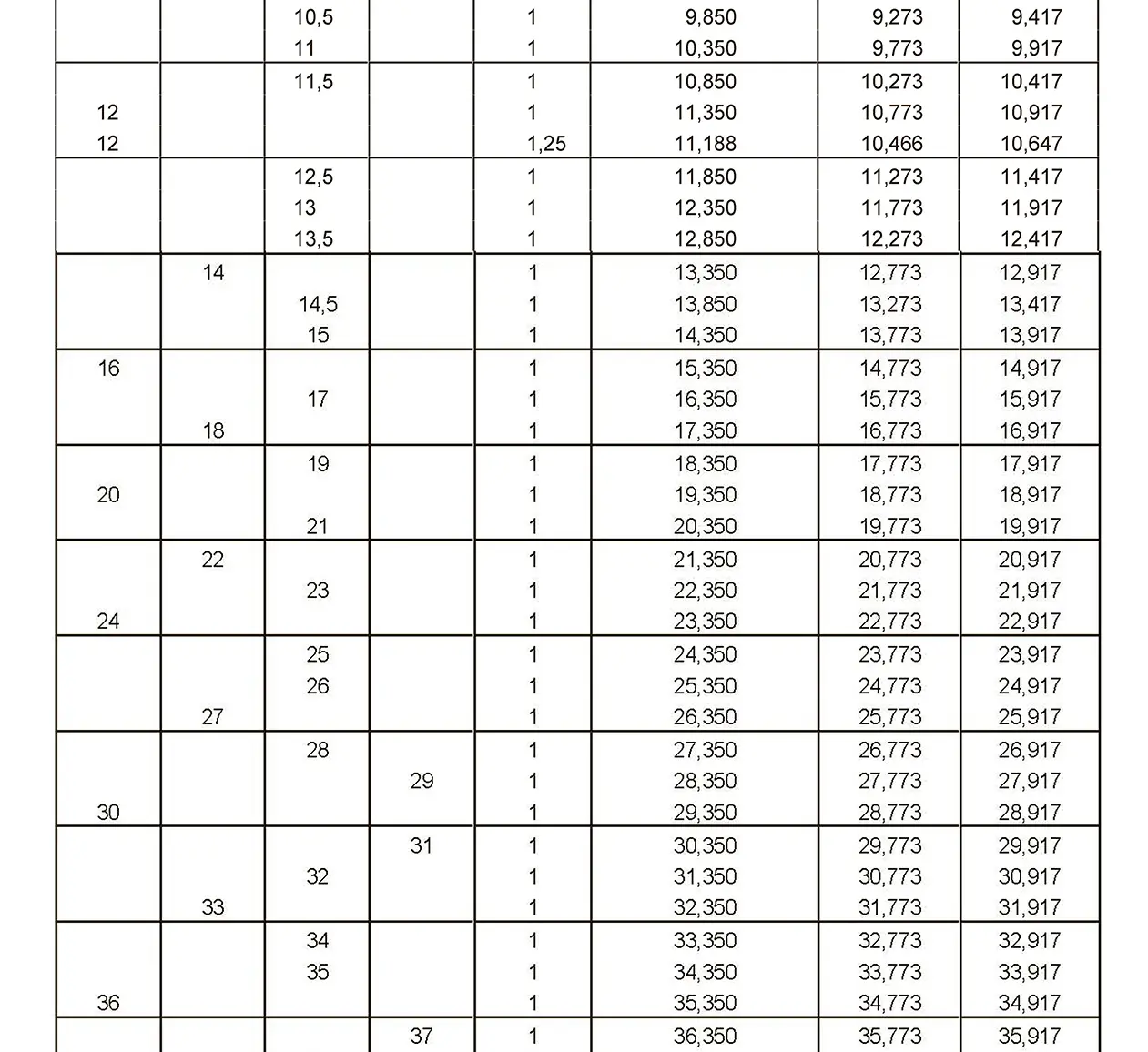
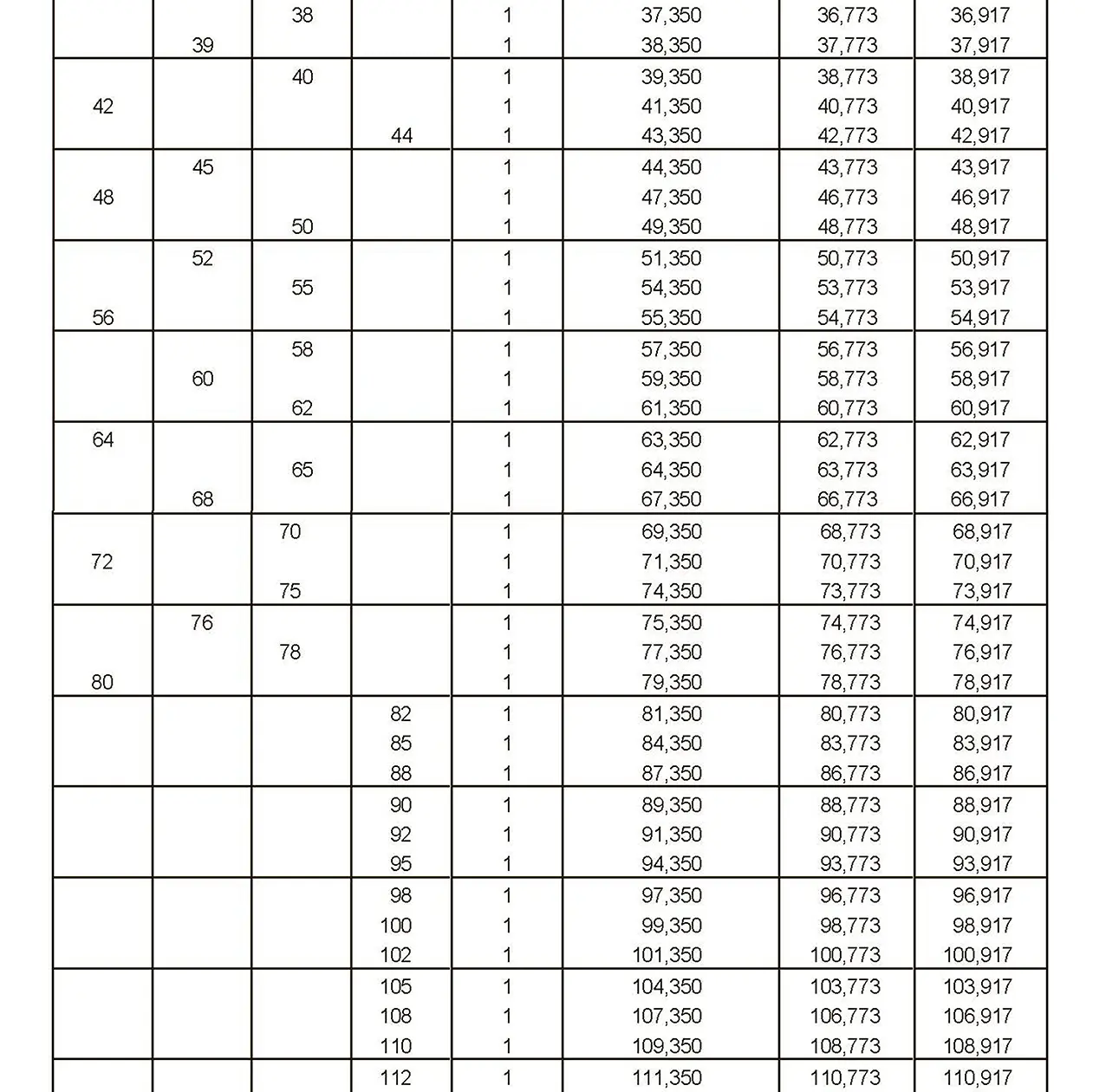
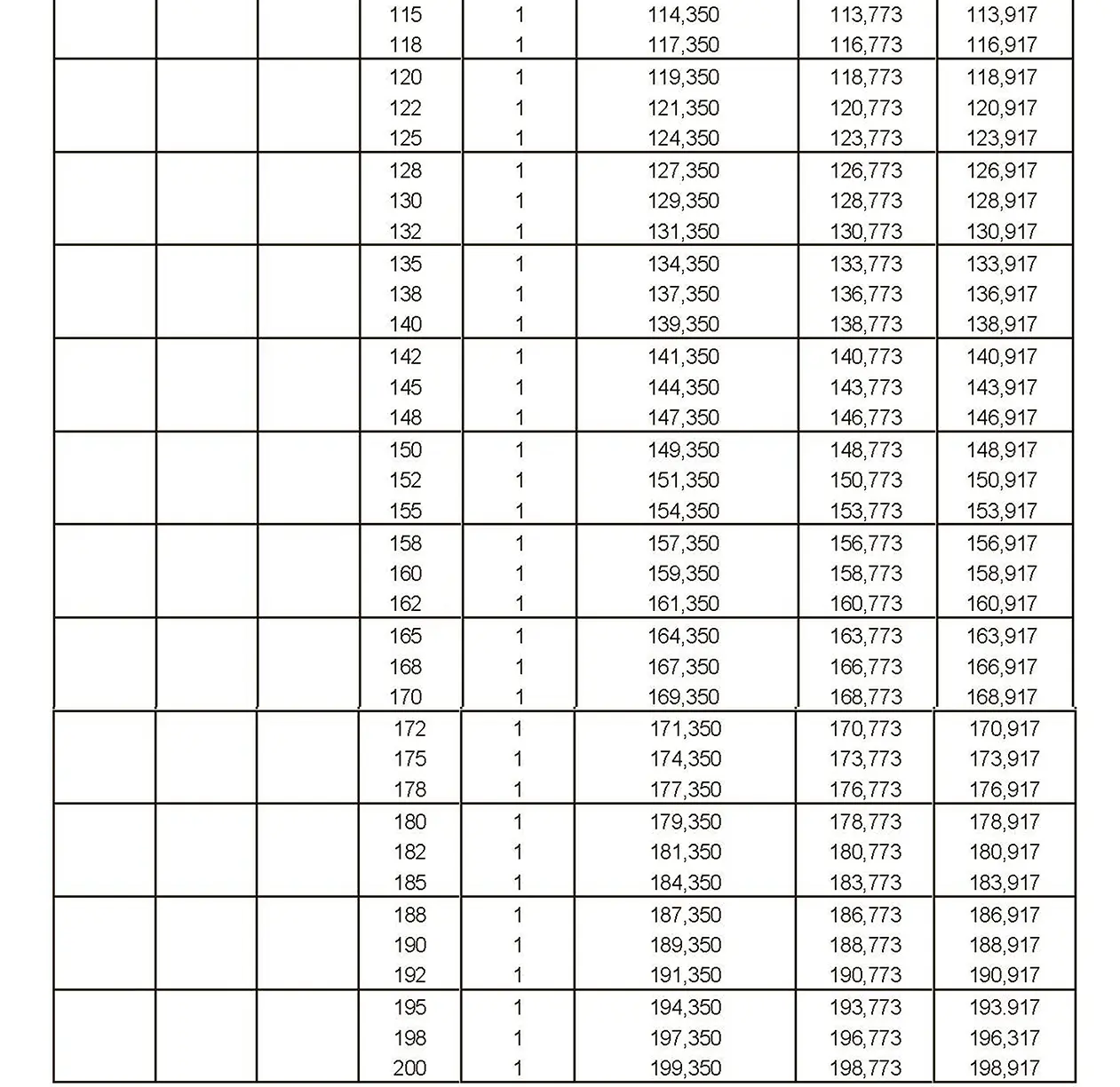
The fine thread ISO DIN 13-6 has a smaller pitch than the coarse thread, which increases its elasticity. This thread is used, for example, for adjusting screws in measuring instruments, which allows for more precise settings. The designation consists of the letter M, nominal diameter and pitch, angle of inclination 60°. Pitch 1.5 mm.
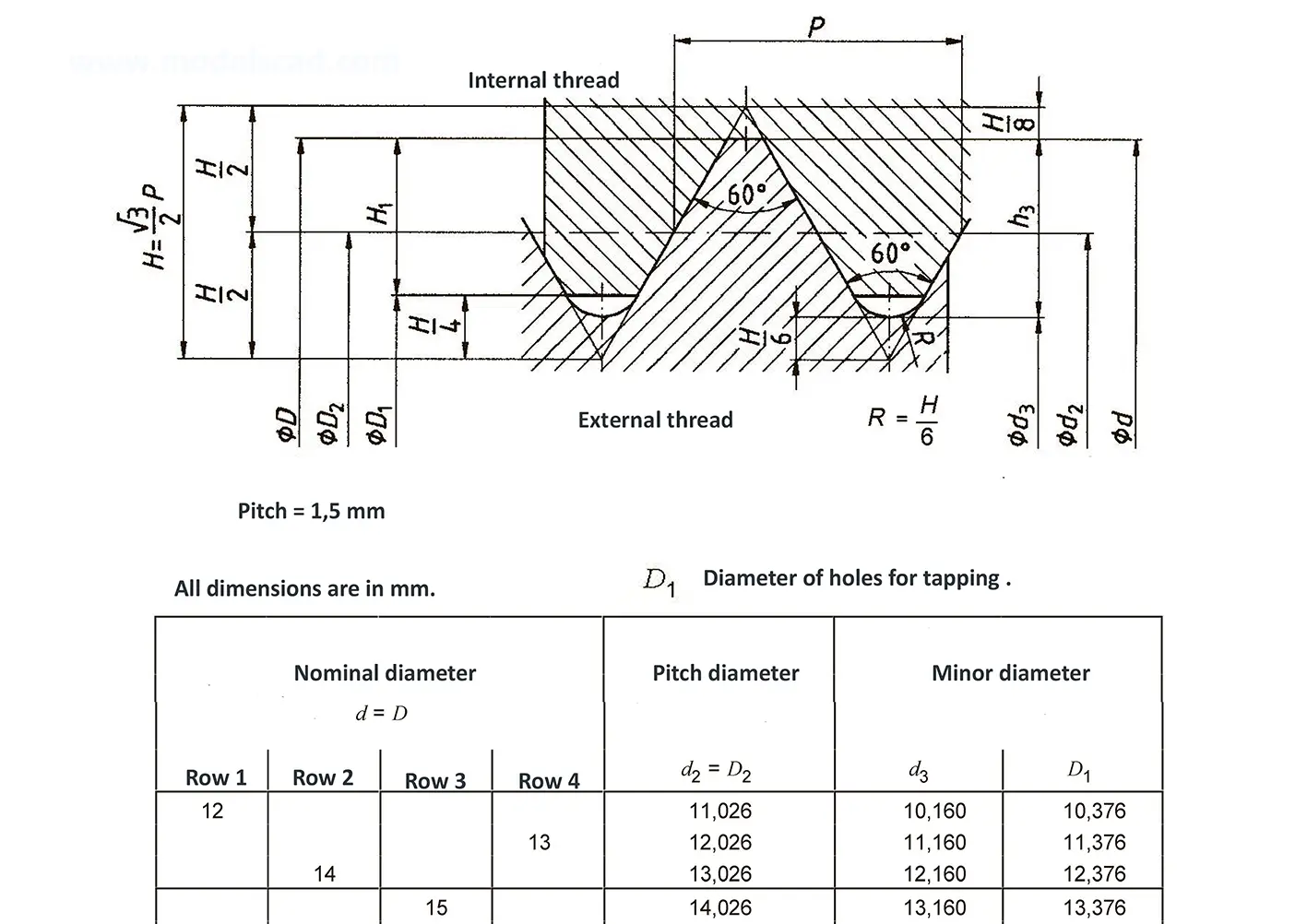
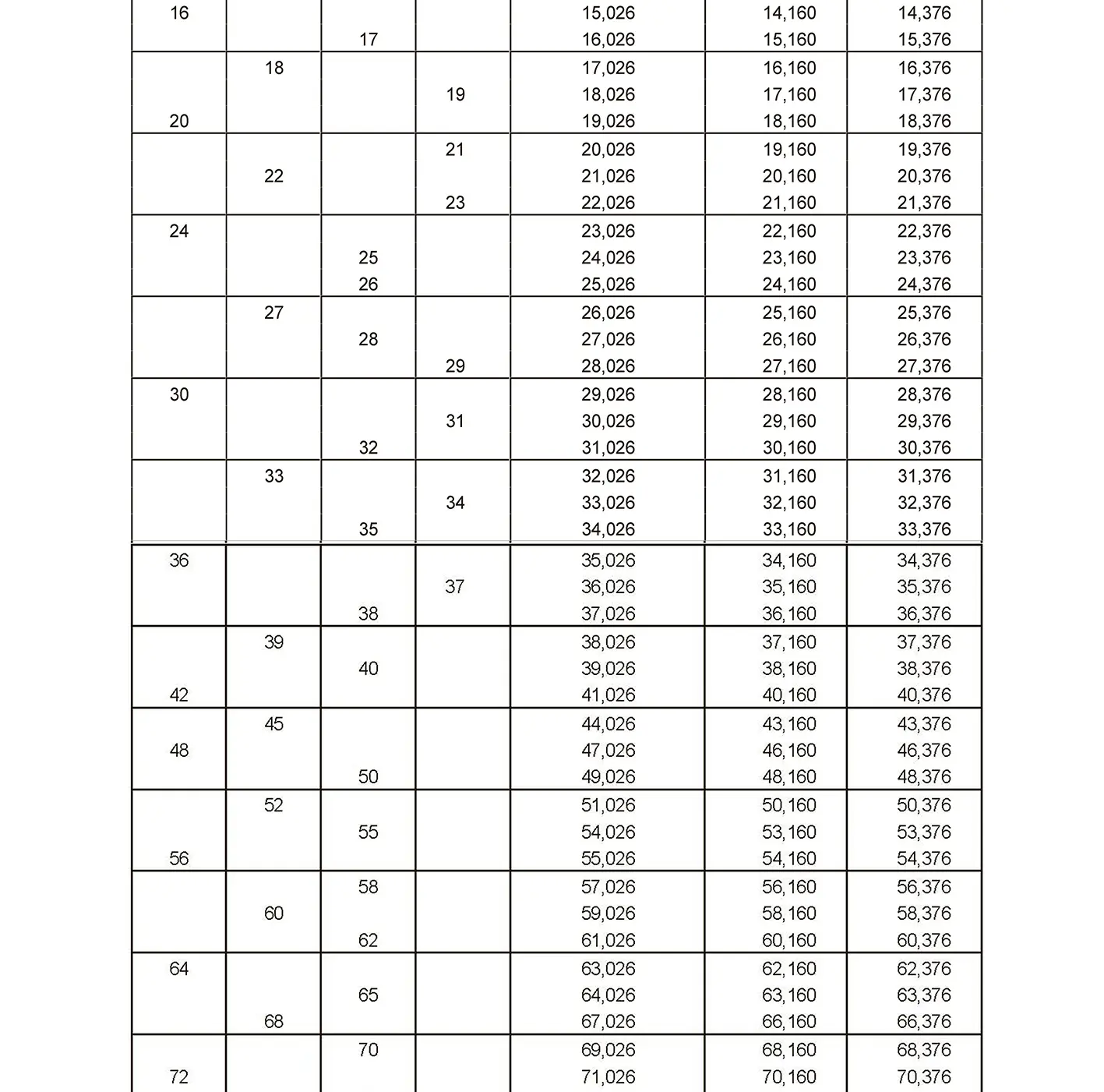
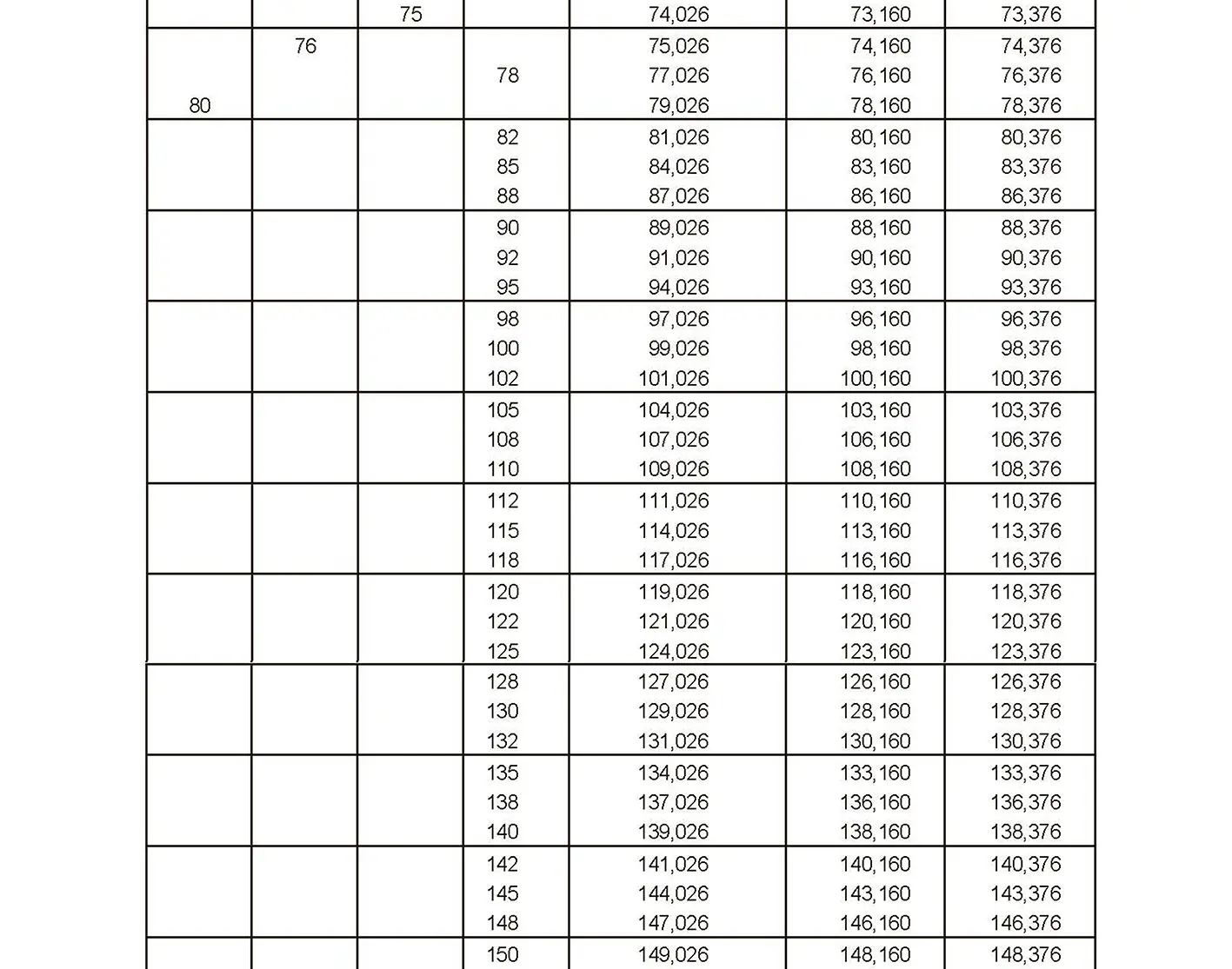
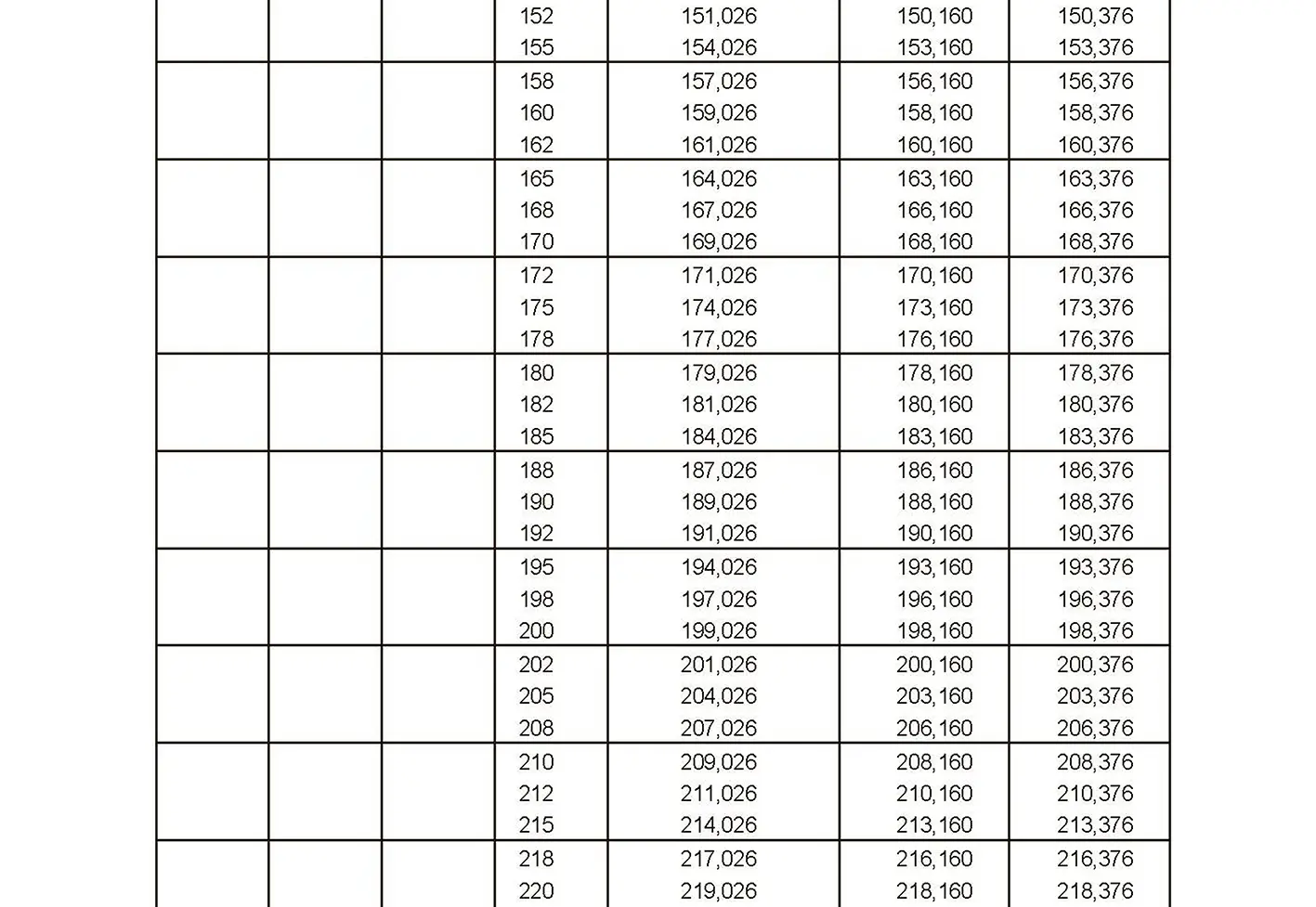
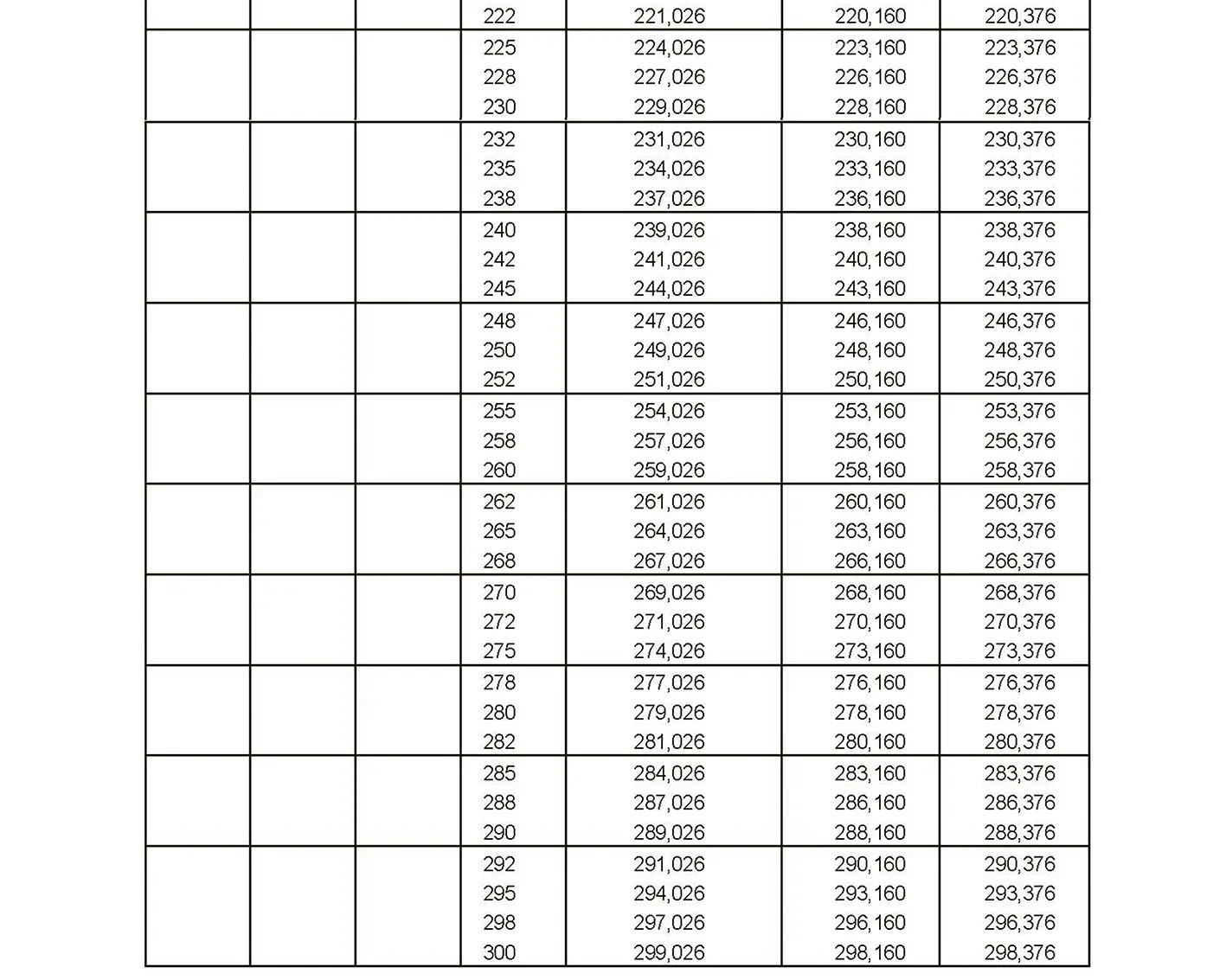
The fine thread ISO DIN 13-7 has a smaller pitch than the coarse thread, which increases its elasticity. This thread is used, for example, for adjusting screws in measuring instruments, which allows for more precise settings. The designation consists of the letter M, nominal diameter and pitch, angle of inclination 60°. Pitch 2 mm.
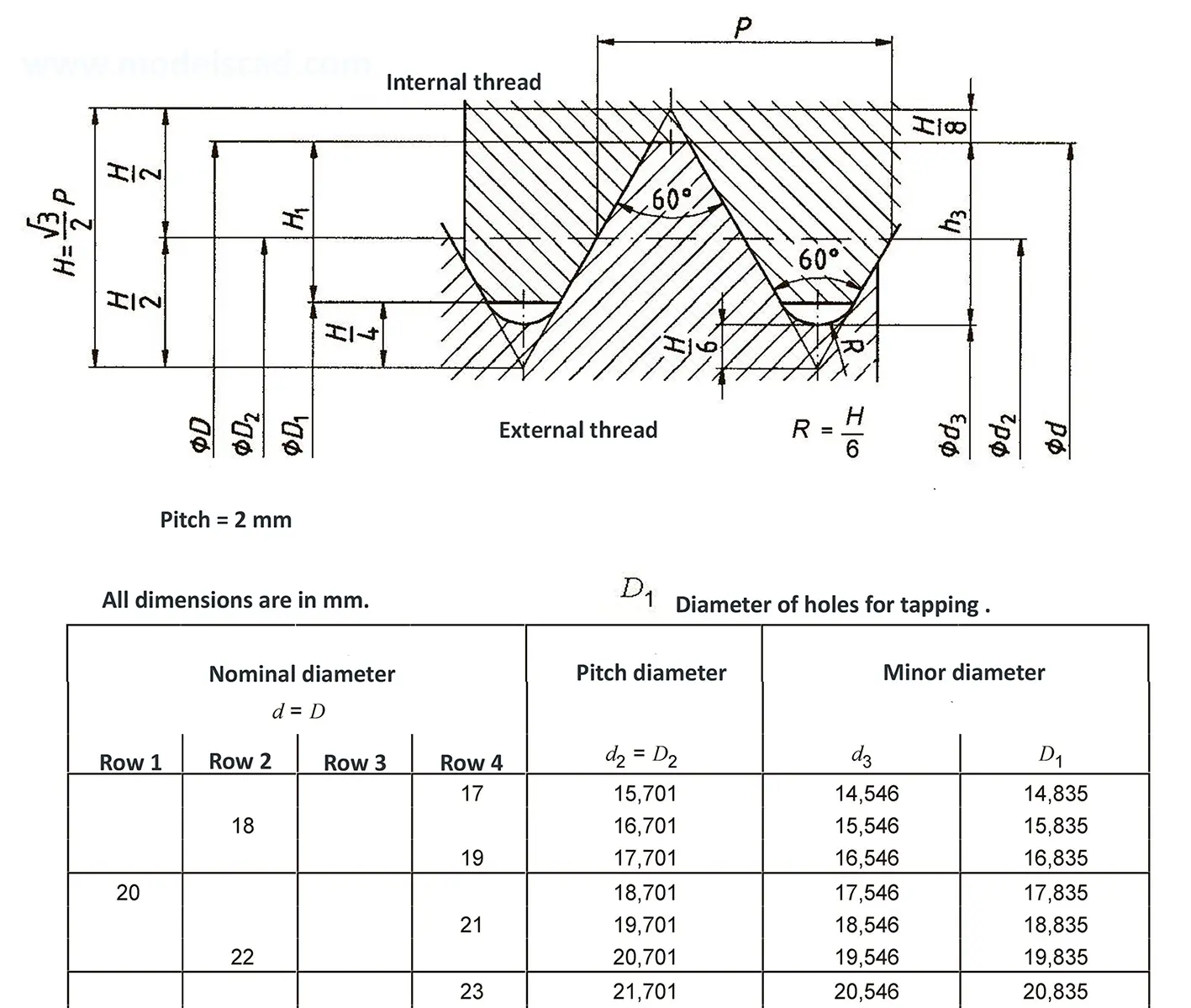
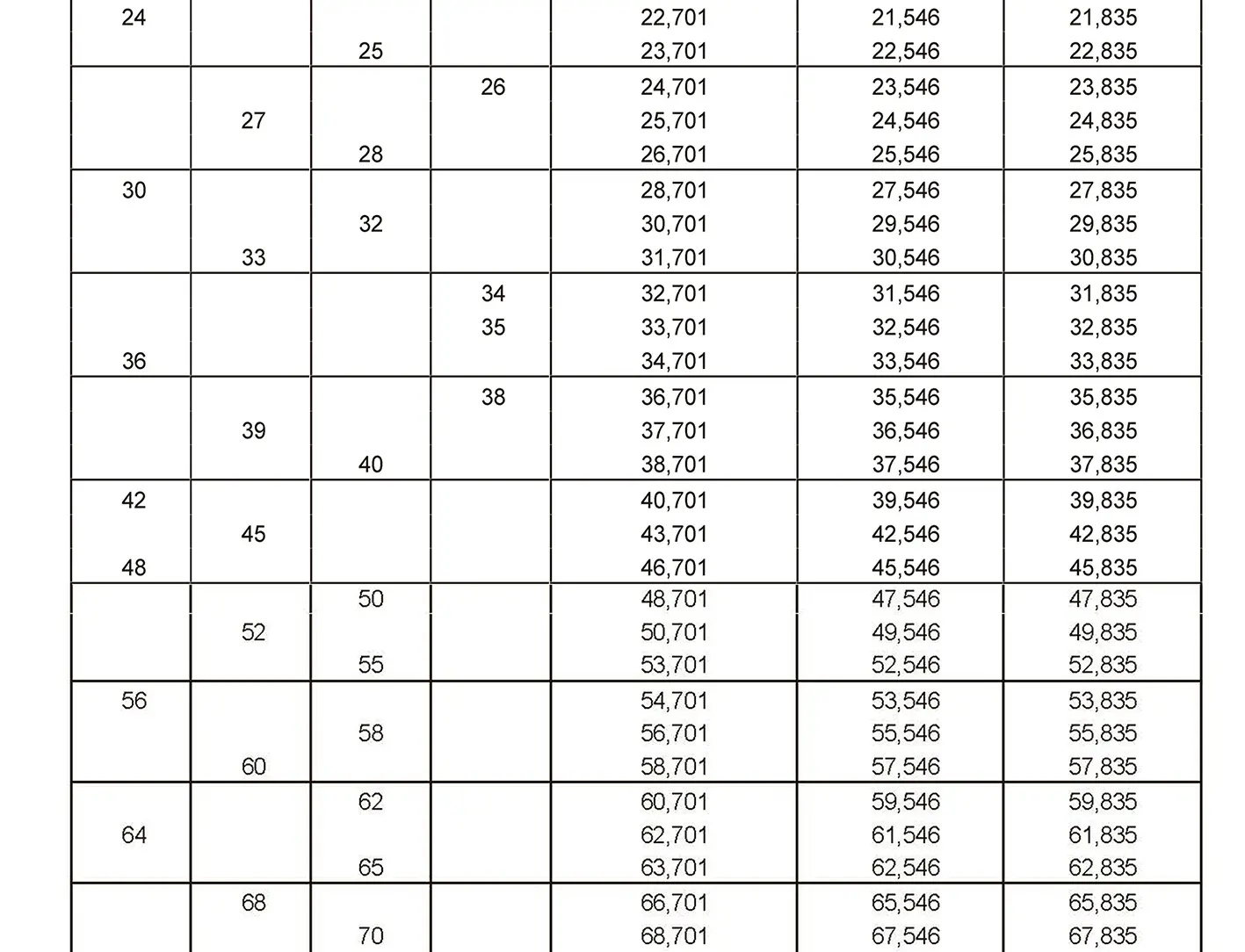

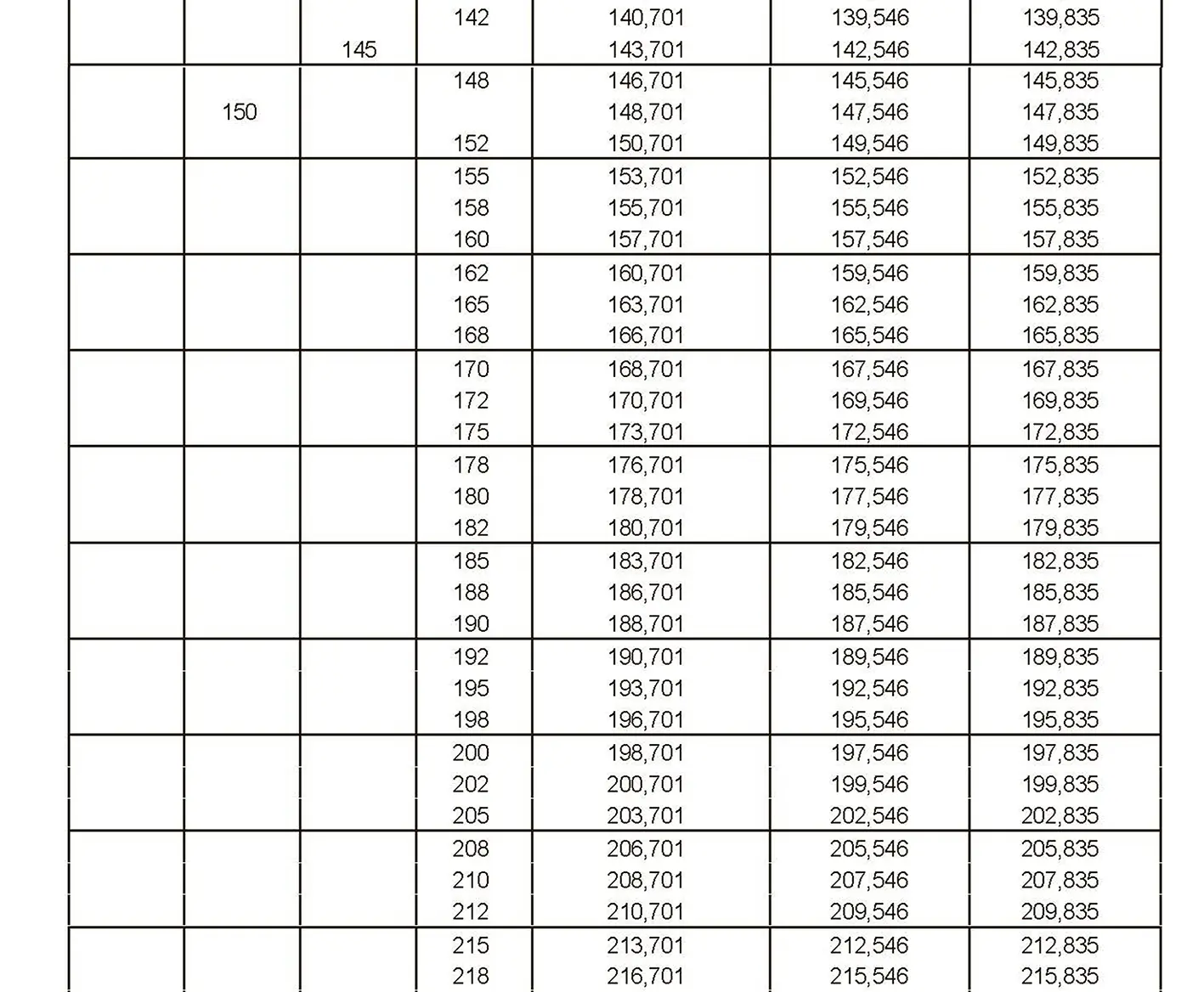
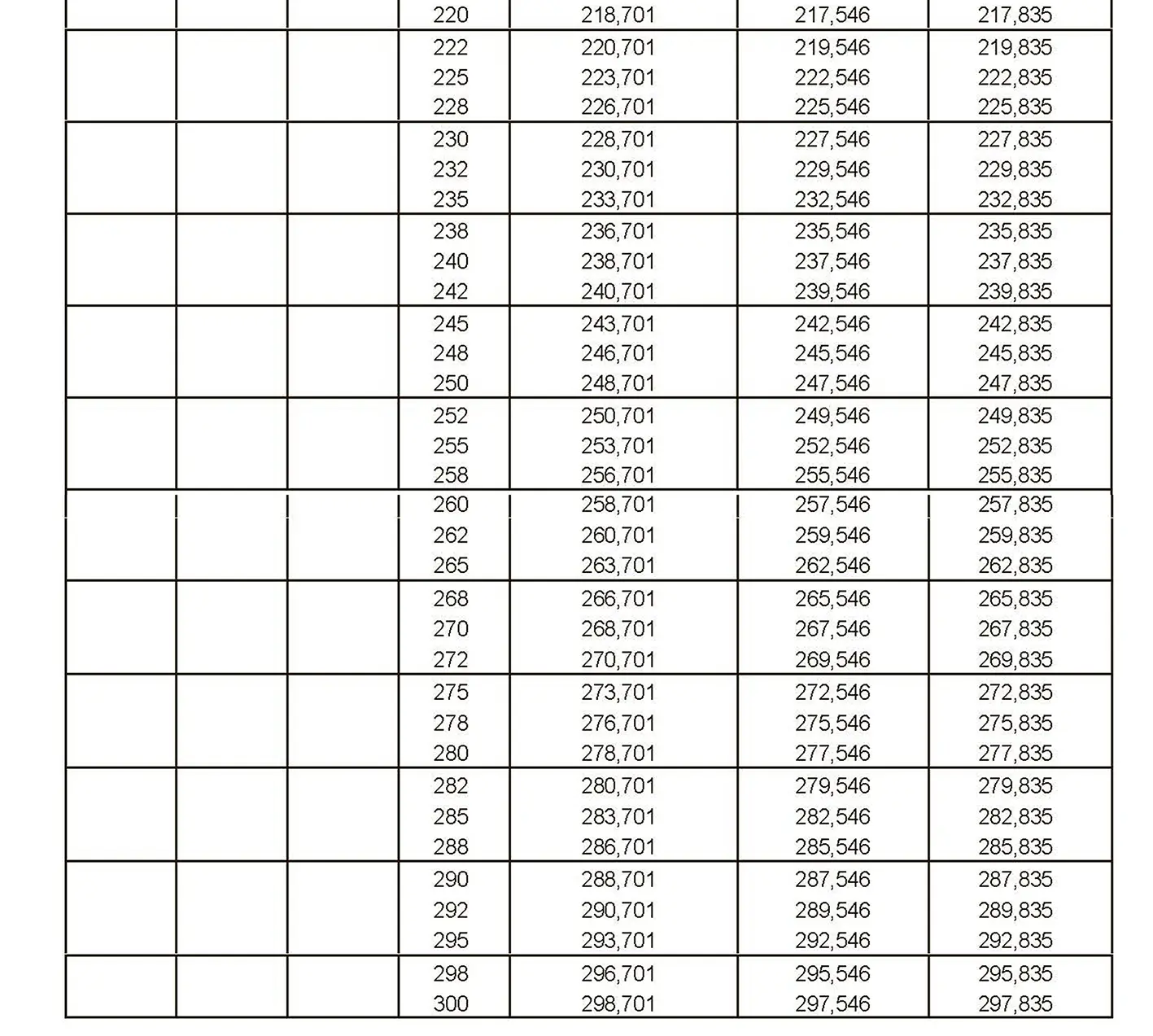
The fine thread ISO DIN 13-8 has a smaller pitch than the coarse thread, which increases its elasticity. This thread is used, for example, for adjusting screws in measuring instruments, which allows for more precise settings. The designation consists of the letter M, nominal diameter and pitch, angle of inclination 60°. Pitch 3 mm.
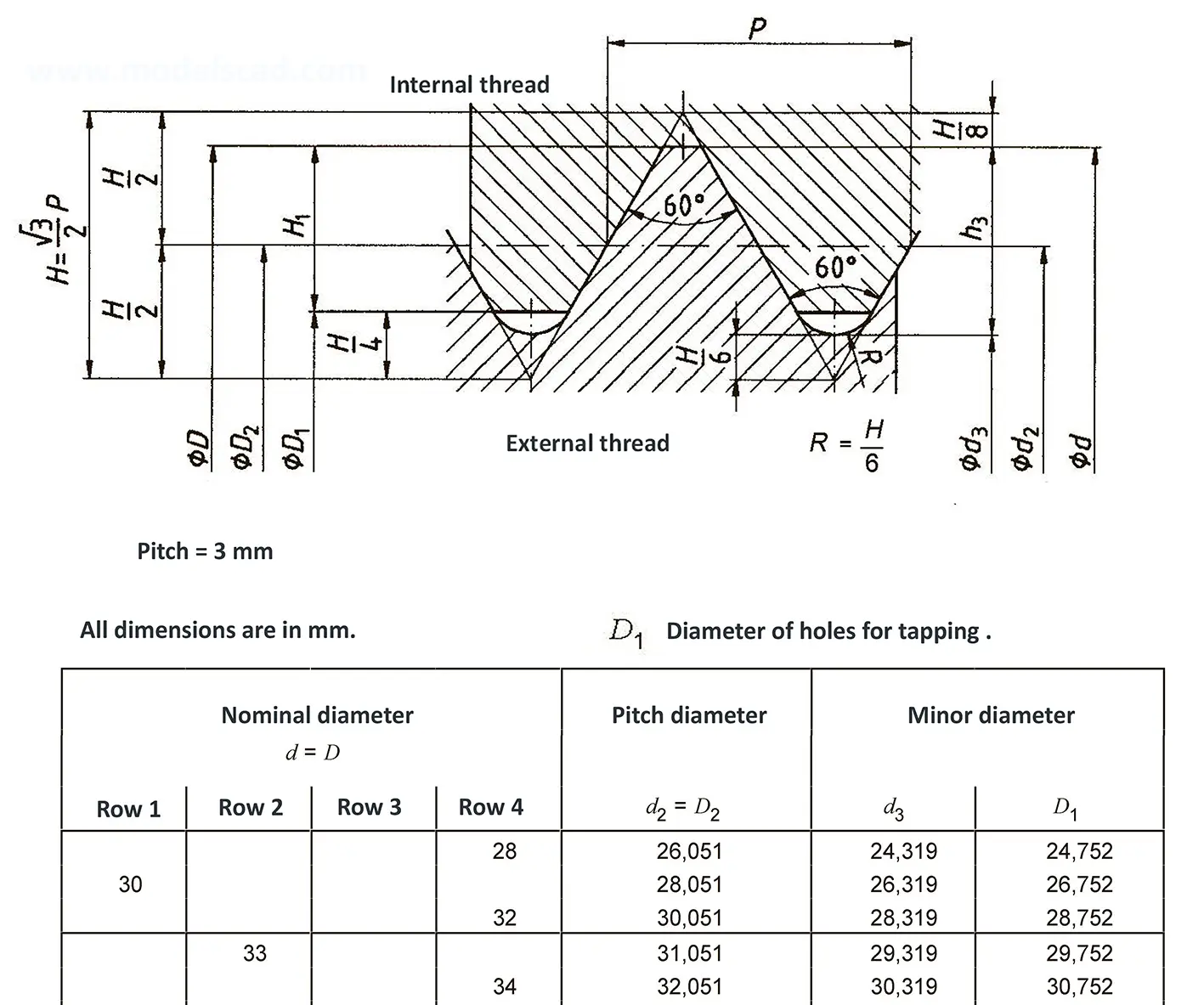

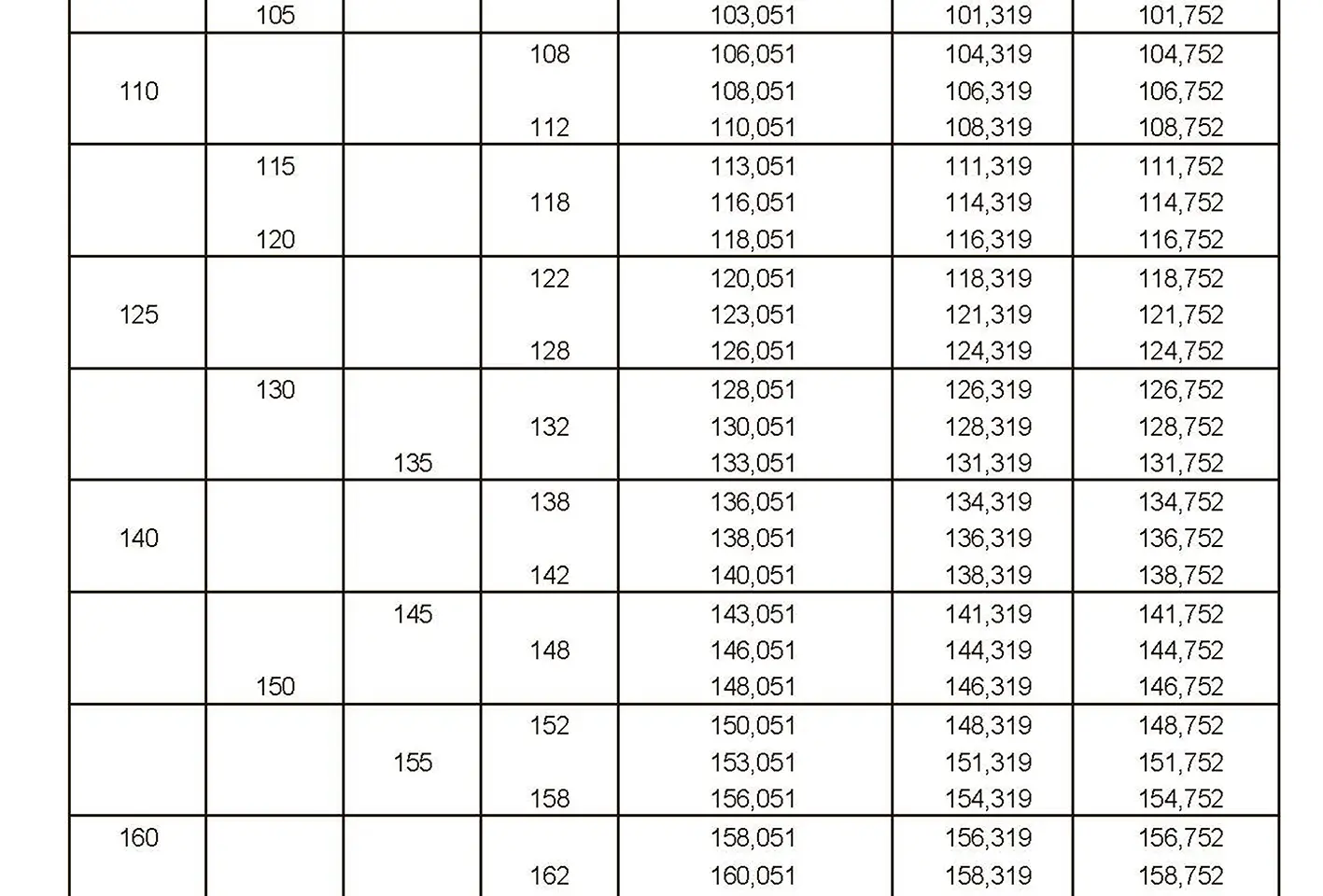
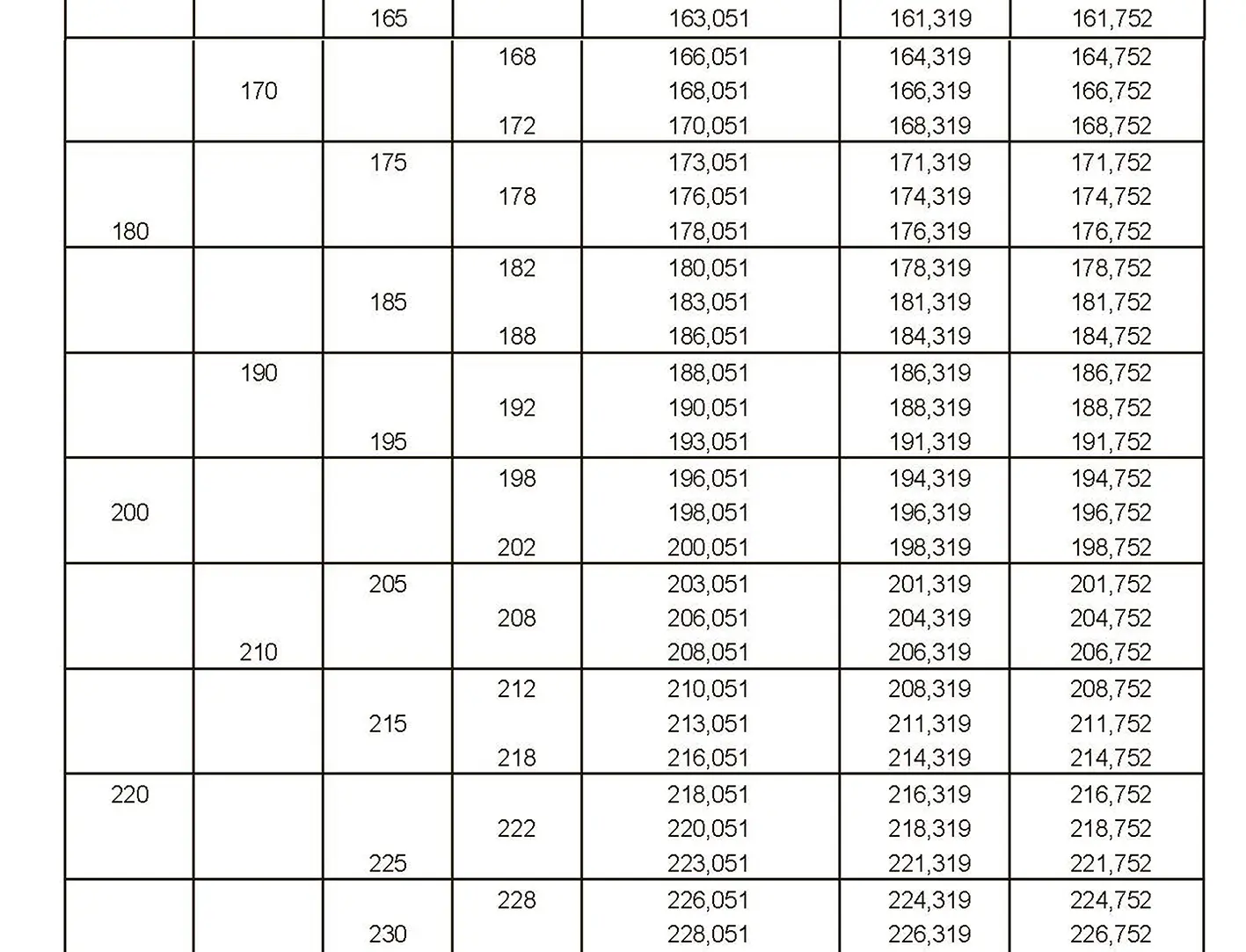
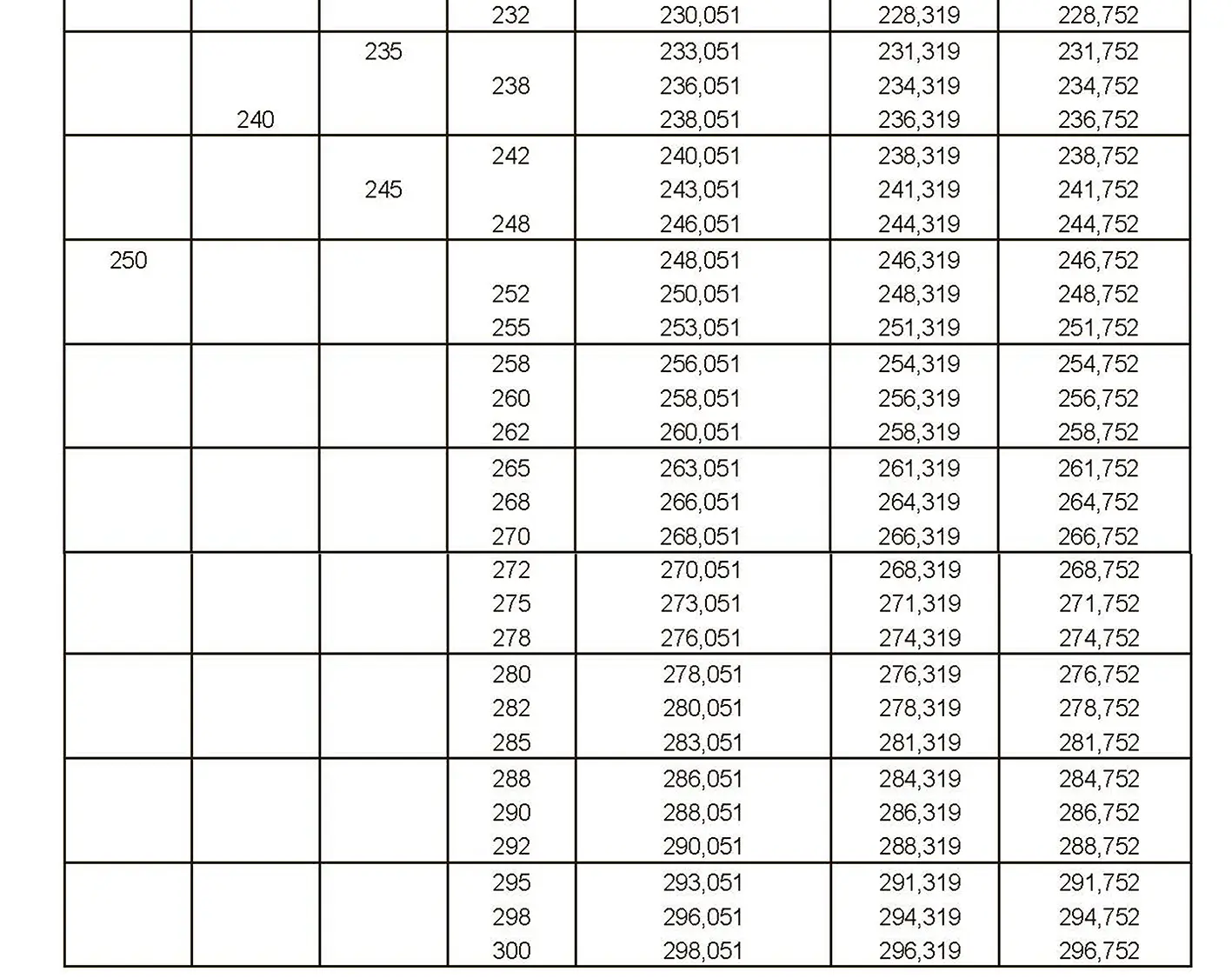
The fine thread ISO DIN 13-9 has a smaller pitch than the coarse thread, which increases its elasticity. This thread is used, for example, for adjusting screws in measuring instruments, which allows for more precise settings. The designation consists of the letter M, nominal diameter and pitch, angle of inclination 60°. Pitch 4 mm.
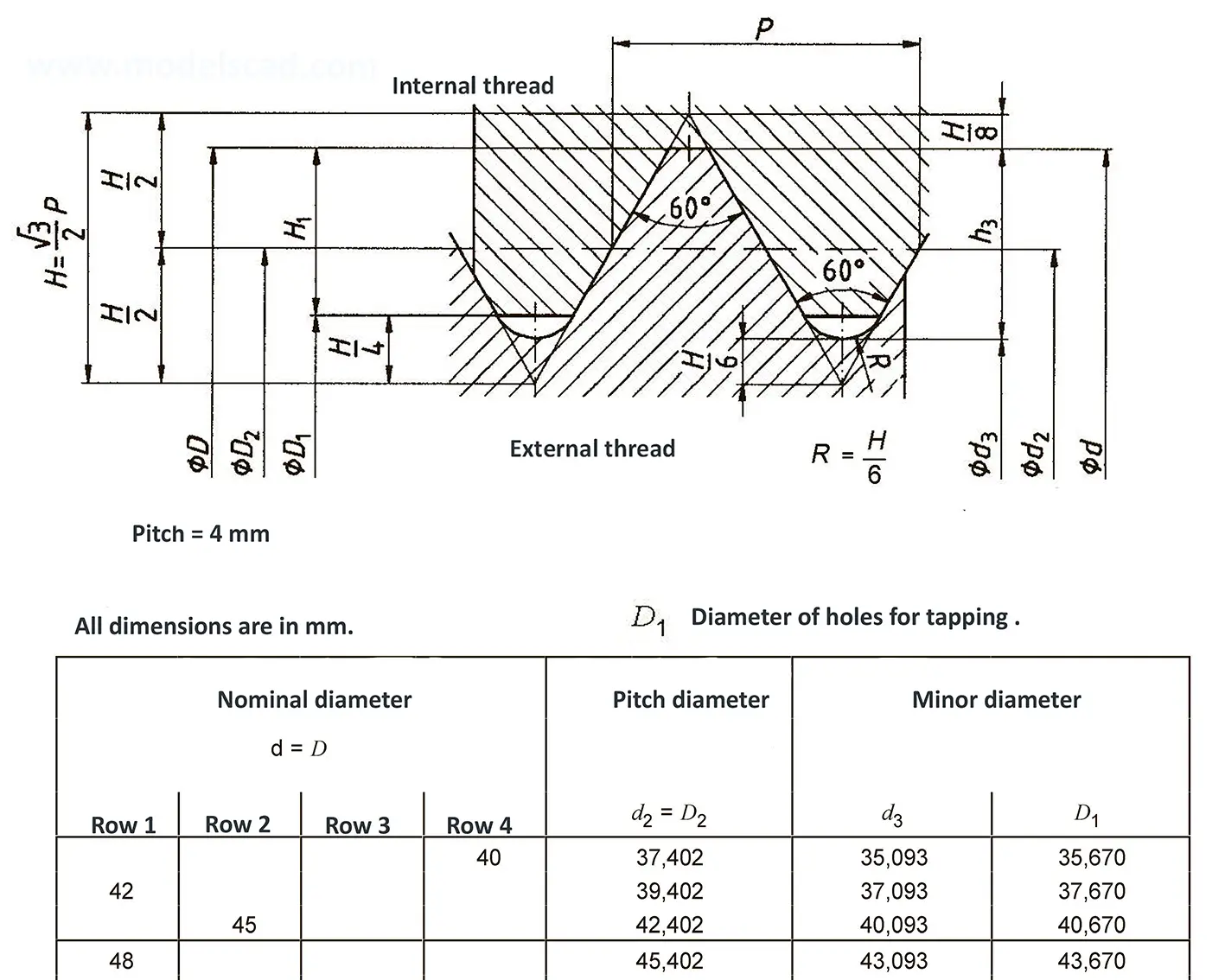
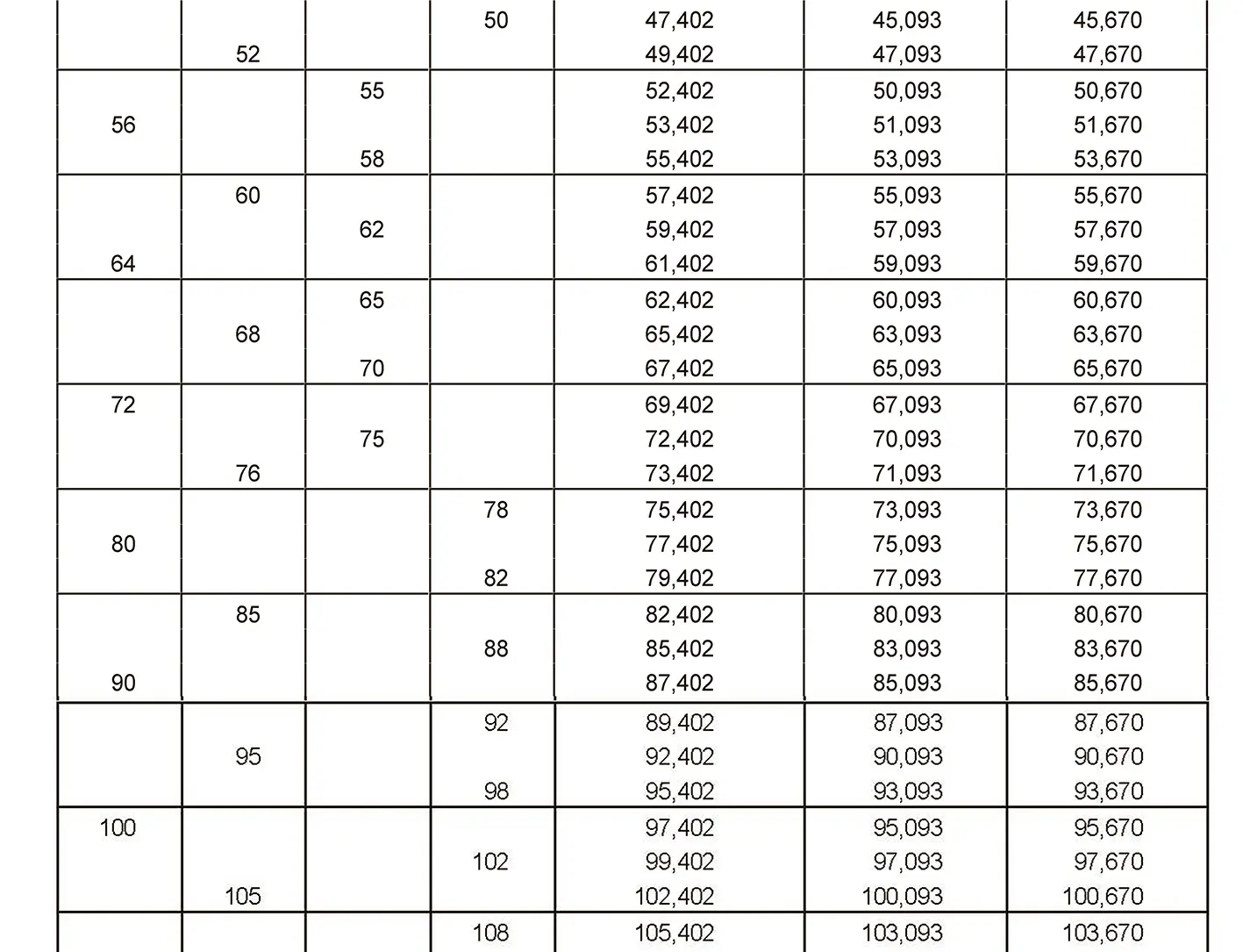
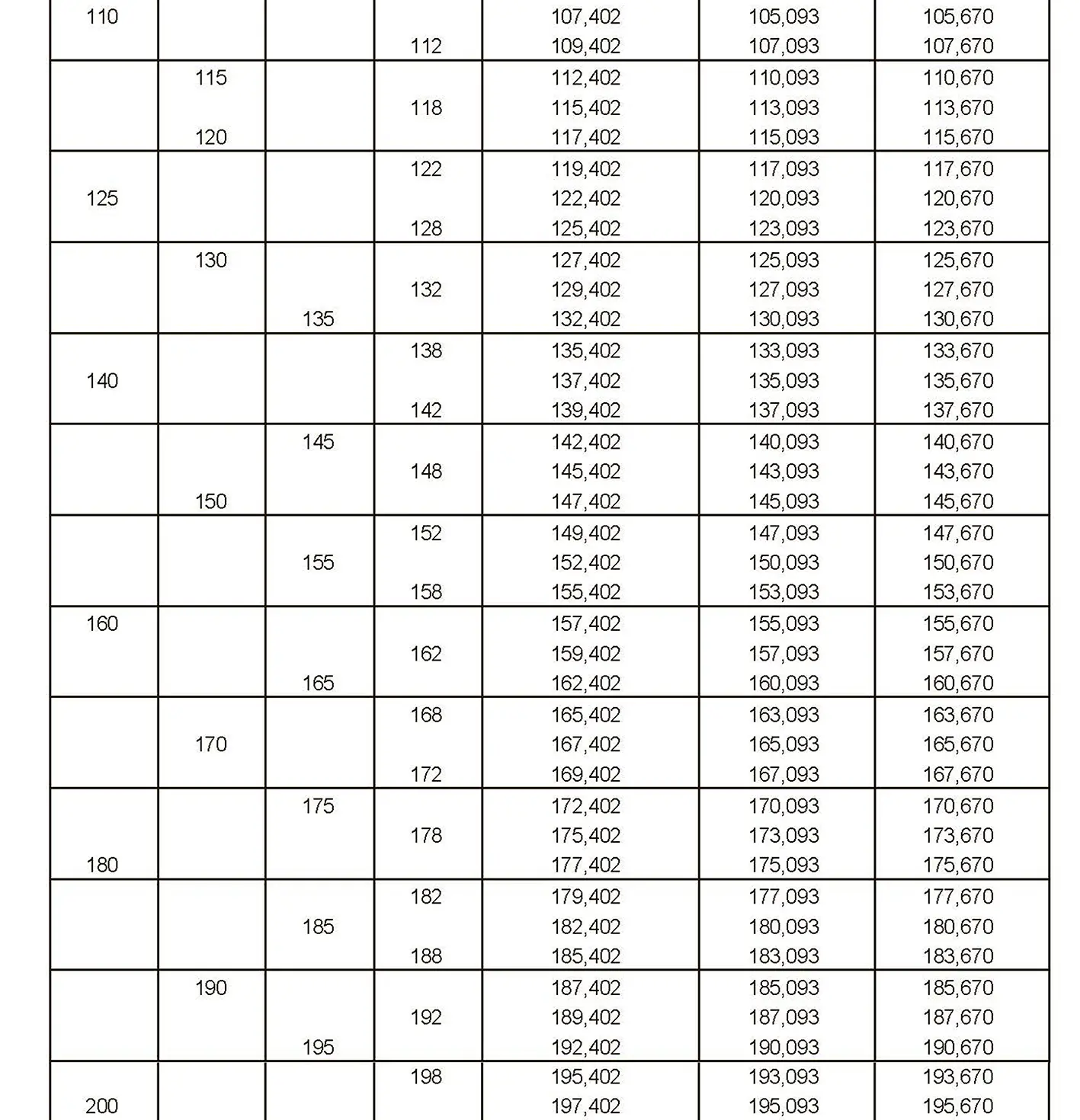
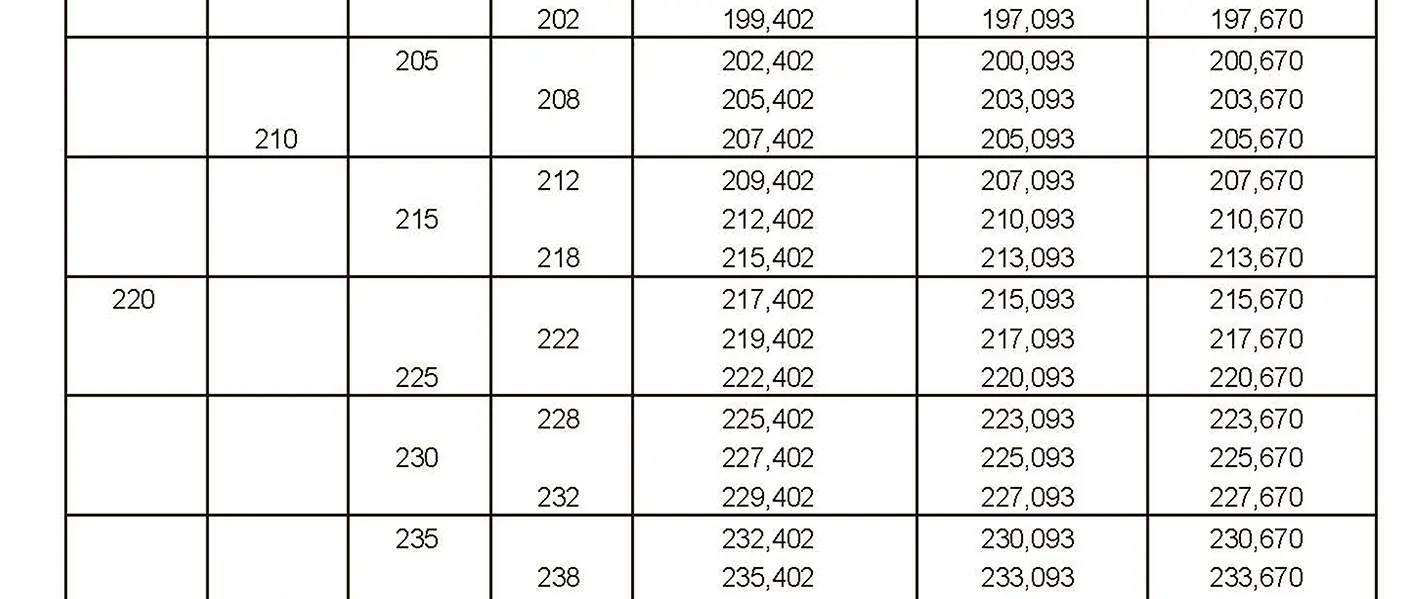
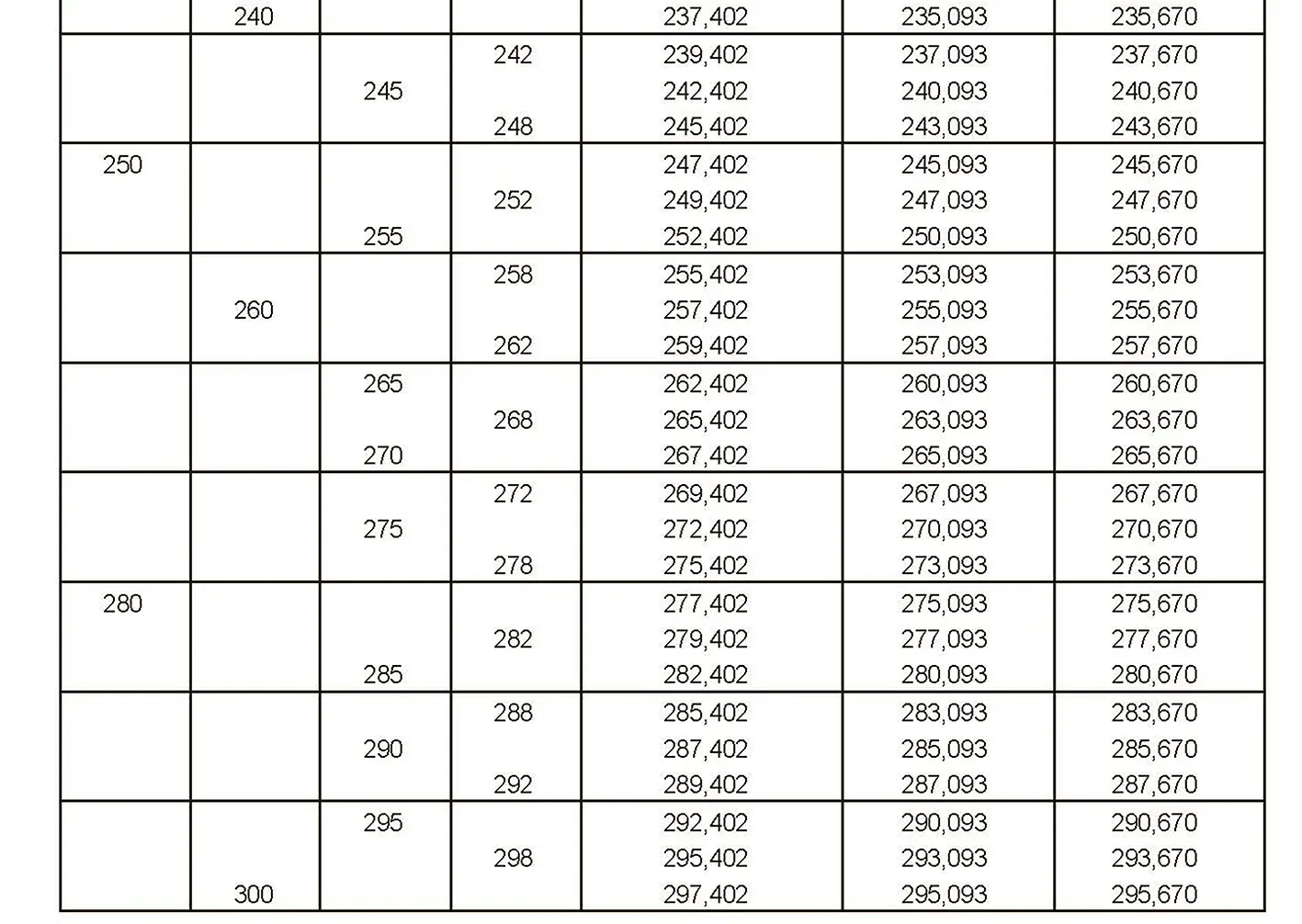
The fine thread ISO DIN 13-10 has a smaller pitch than the coarse thread, which increases its elasticity. This thread is used, for example, for adjusting screws in measuring instruments, which allows for more precise settings. The designation consists of the letter M, nominal diameter and pitch, angle of inclination 60°. Pitch 6 mm.
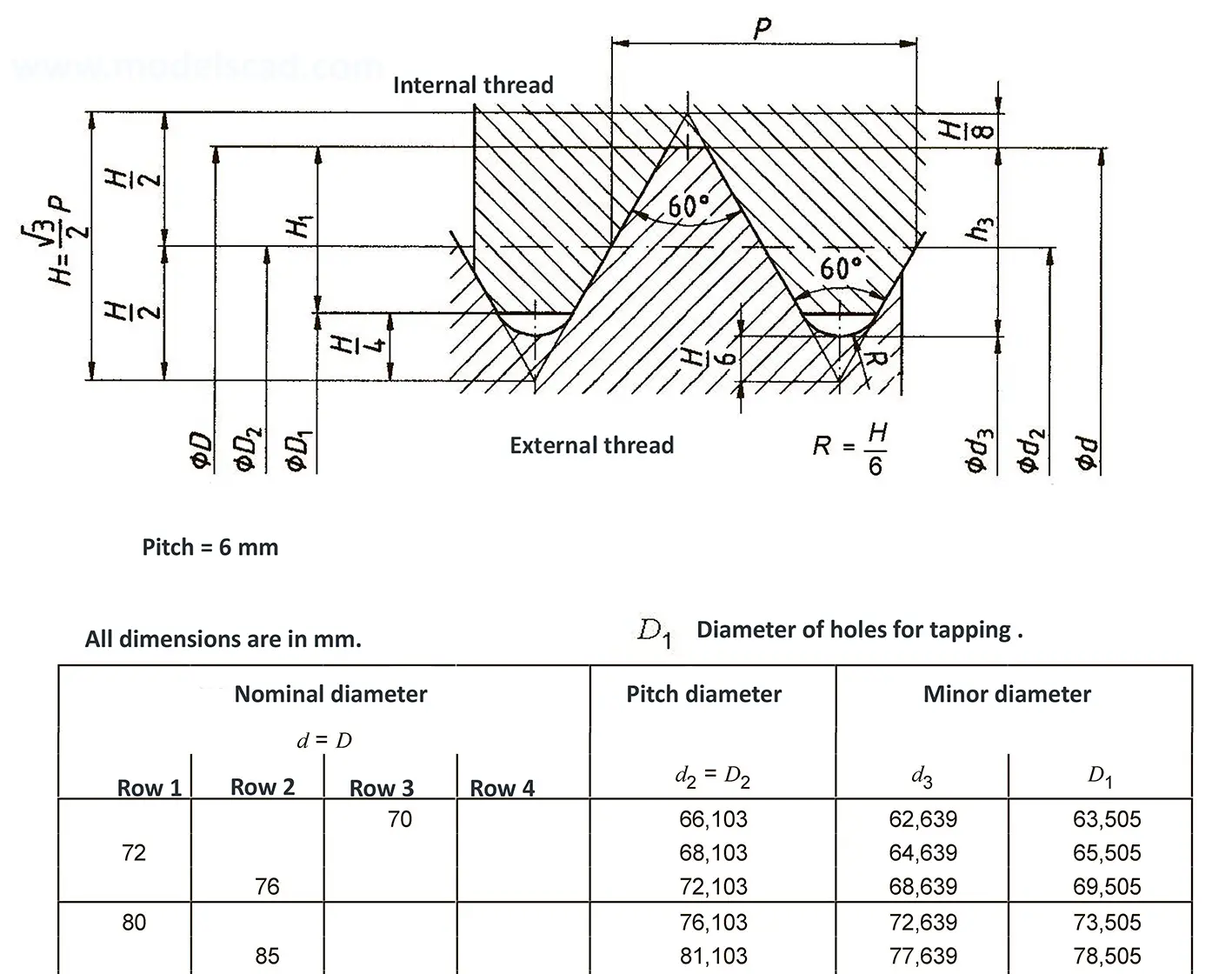
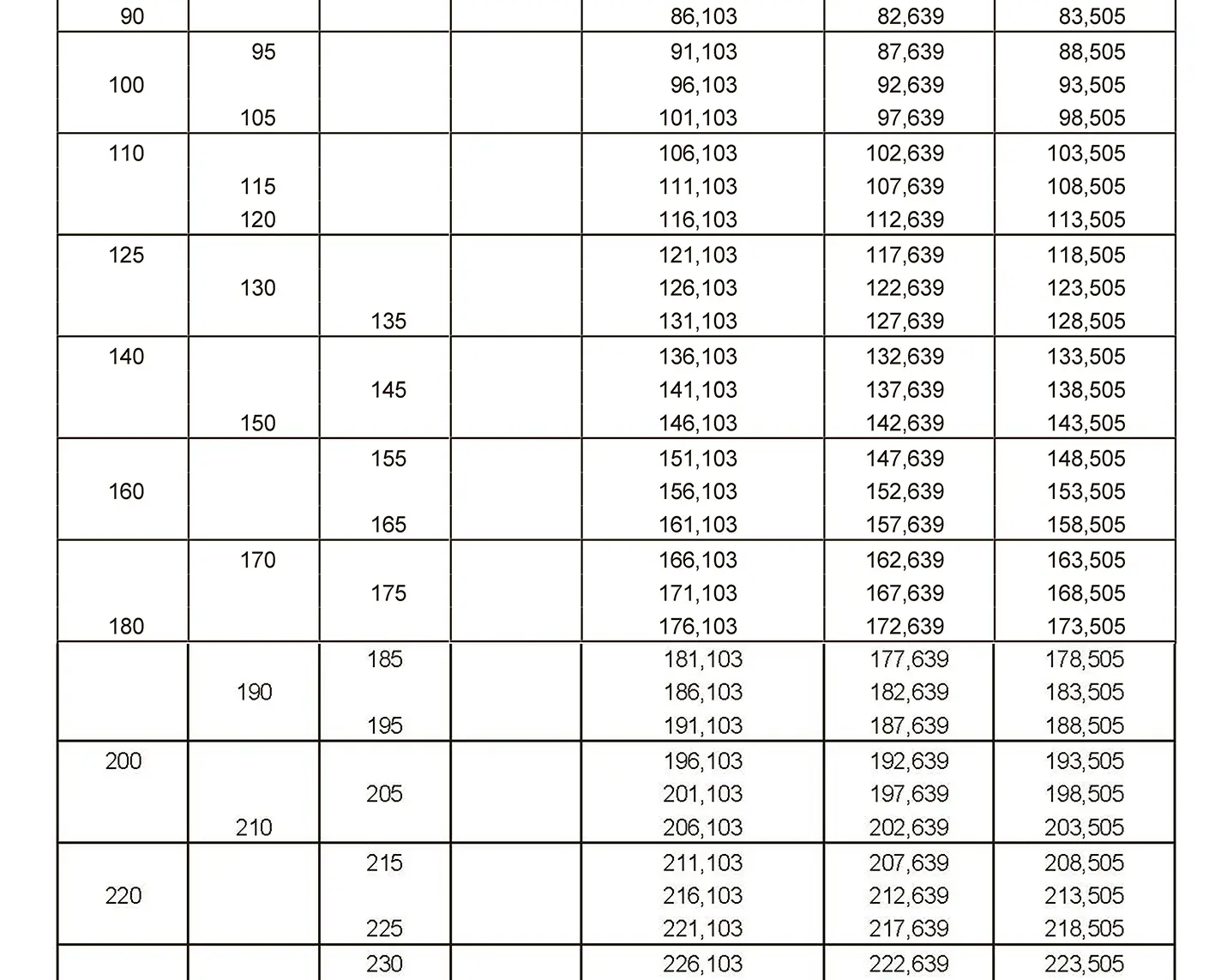
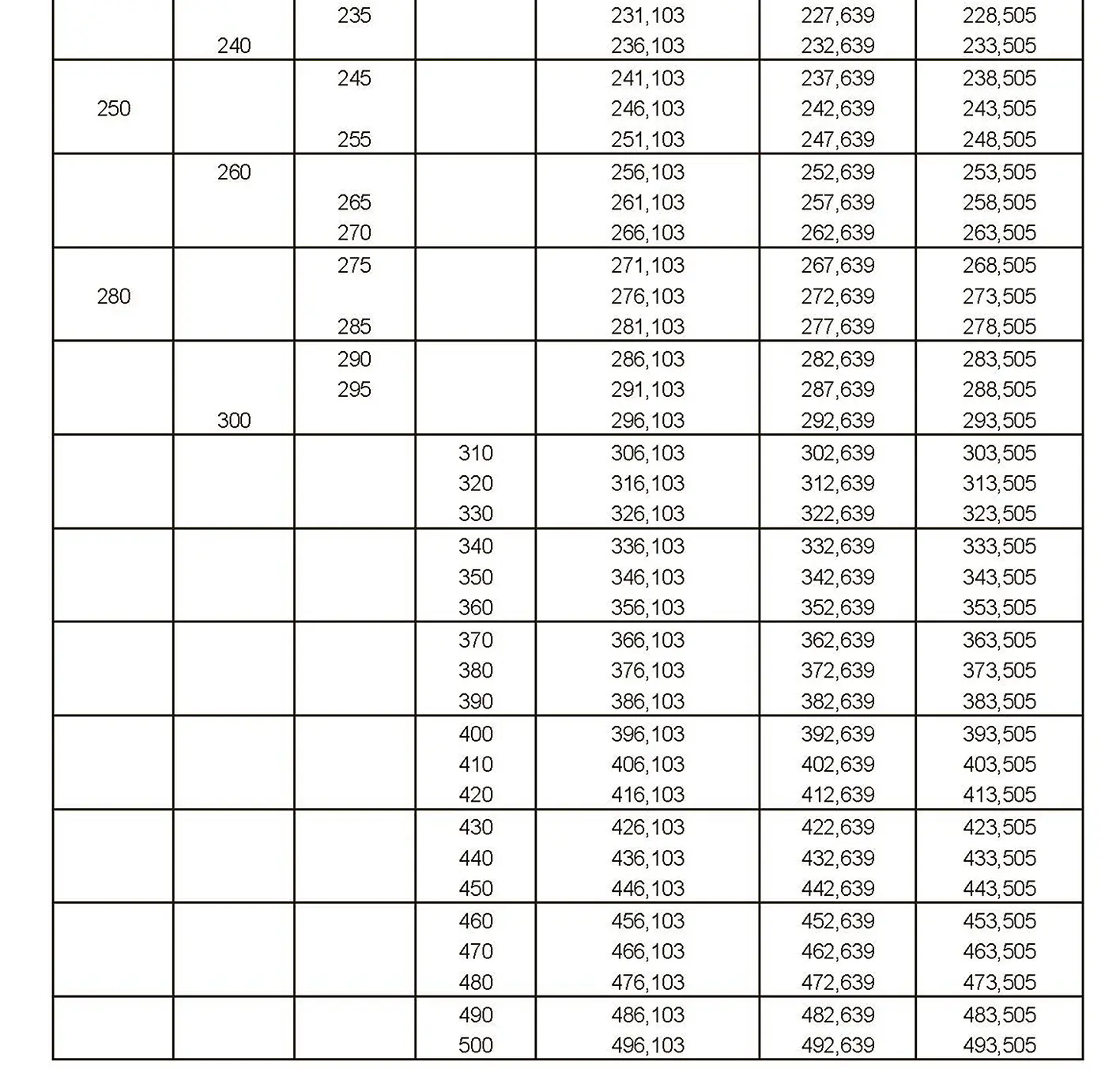
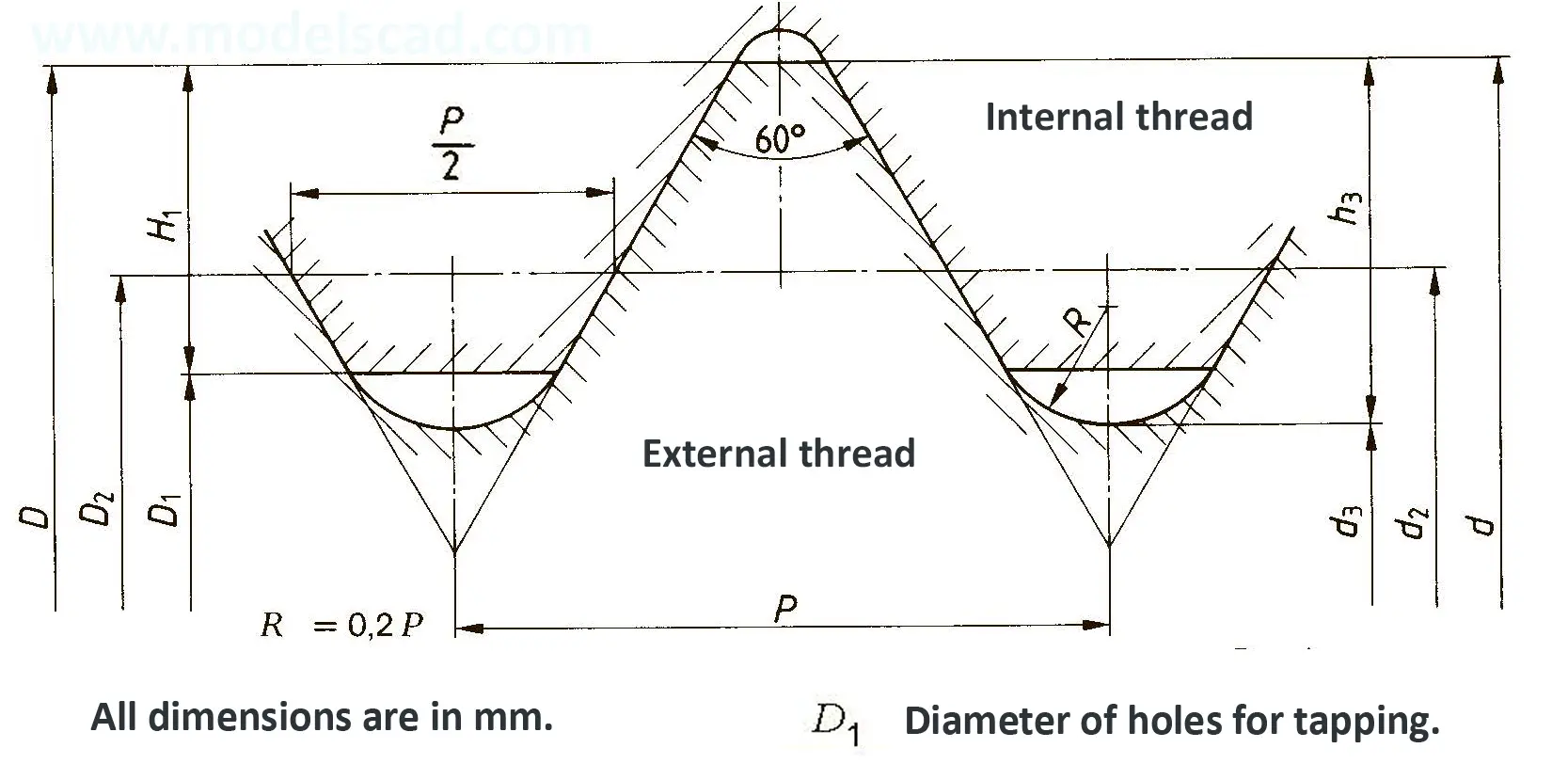
The fine thread ISO DIN 13-11 has a smaller pitch than the coarse thread, which increases its elasticity. This thread is used, for example, for adjusting screws in measuring instruments, which allows for more precise settings. The designation consists of the letter M, nominal diameter and pitch, angle of inclination 60°. Pitch 8 mm.
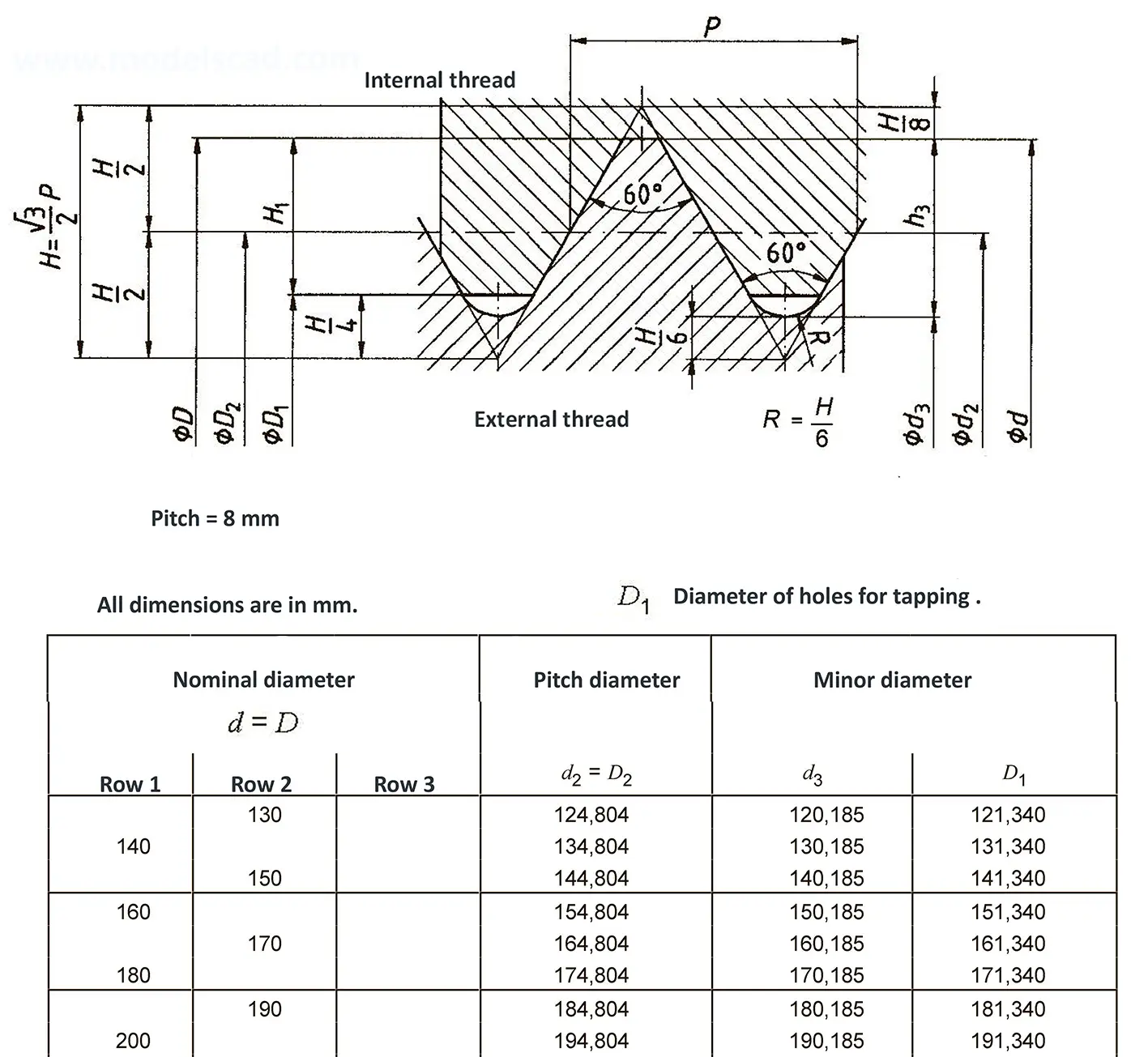
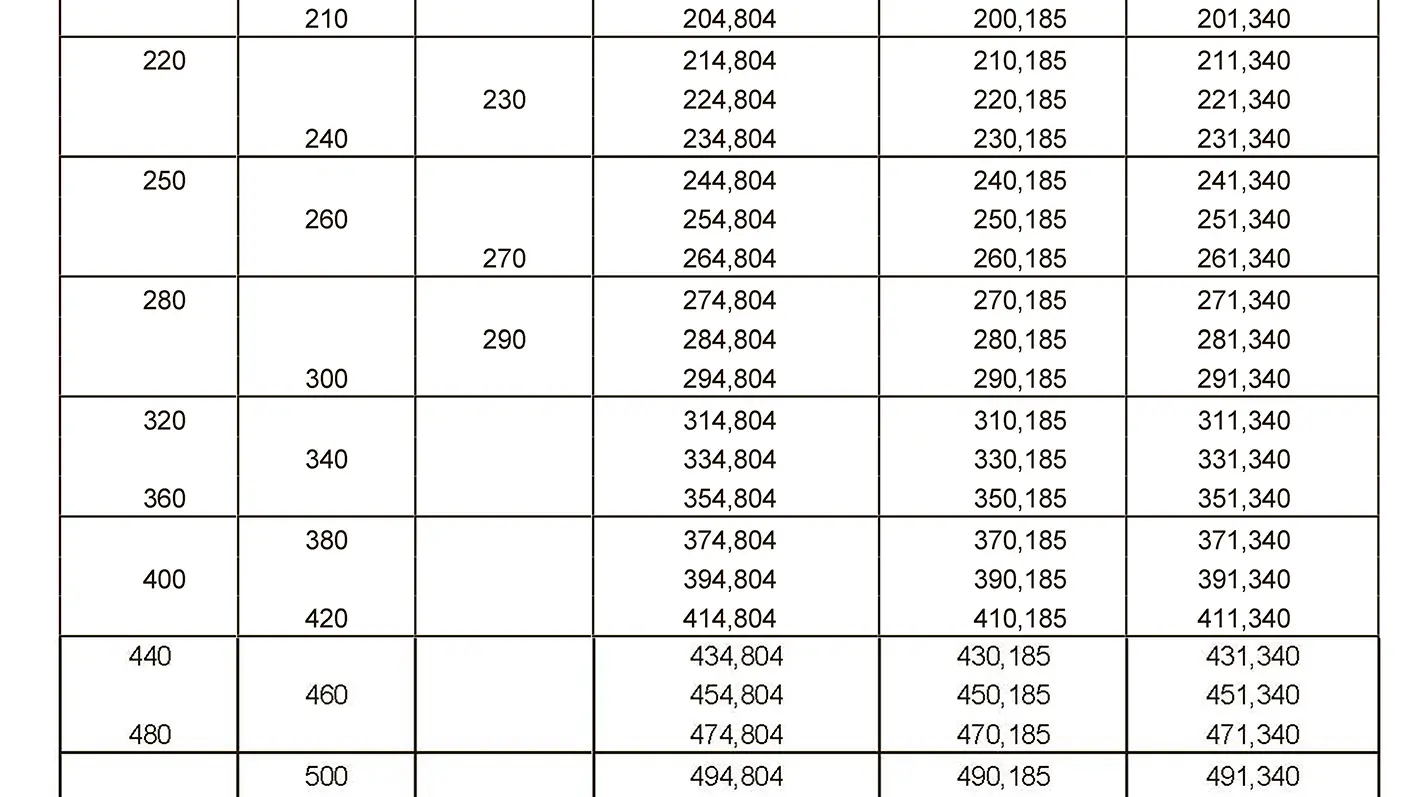
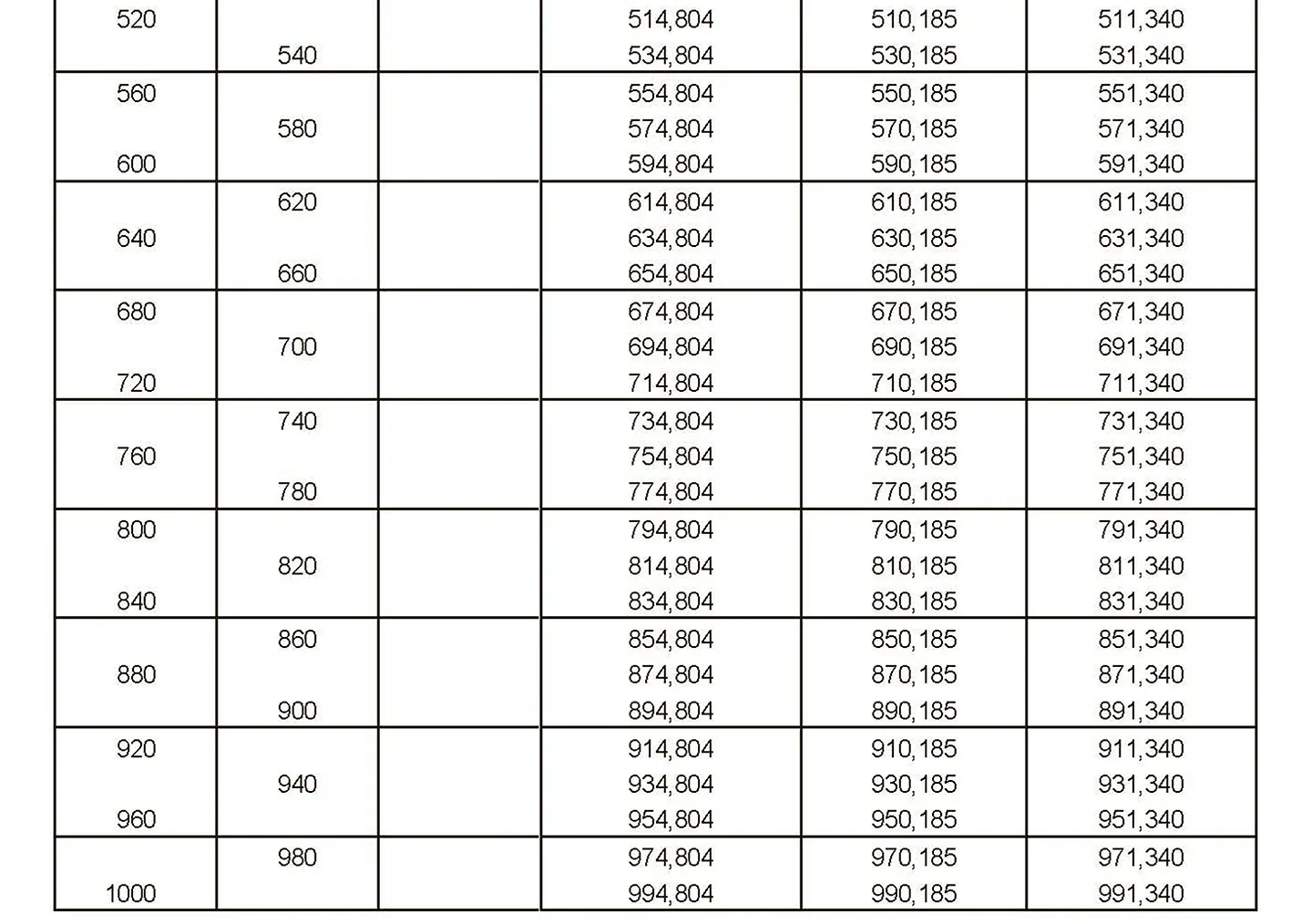
Metric thread ISO DIN 14-2. Metric thread with a nominal diameter less than 1 mm. It is used in precision mechanisms. The term consists of the letter M, the nominal diameter and the pitch, the flank angle is 60°.
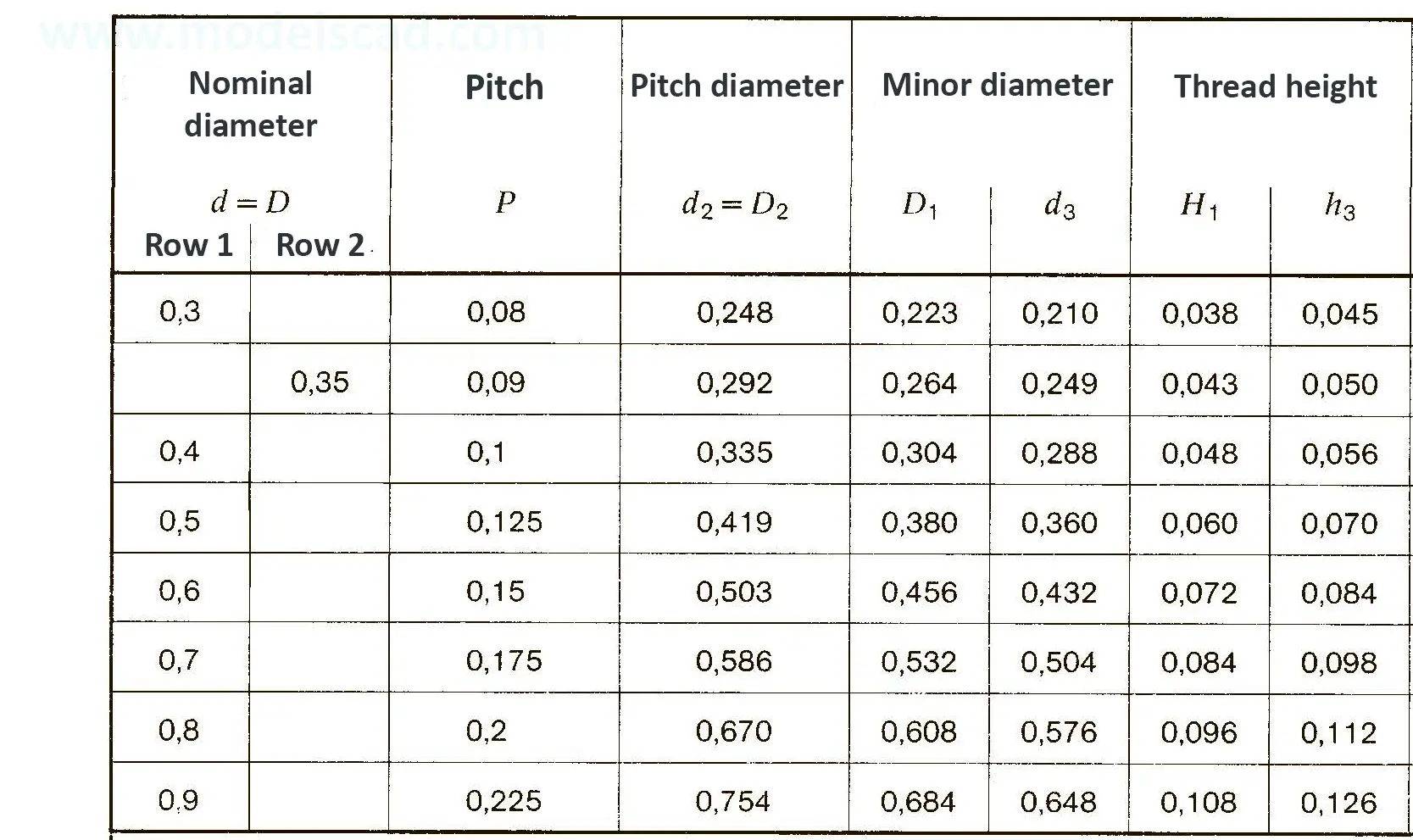
USA standards
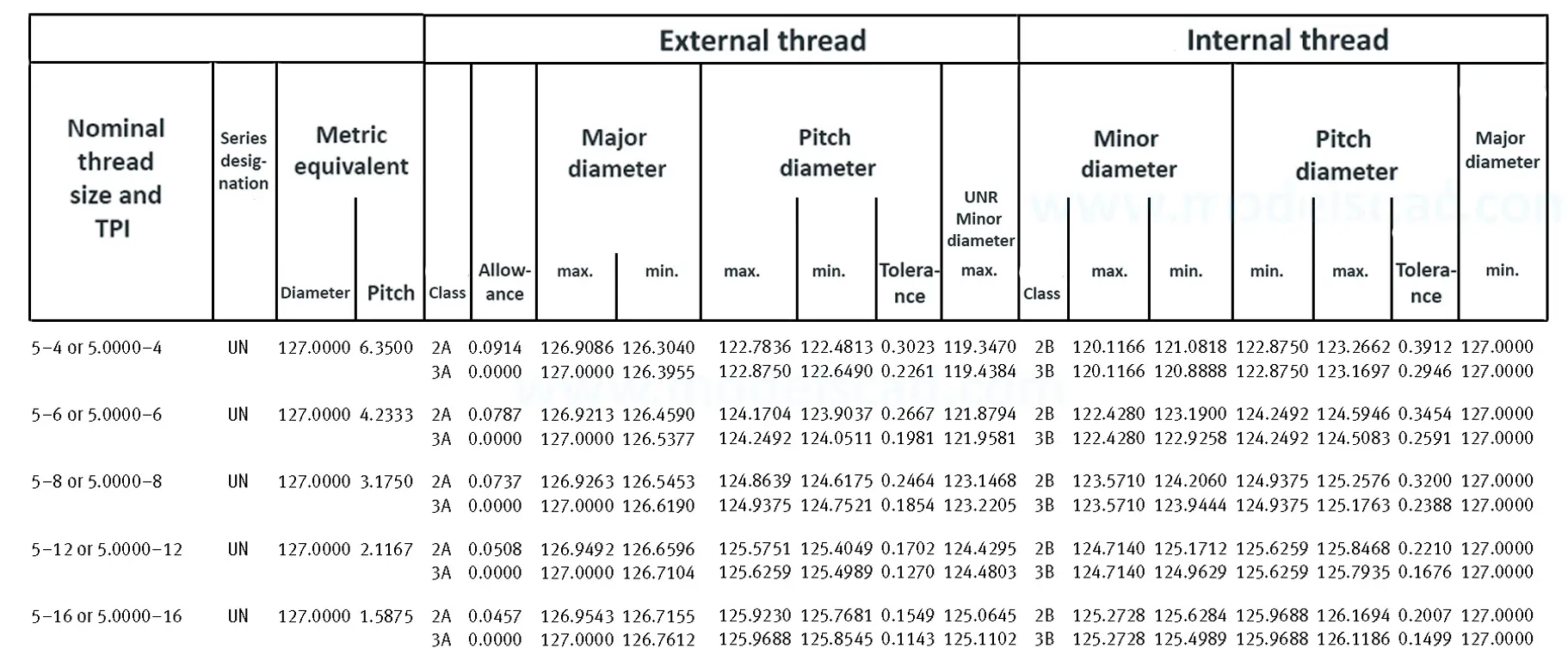
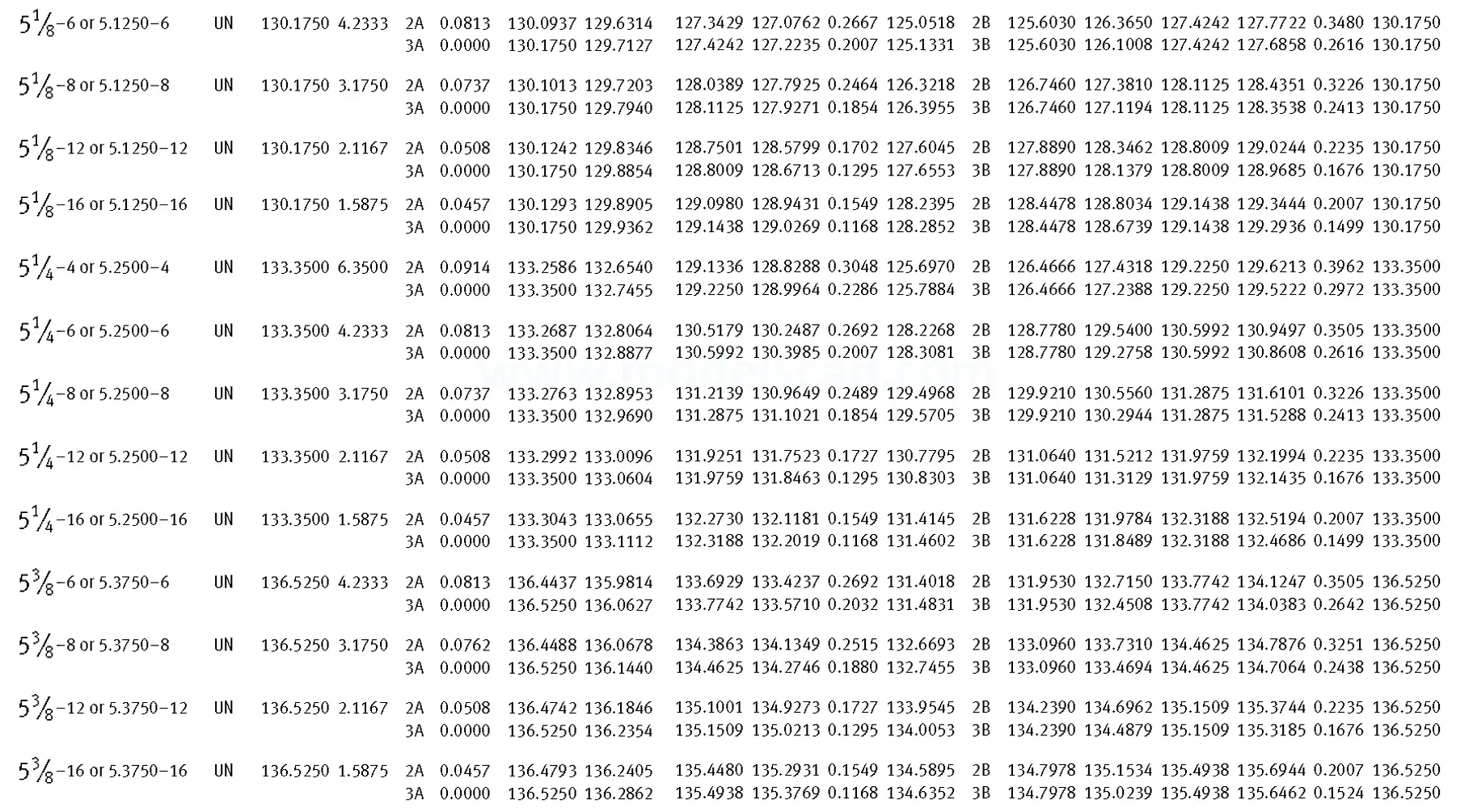
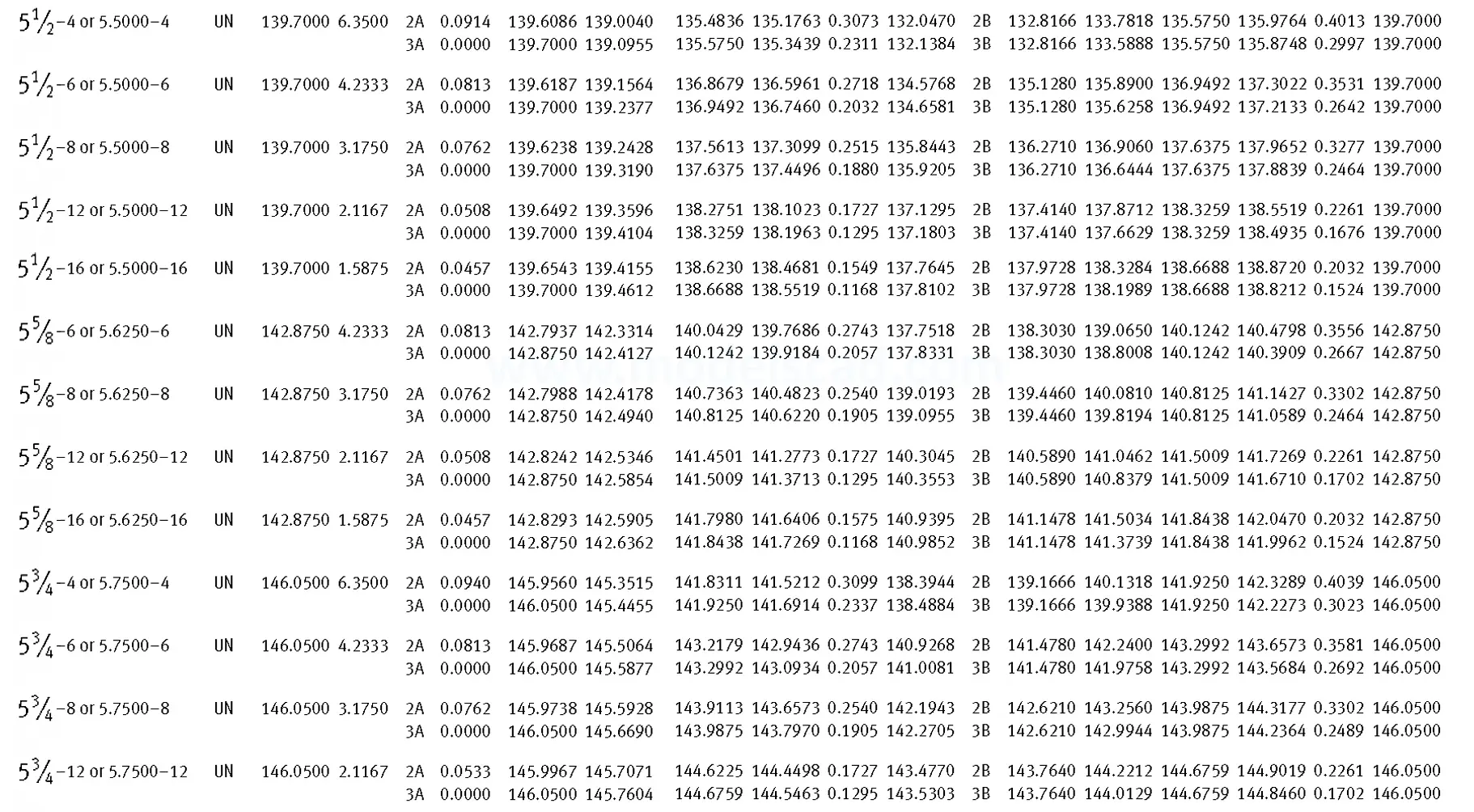
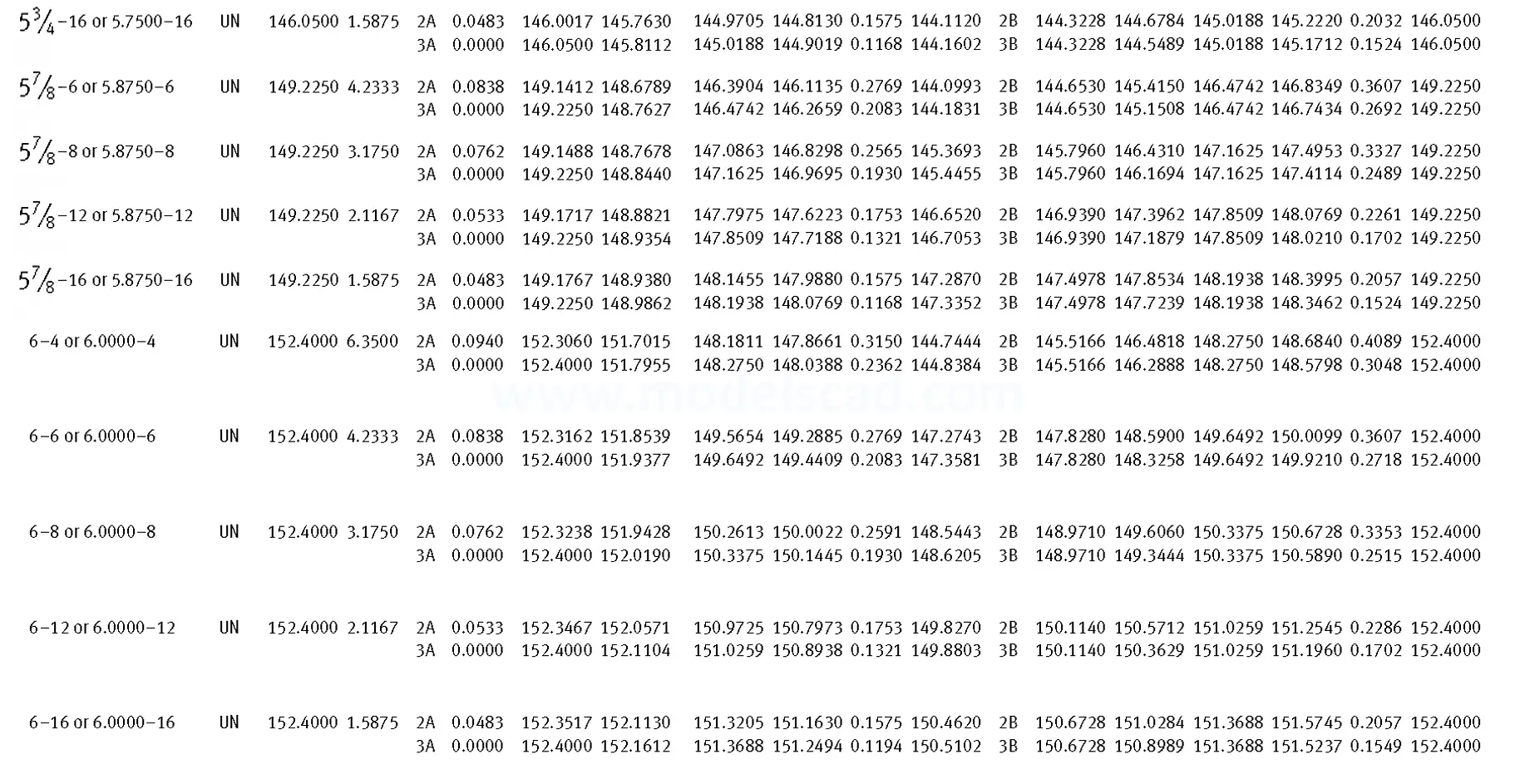
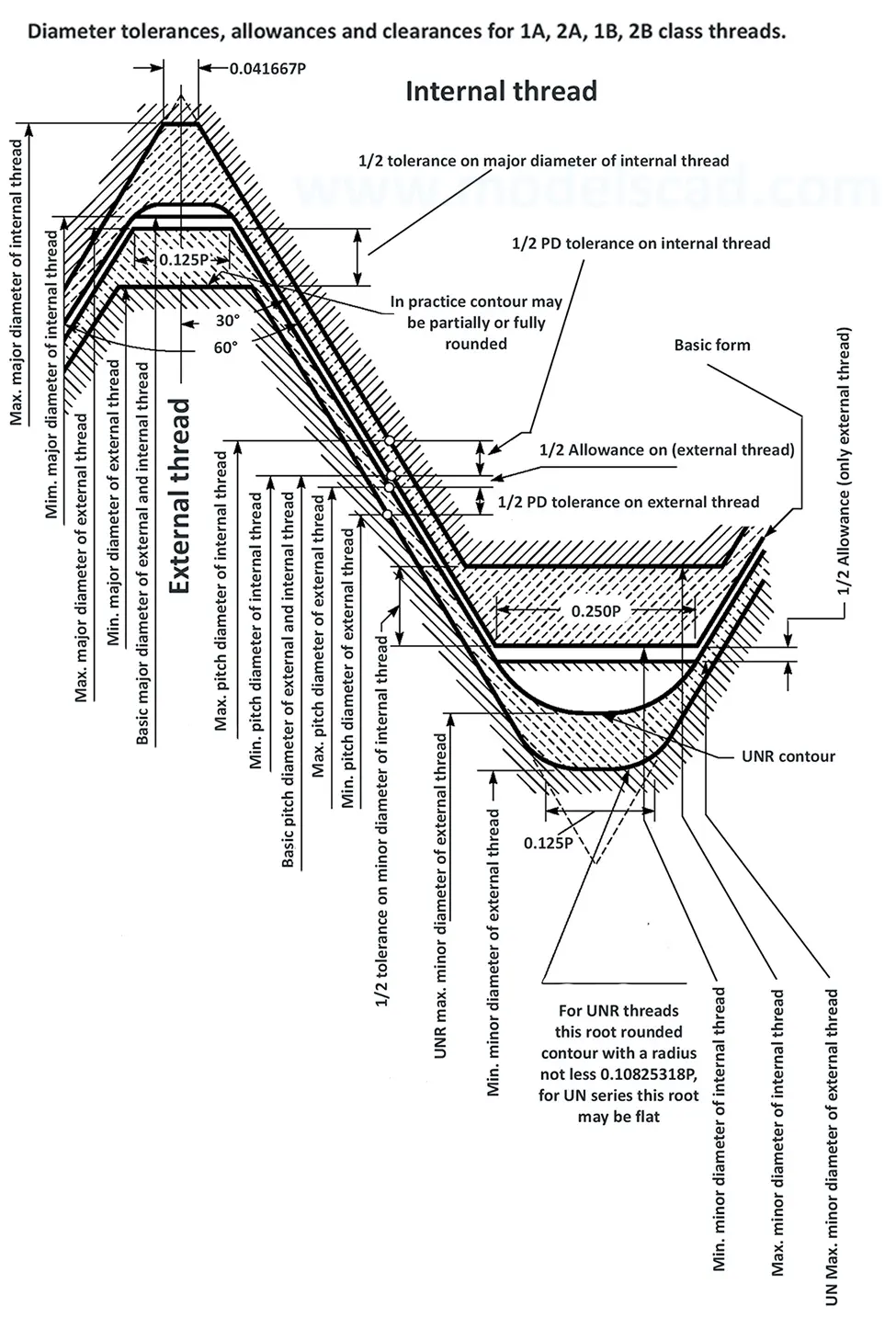
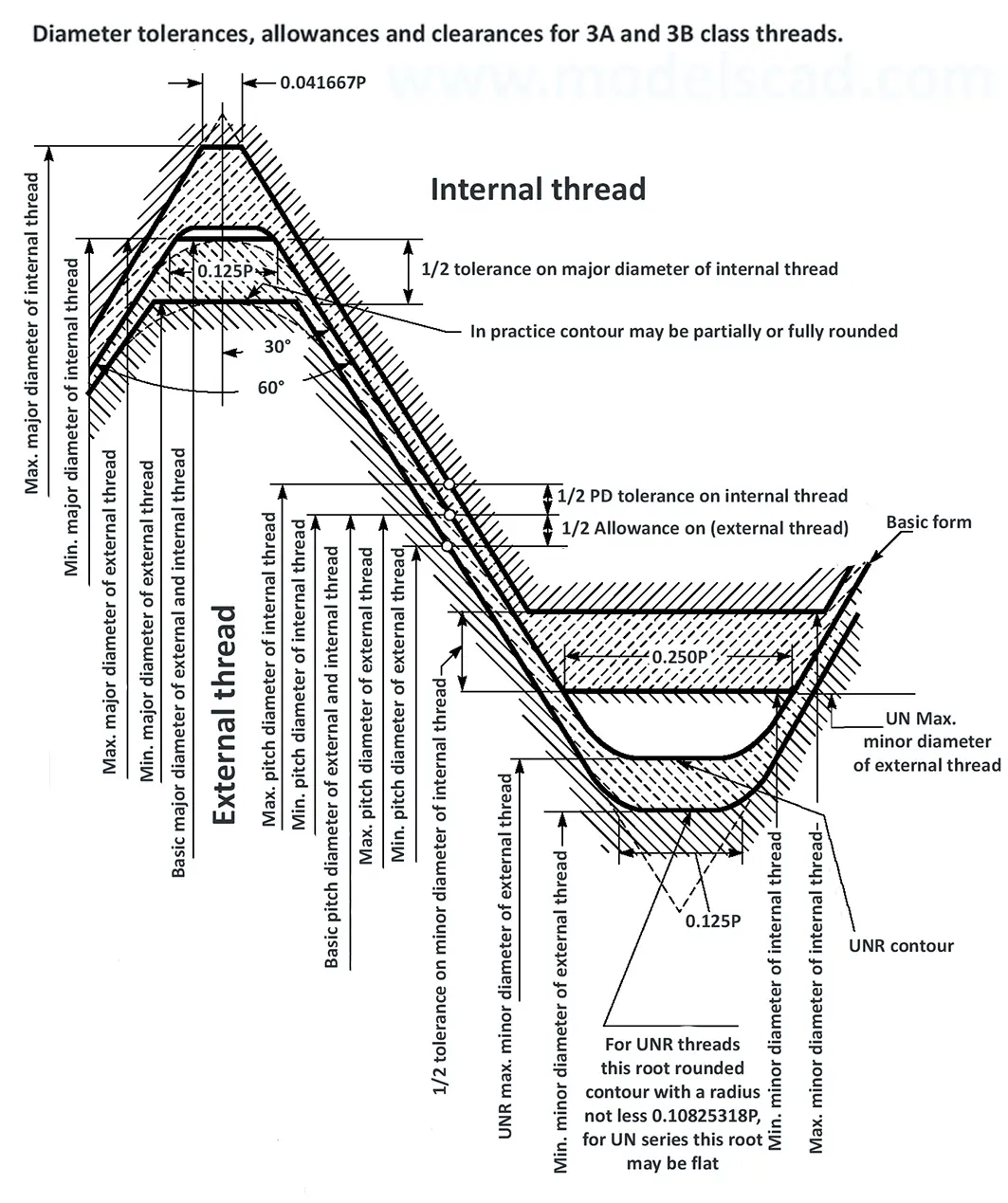
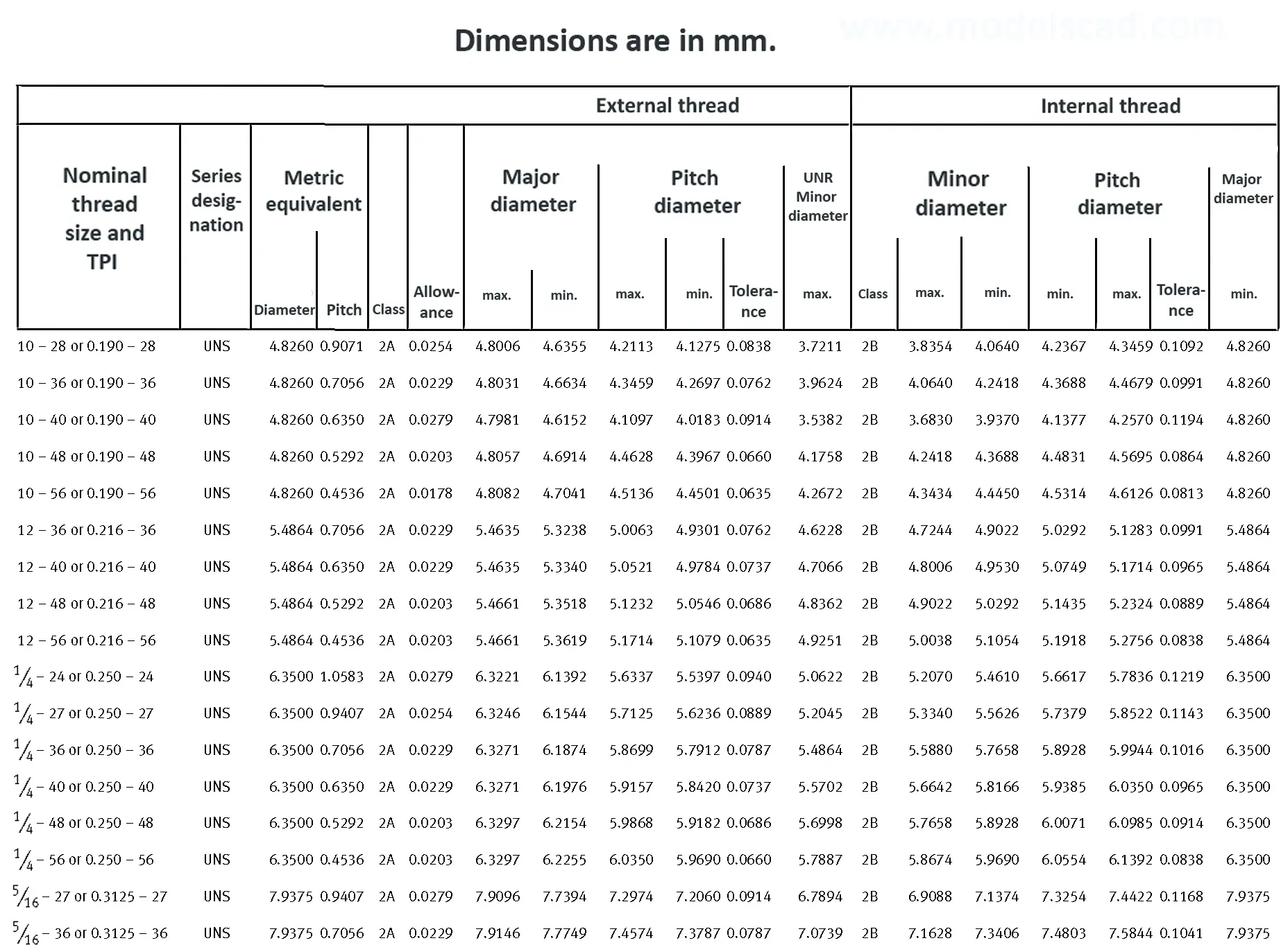
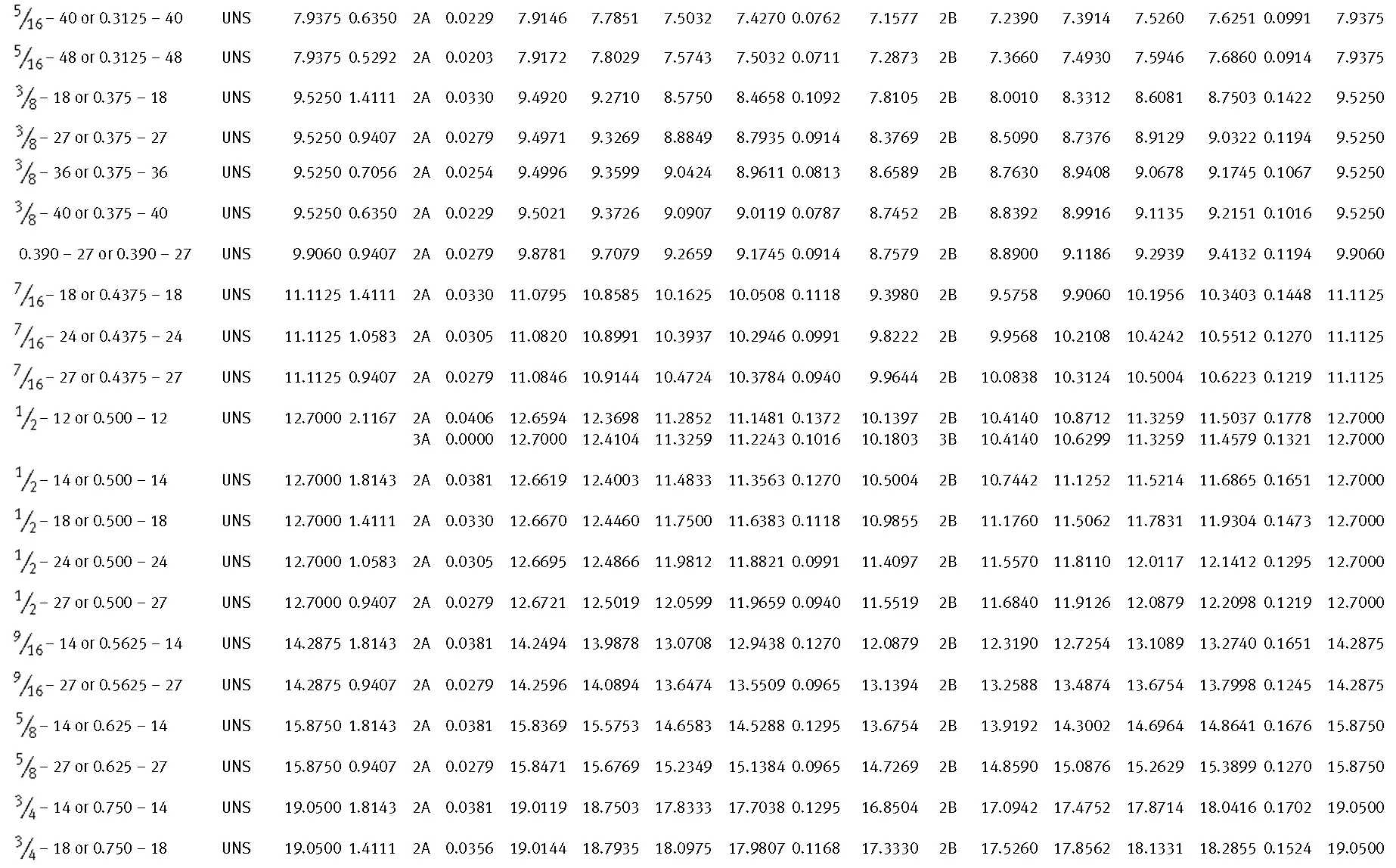
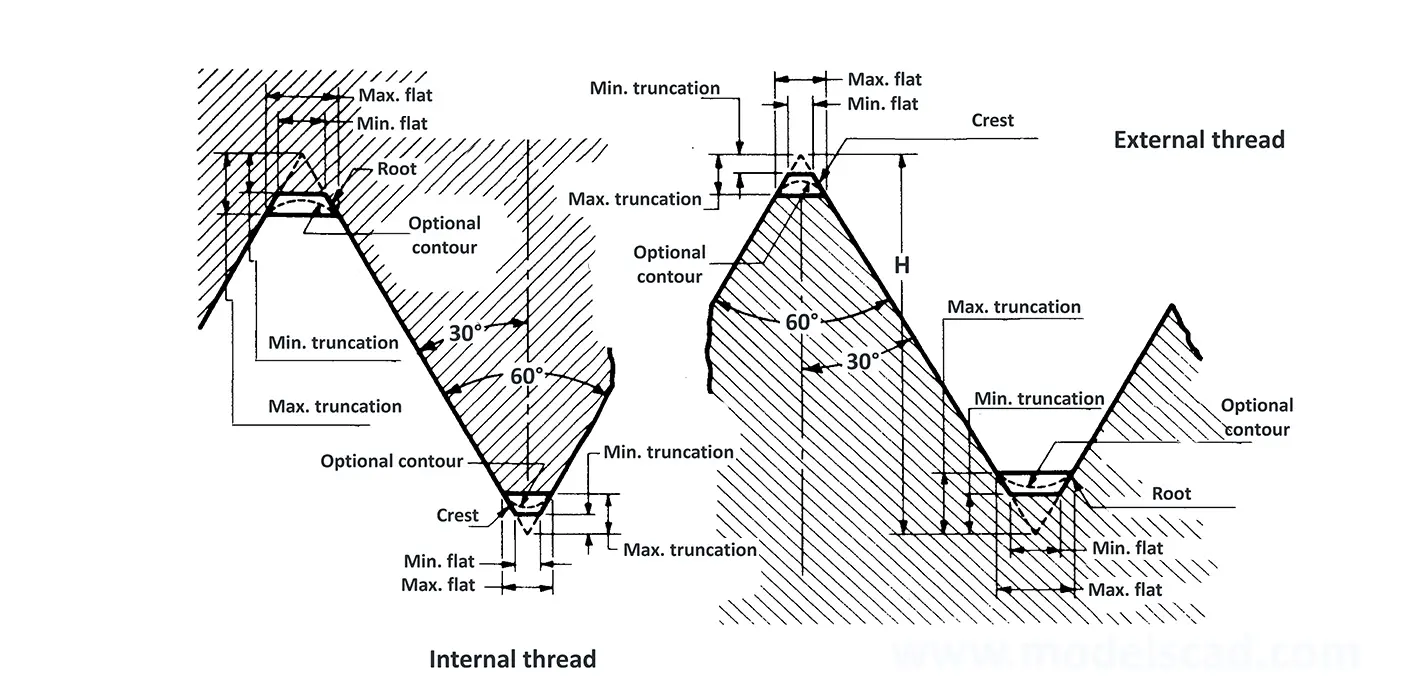
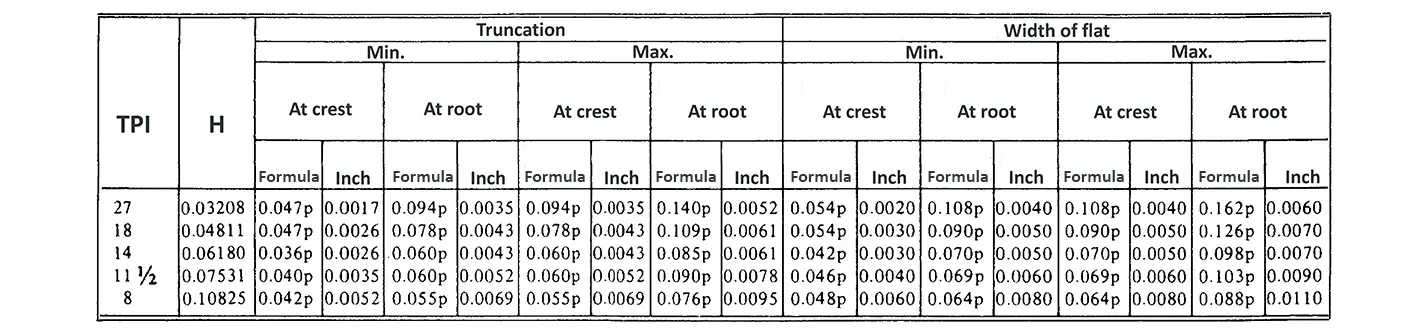
Unified ANSI ASME B1.1 inch thread, profile angle 60°, thread profile UN and UNR. UNR only applies to male threads, the difference between UN and UNR threads is that a flat or rounded base is specified for UN threads, and only a rounded base is specified for UNR threads. The catalog contains thread types UN, UNC, UNF, UNEF.
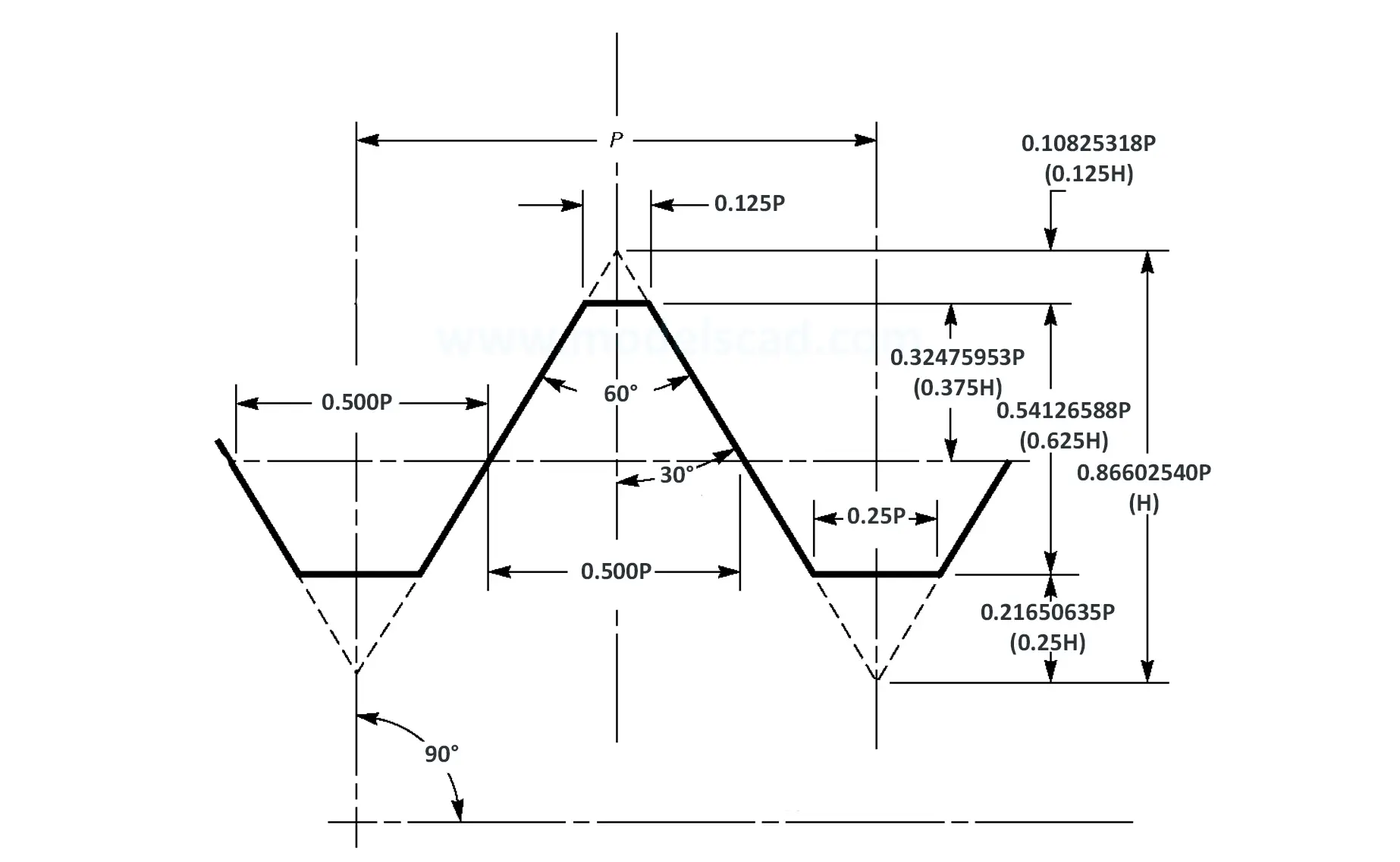
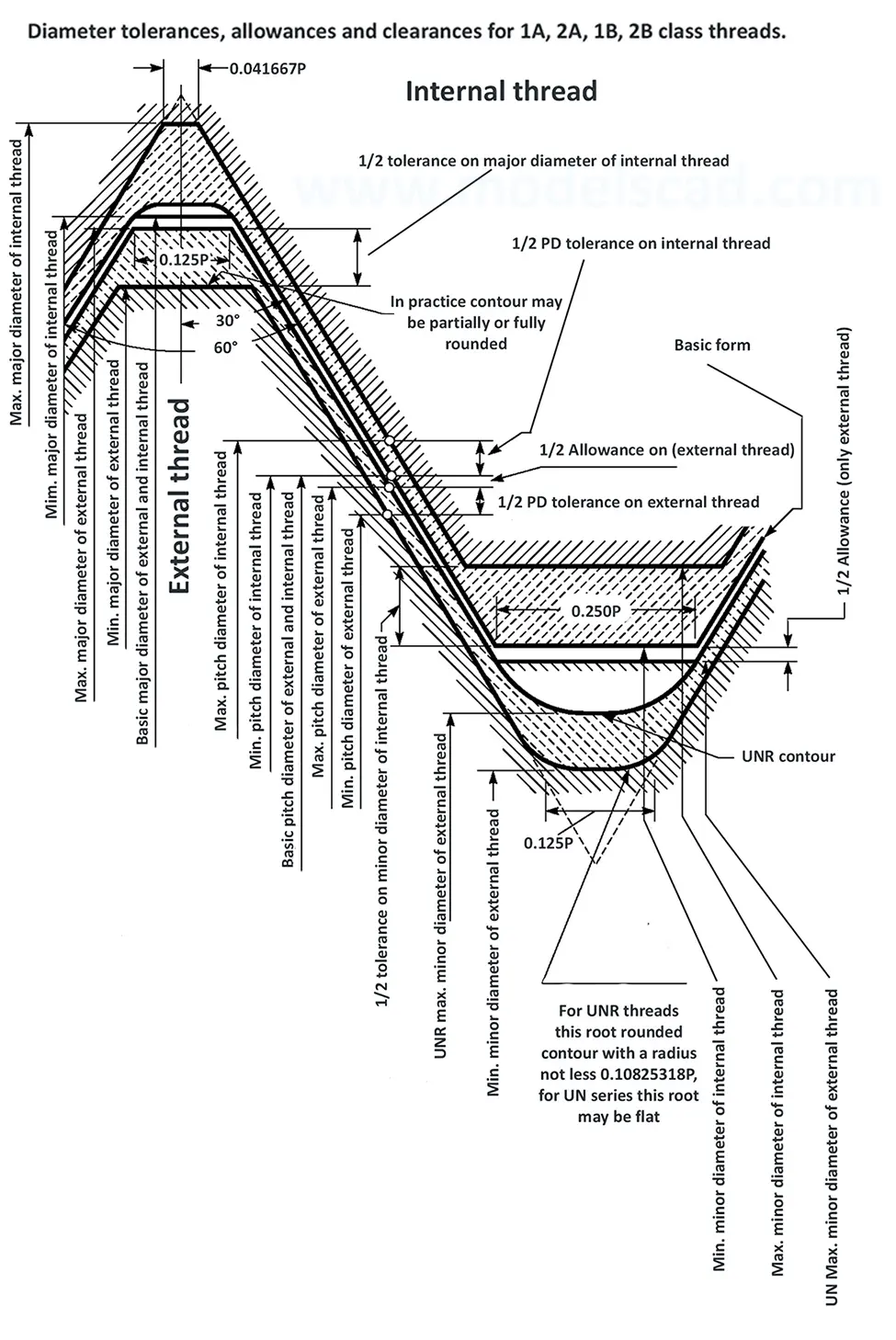
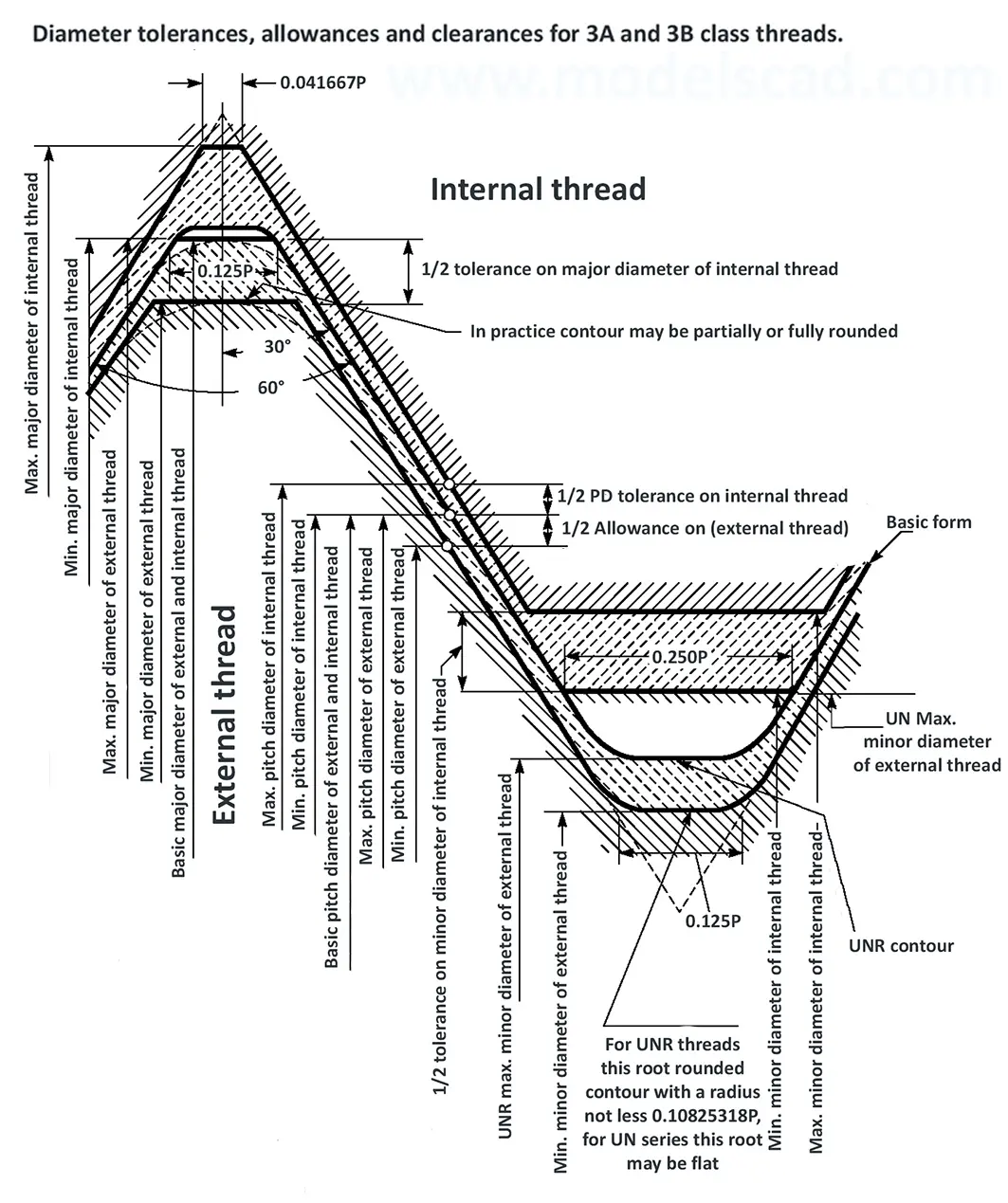
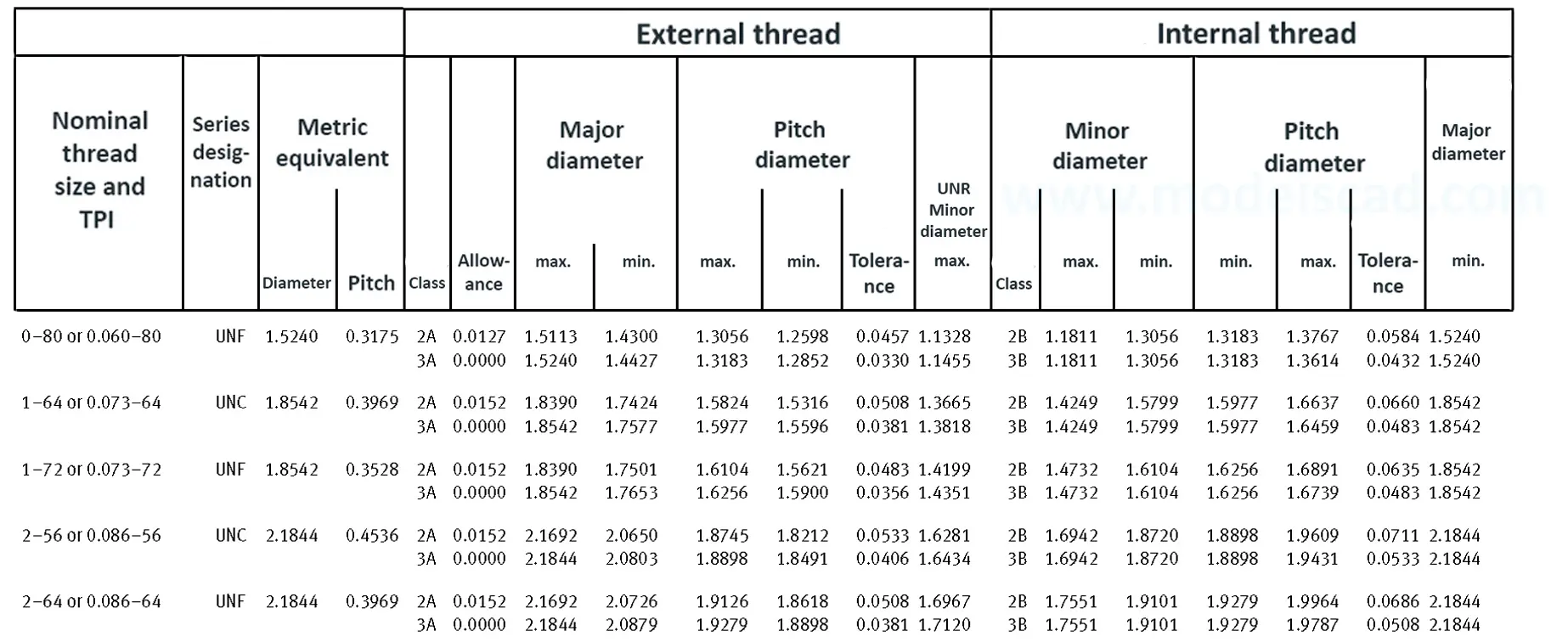
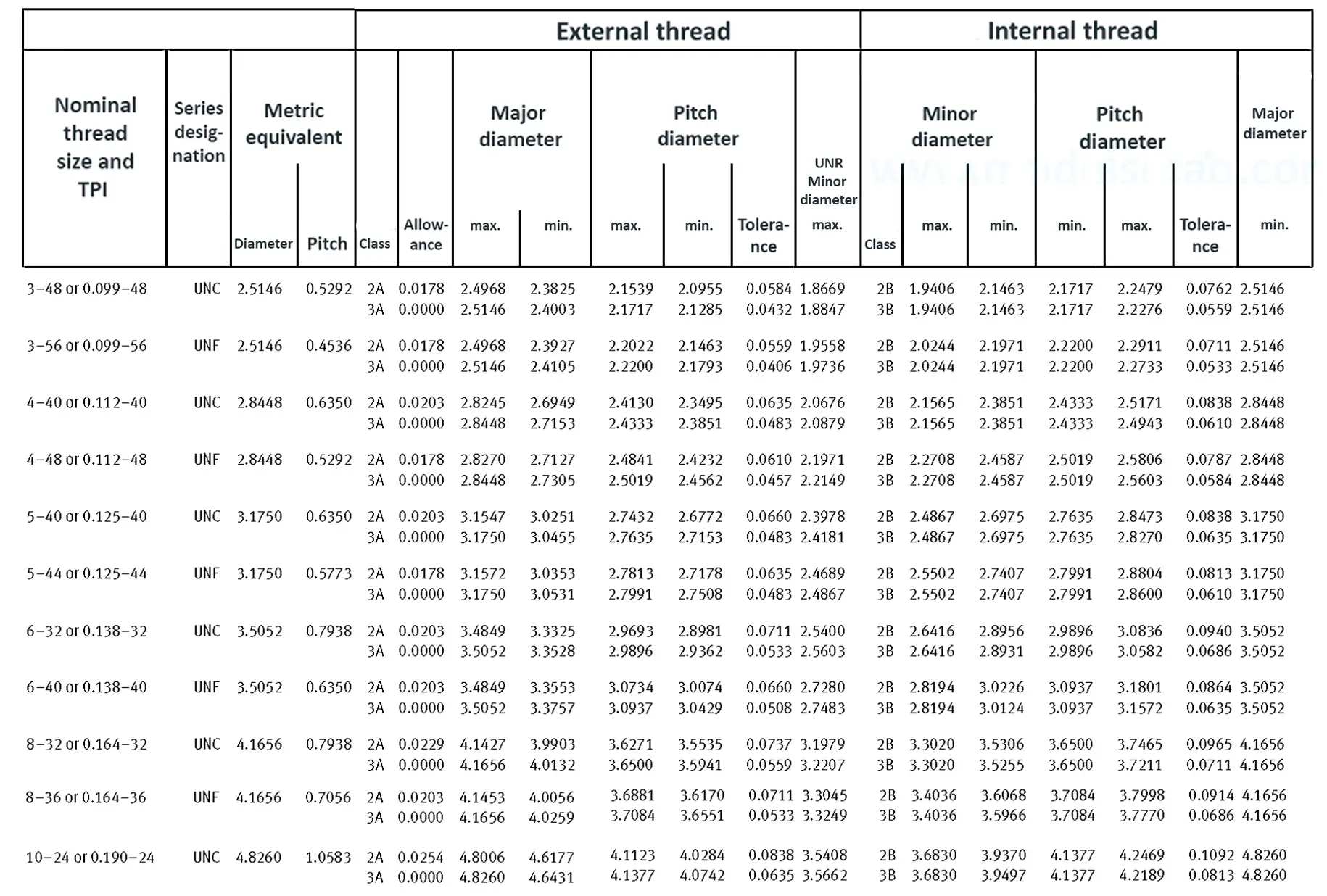
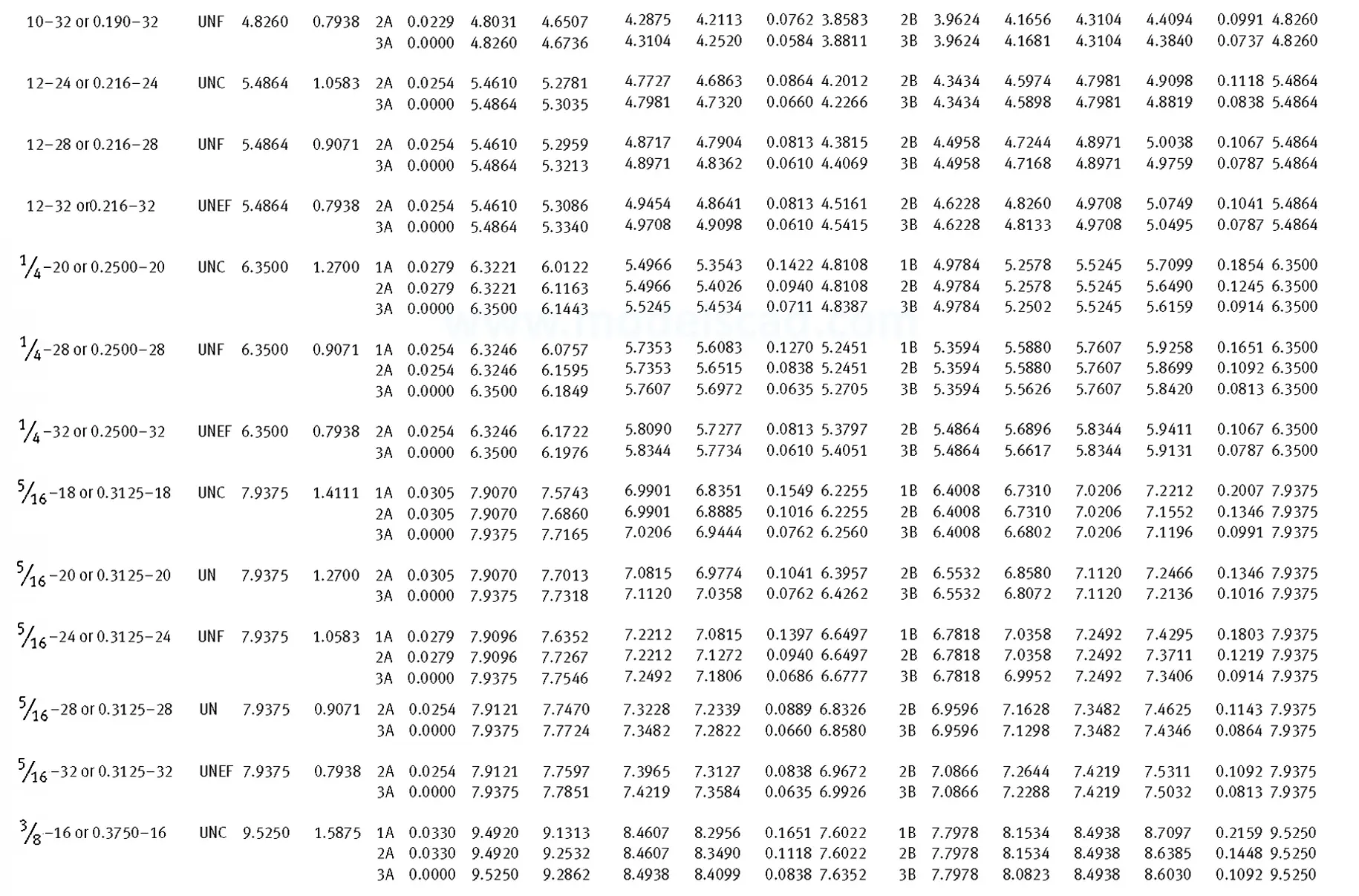
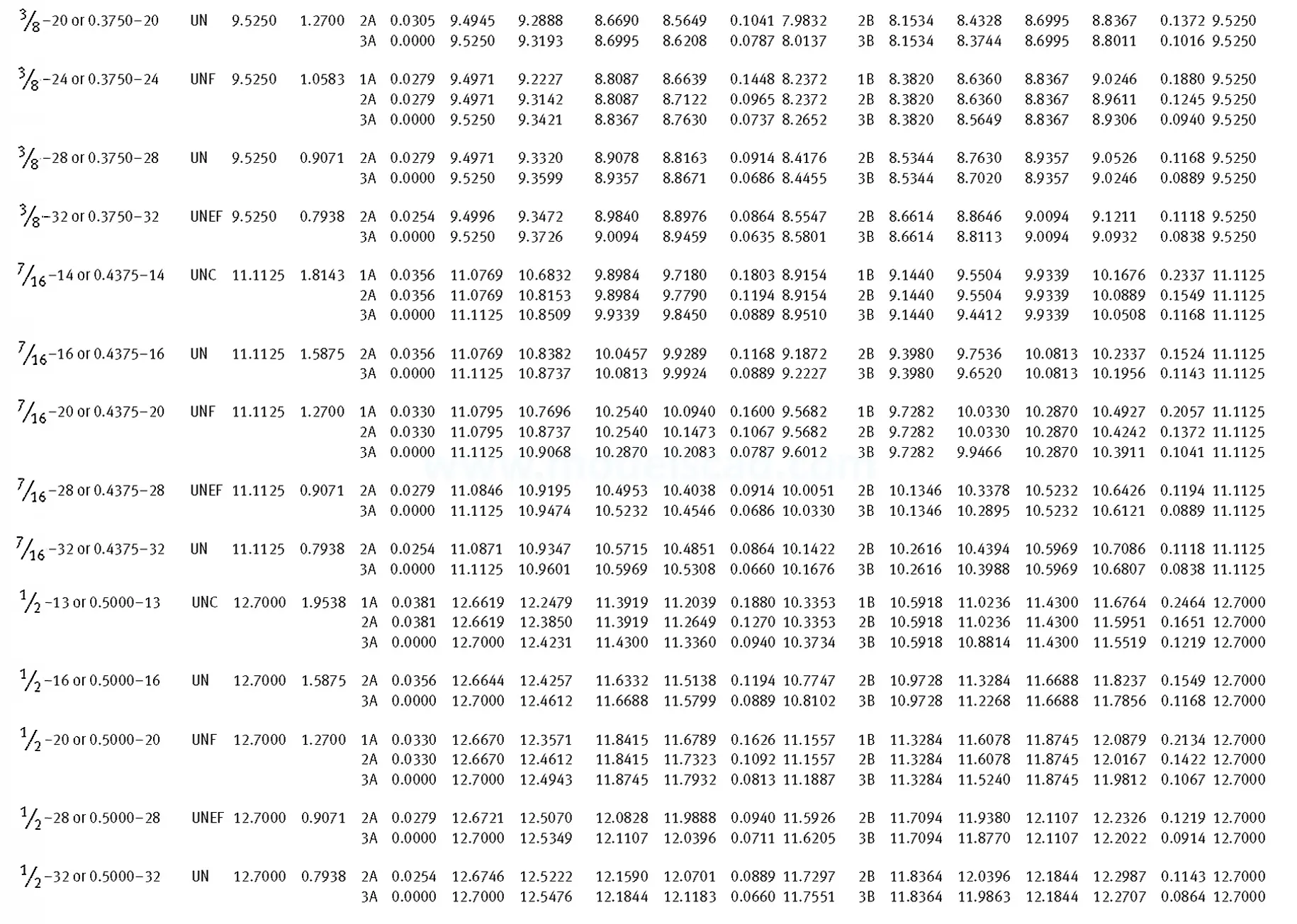
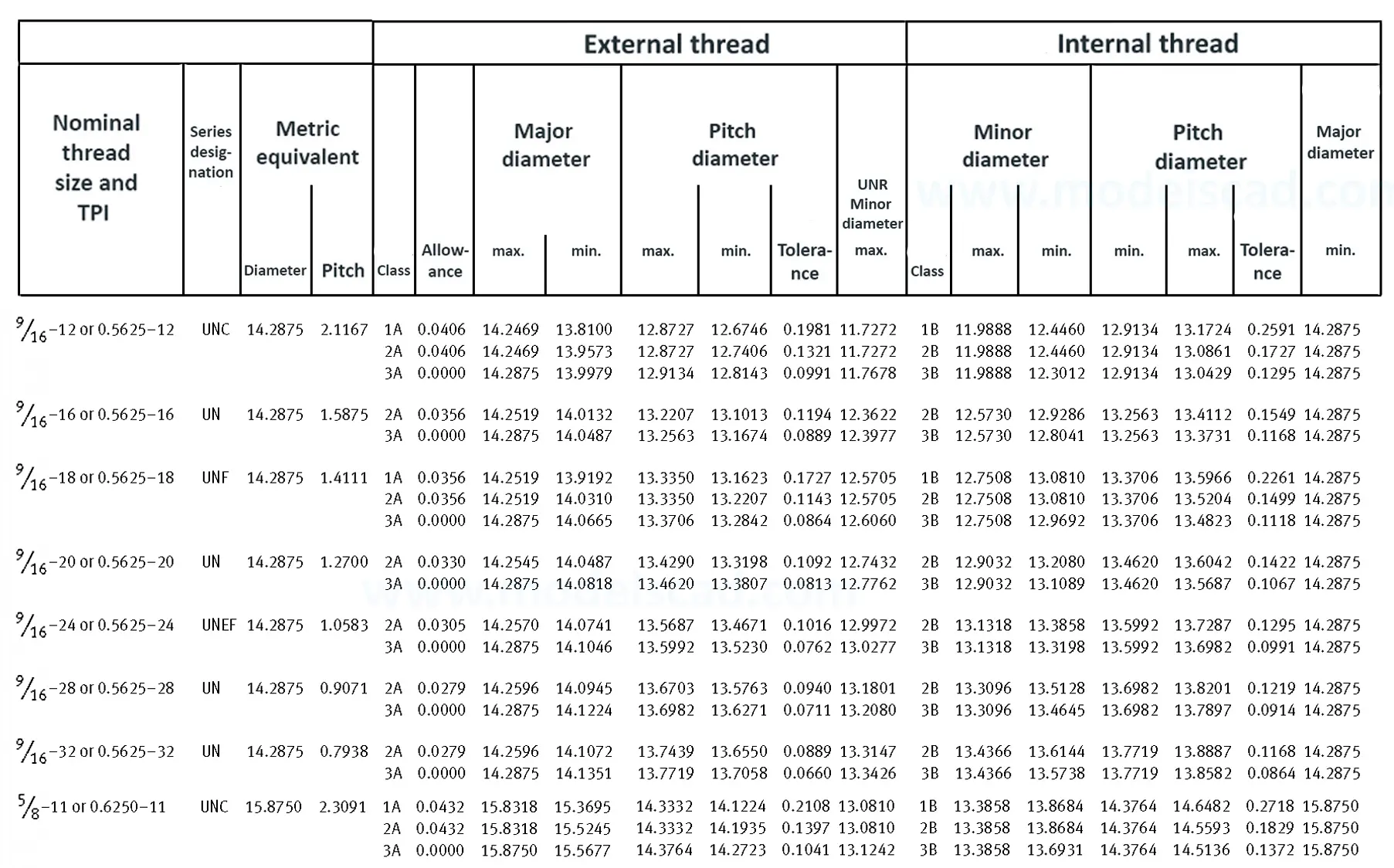
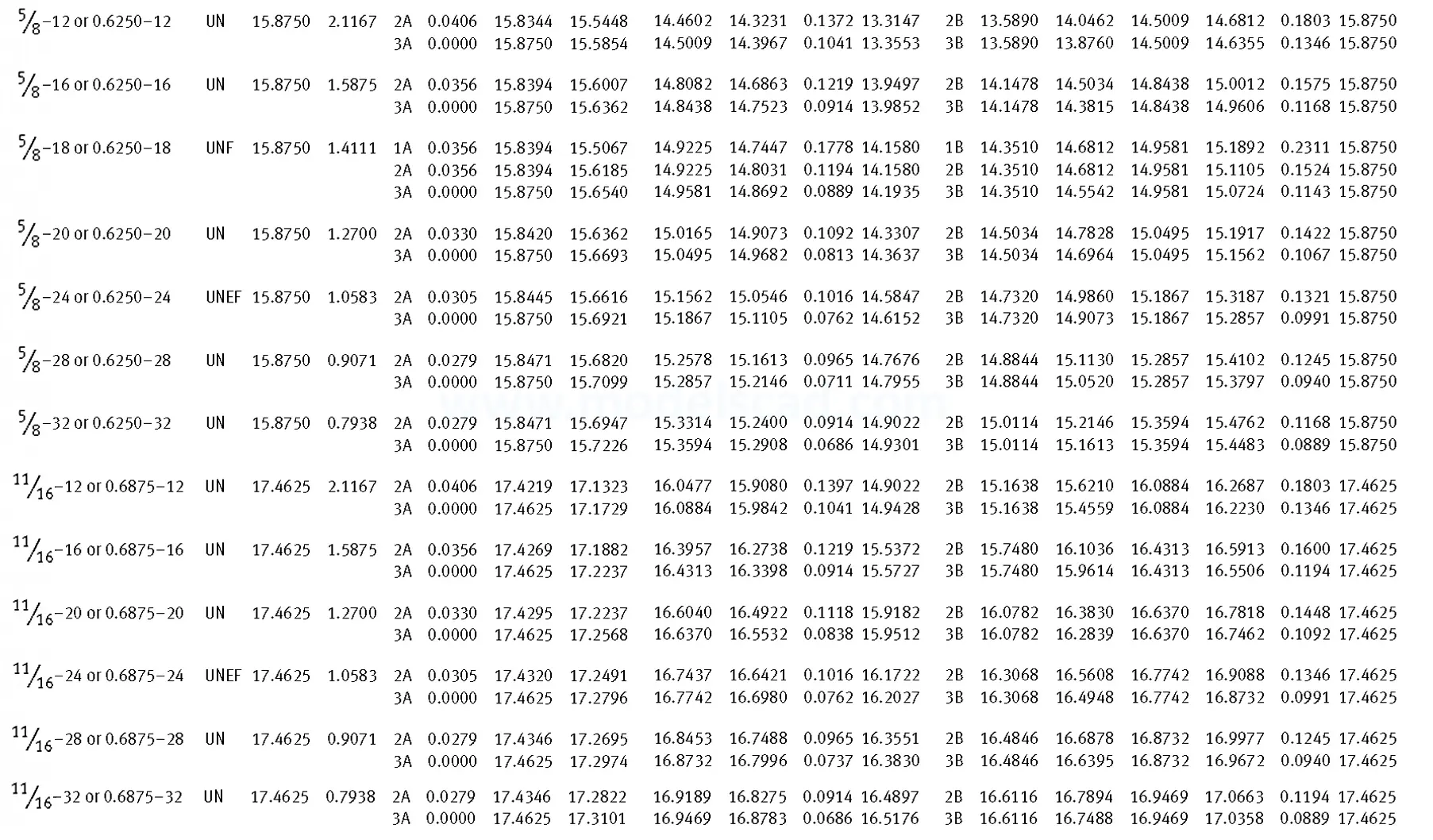
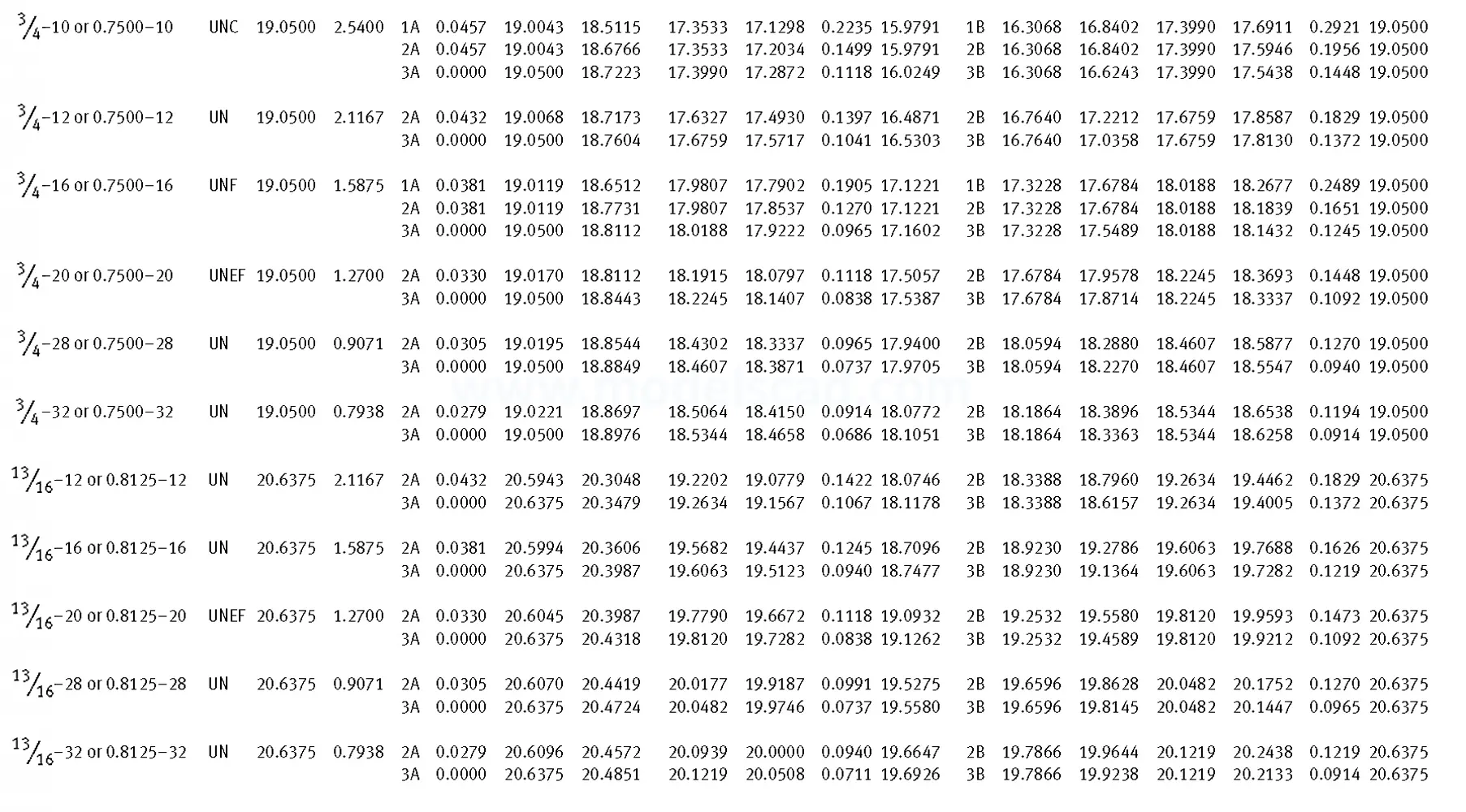
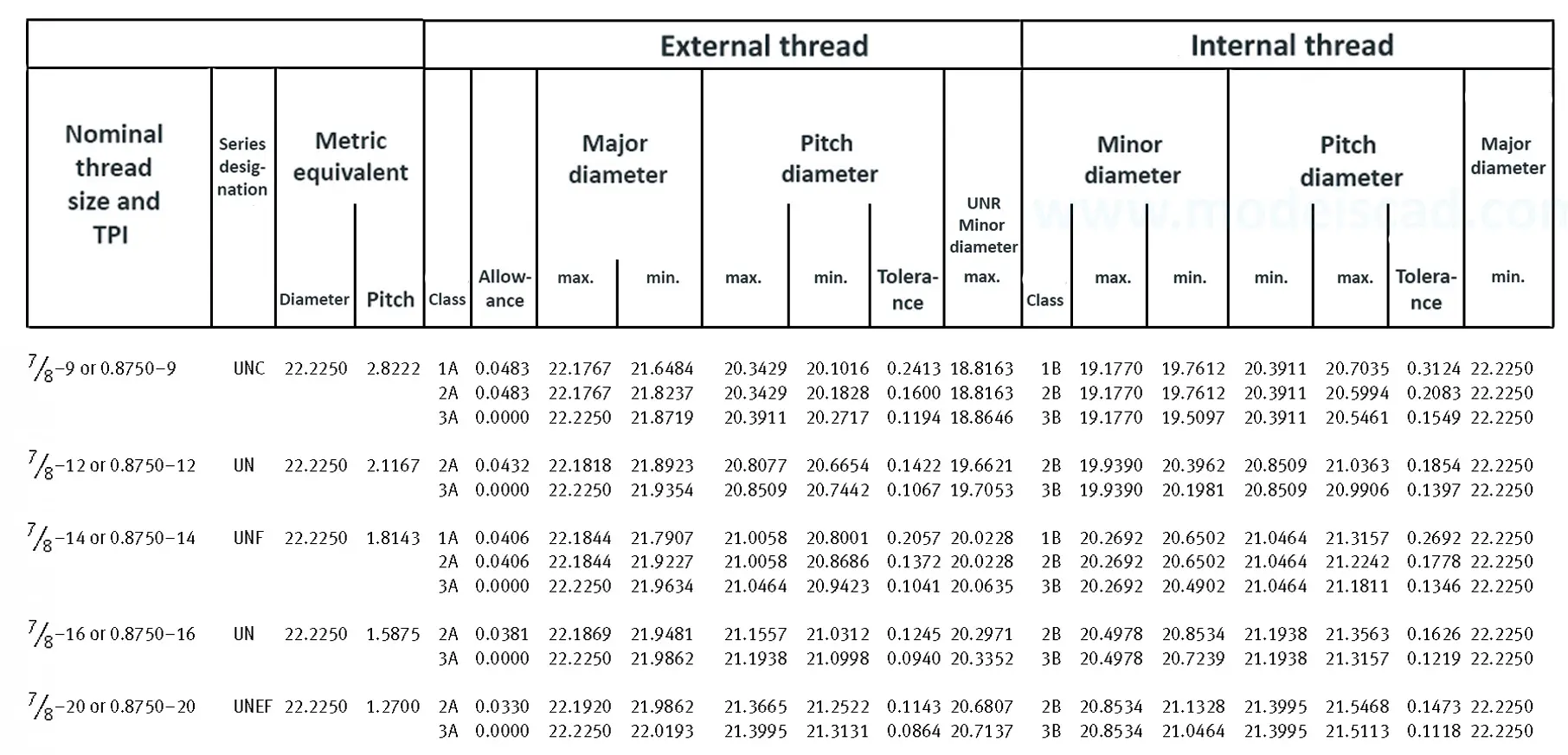
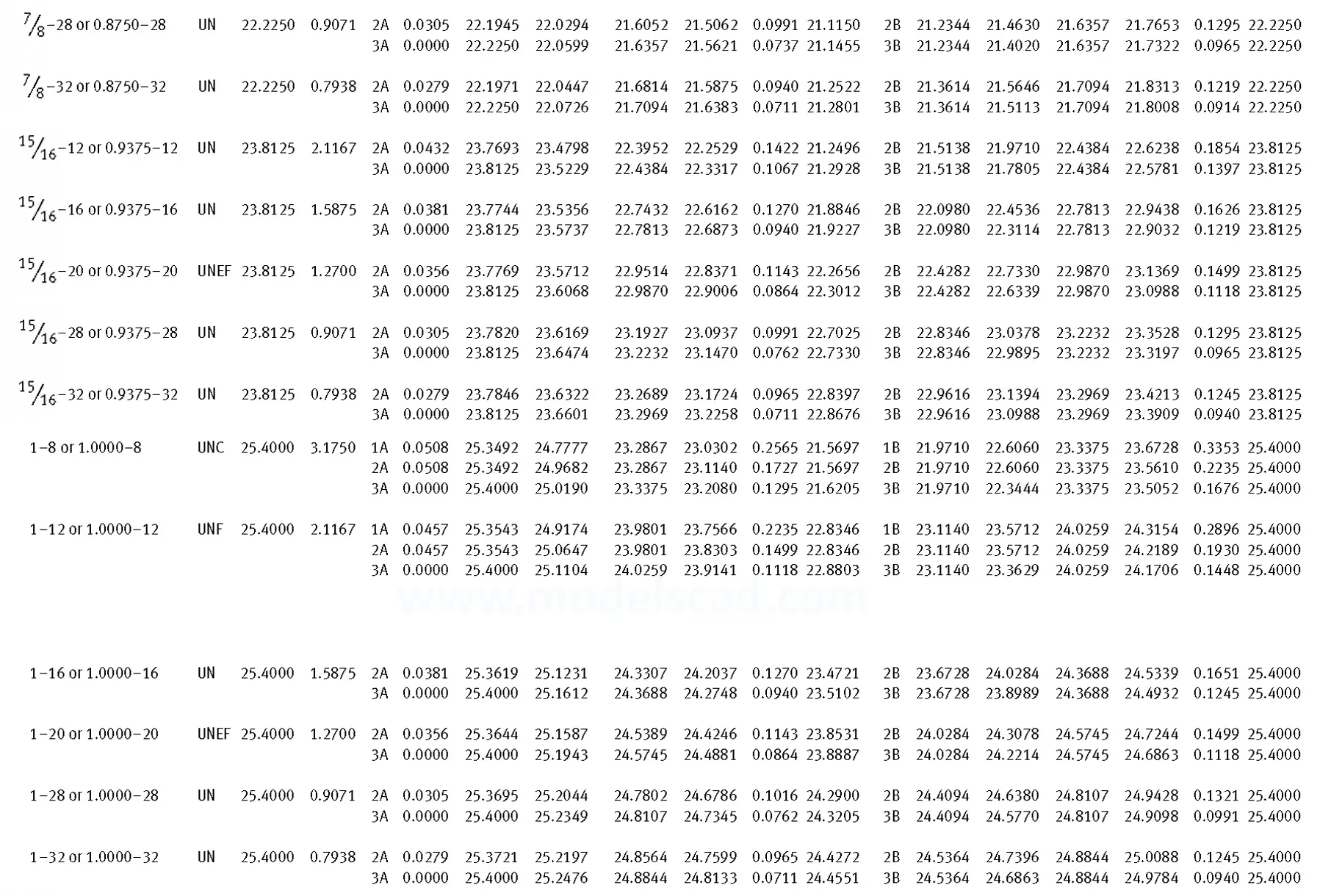
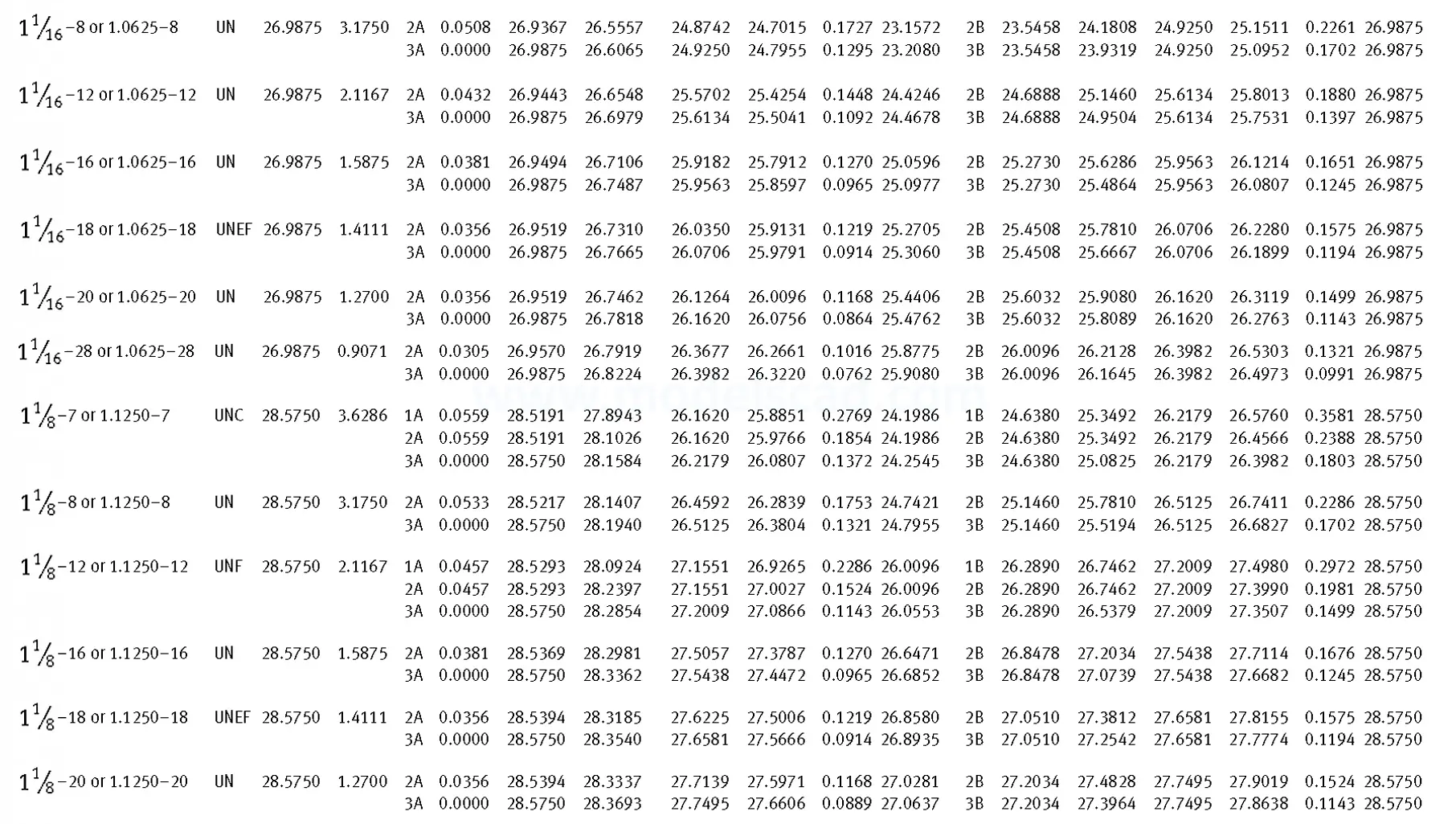
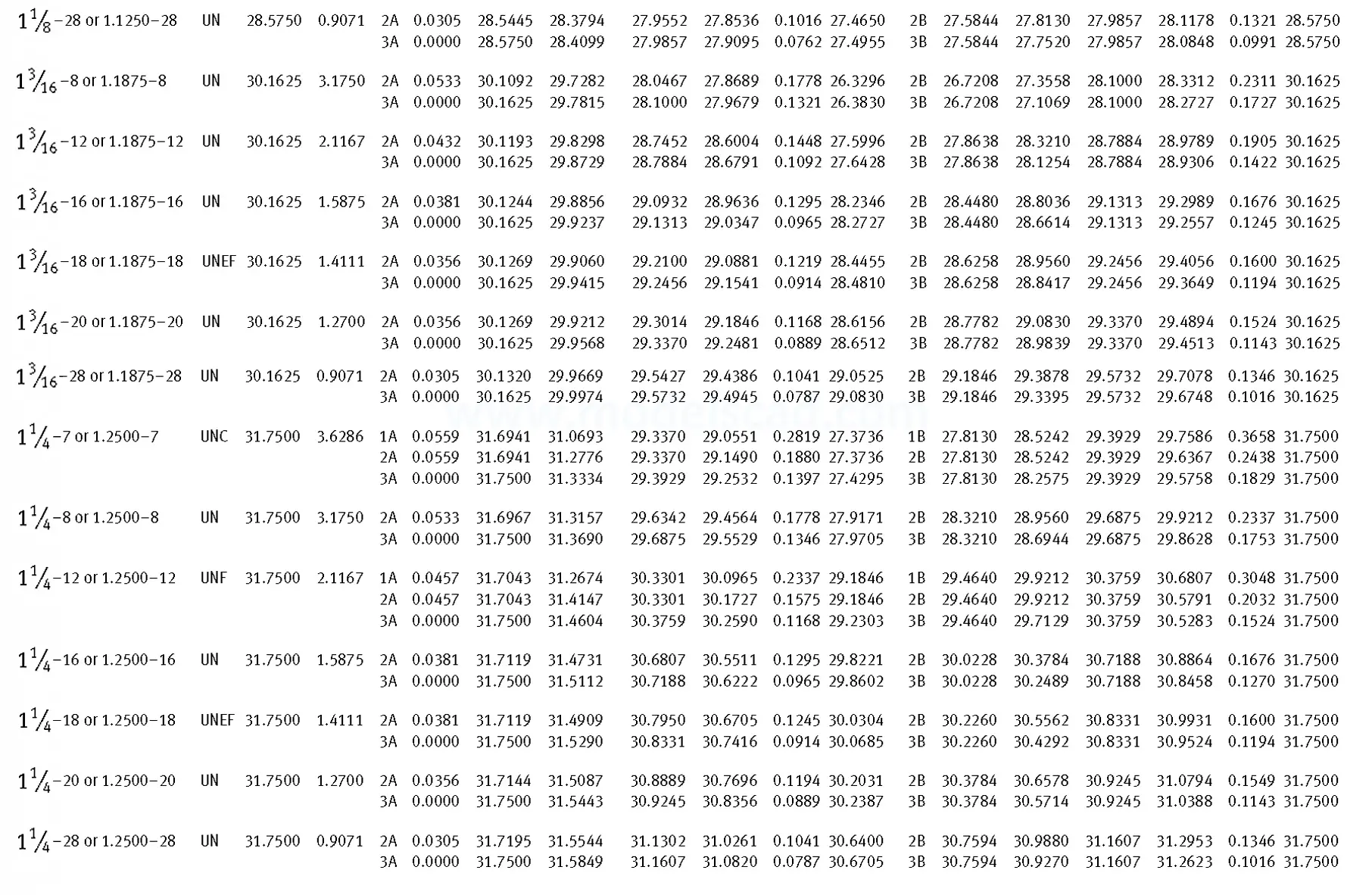
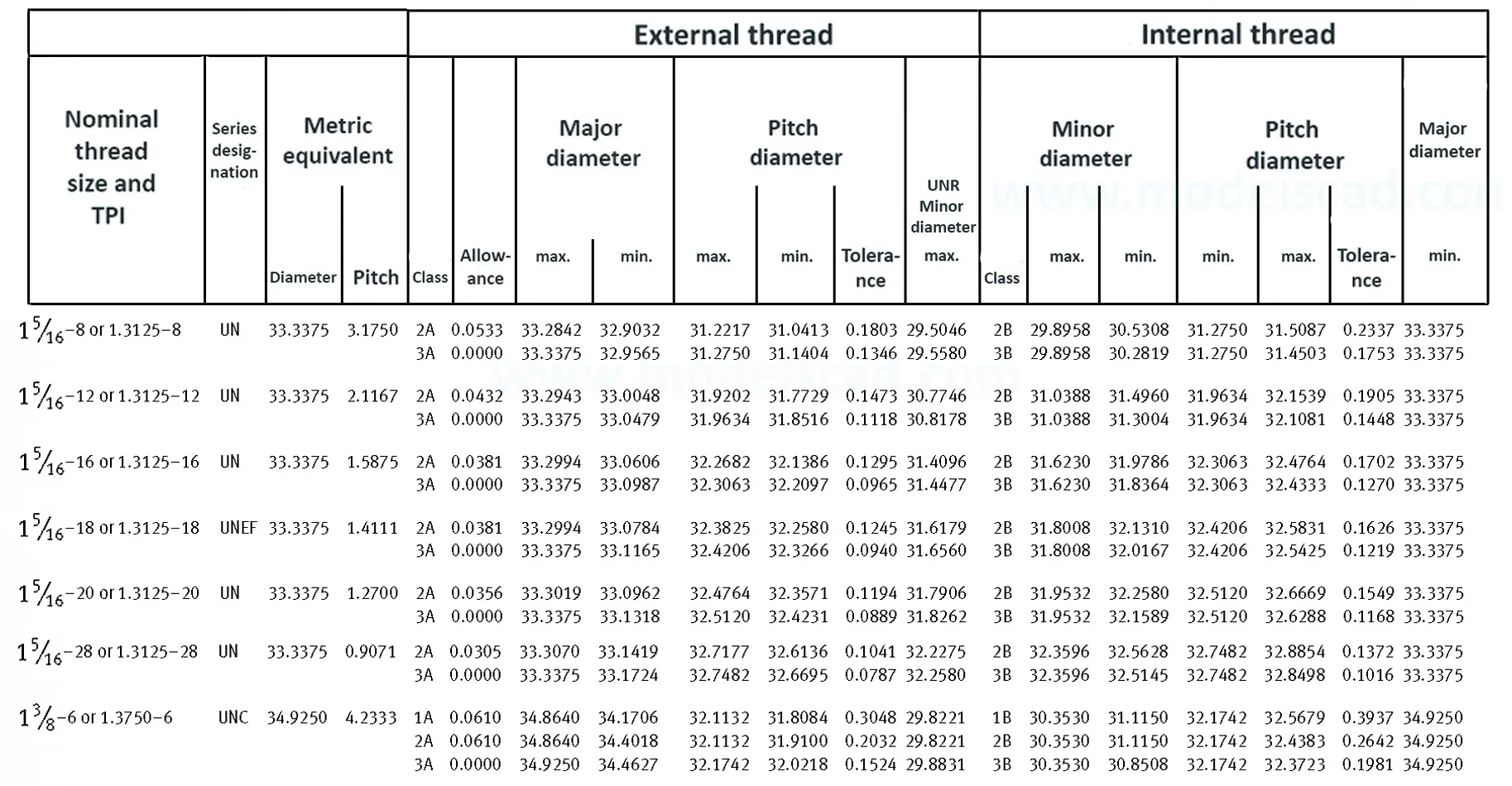
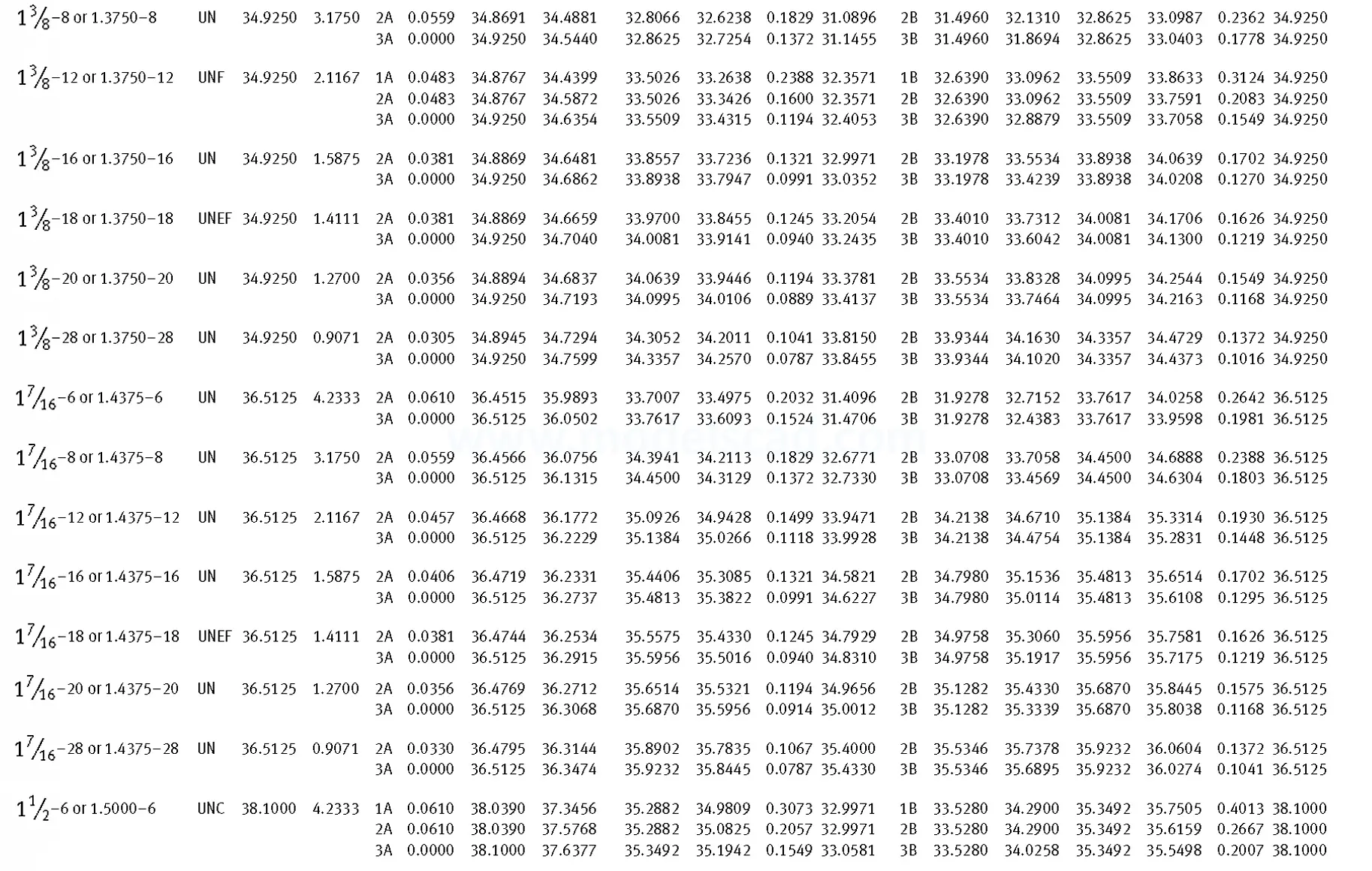
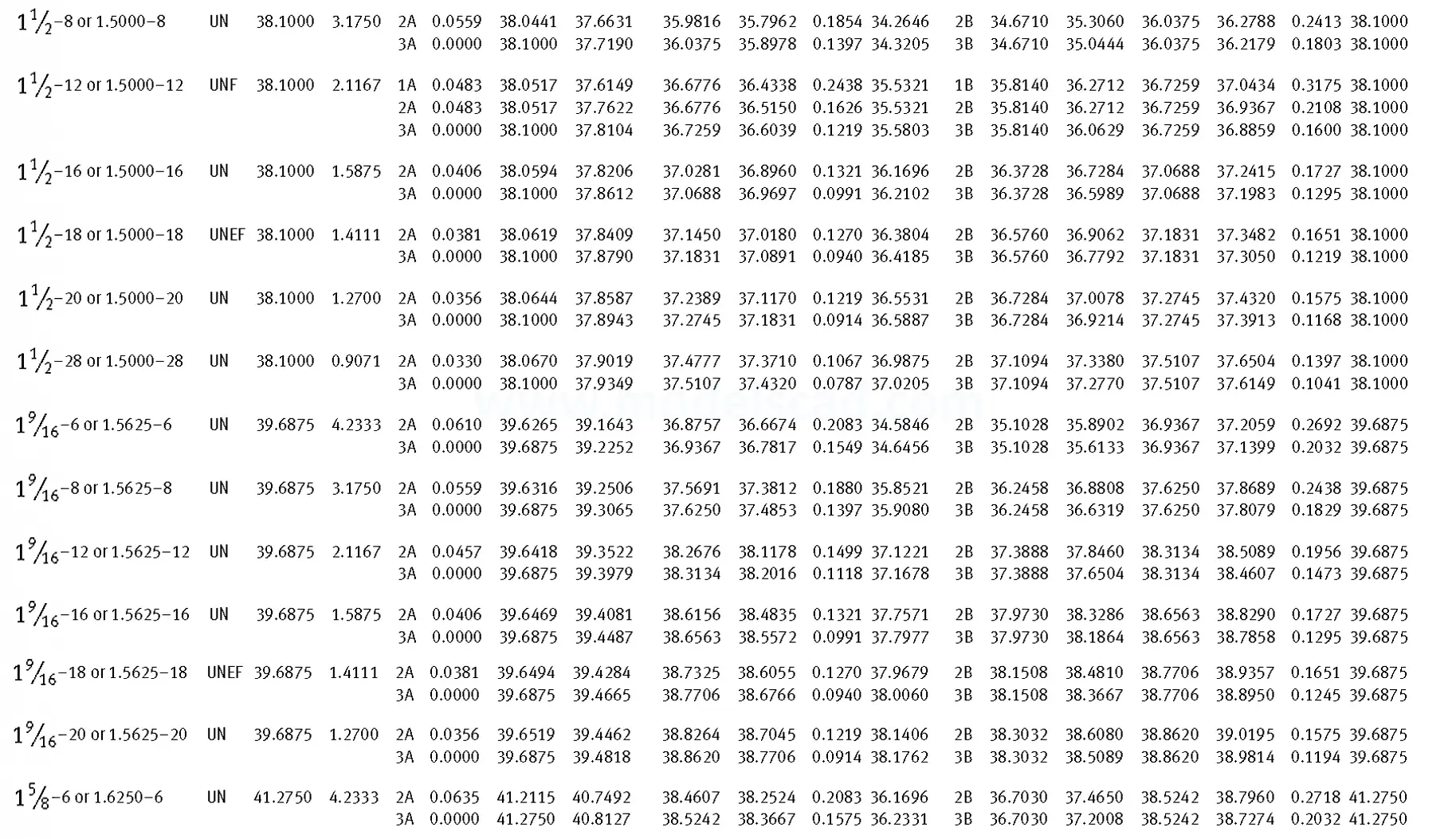
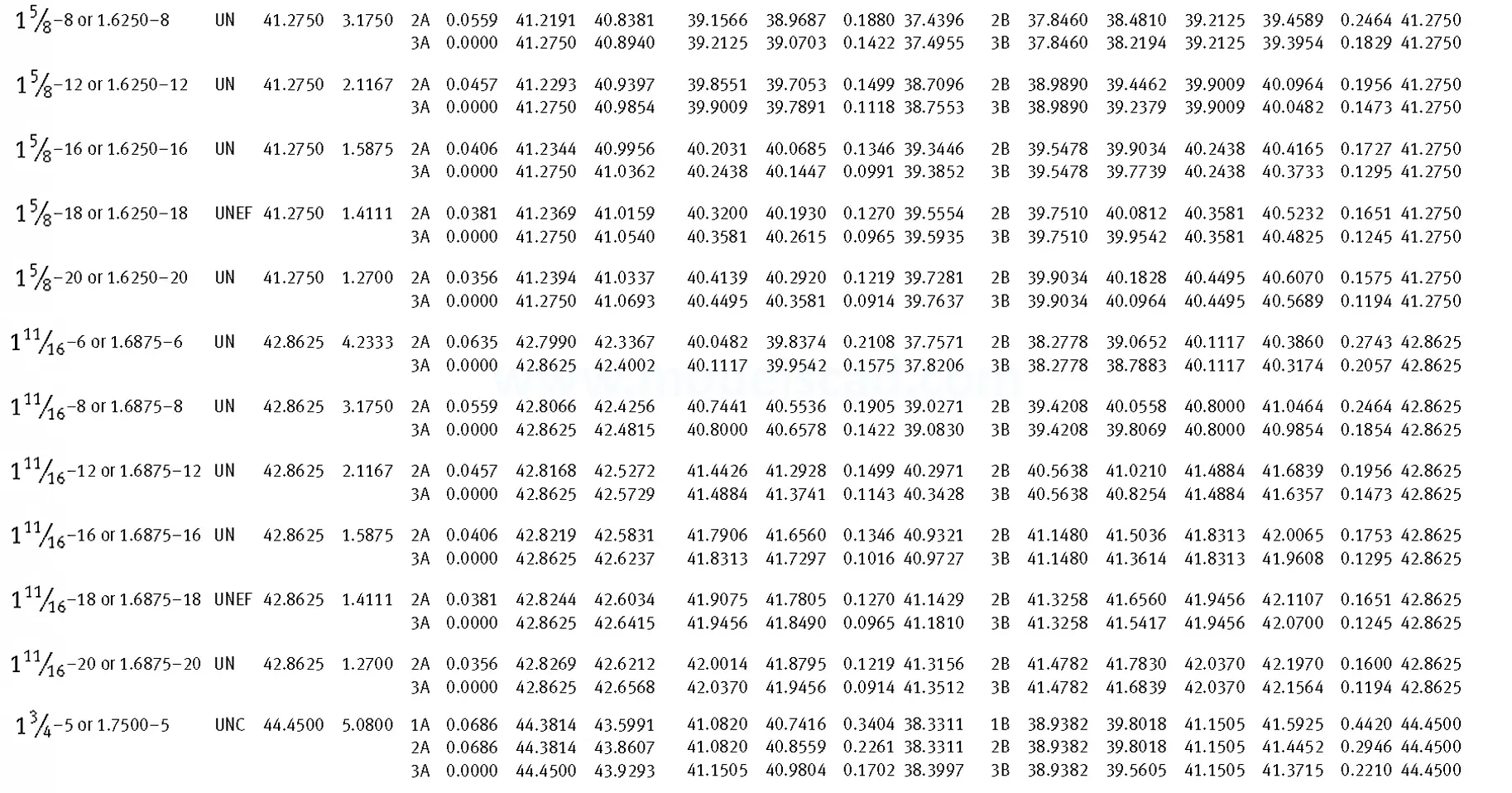
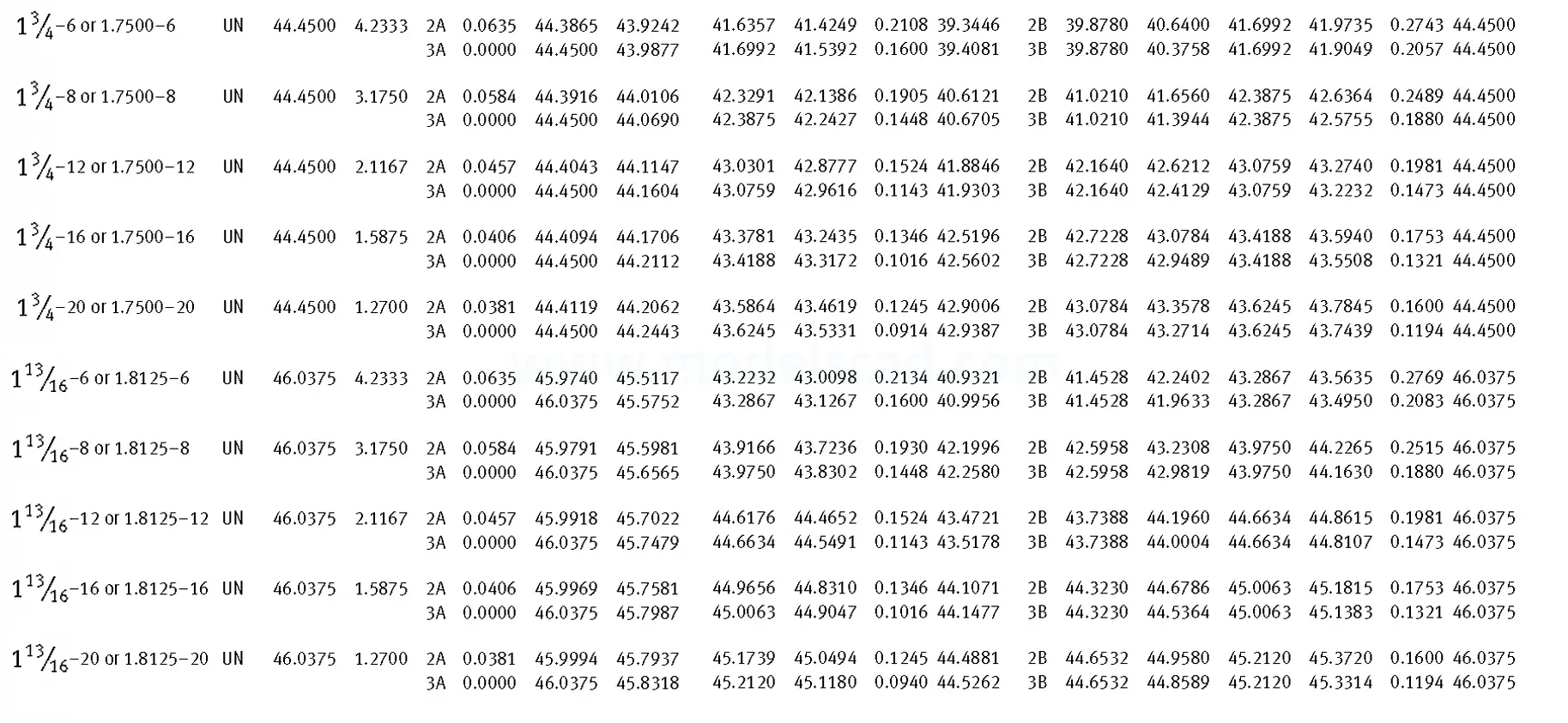
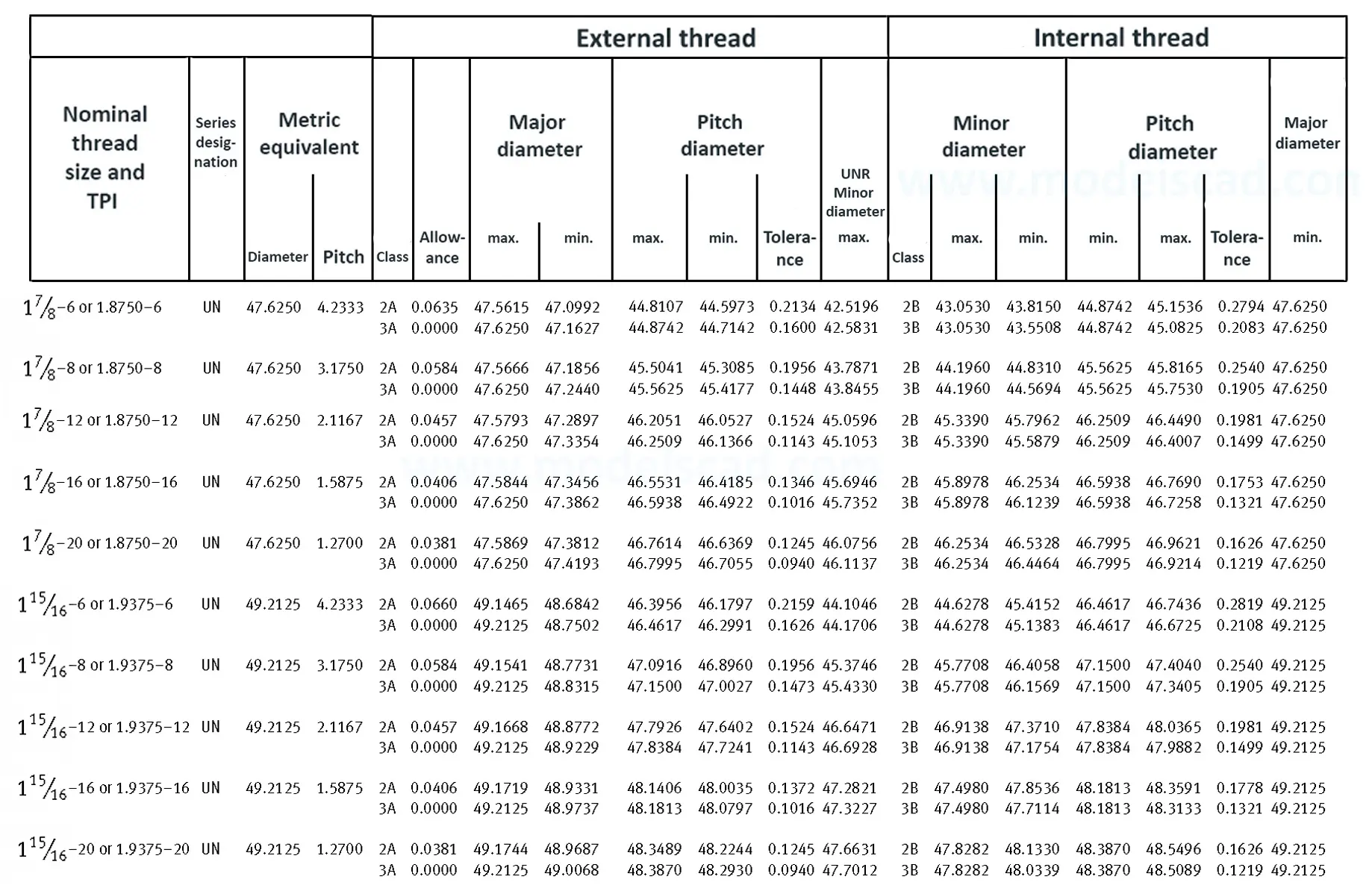
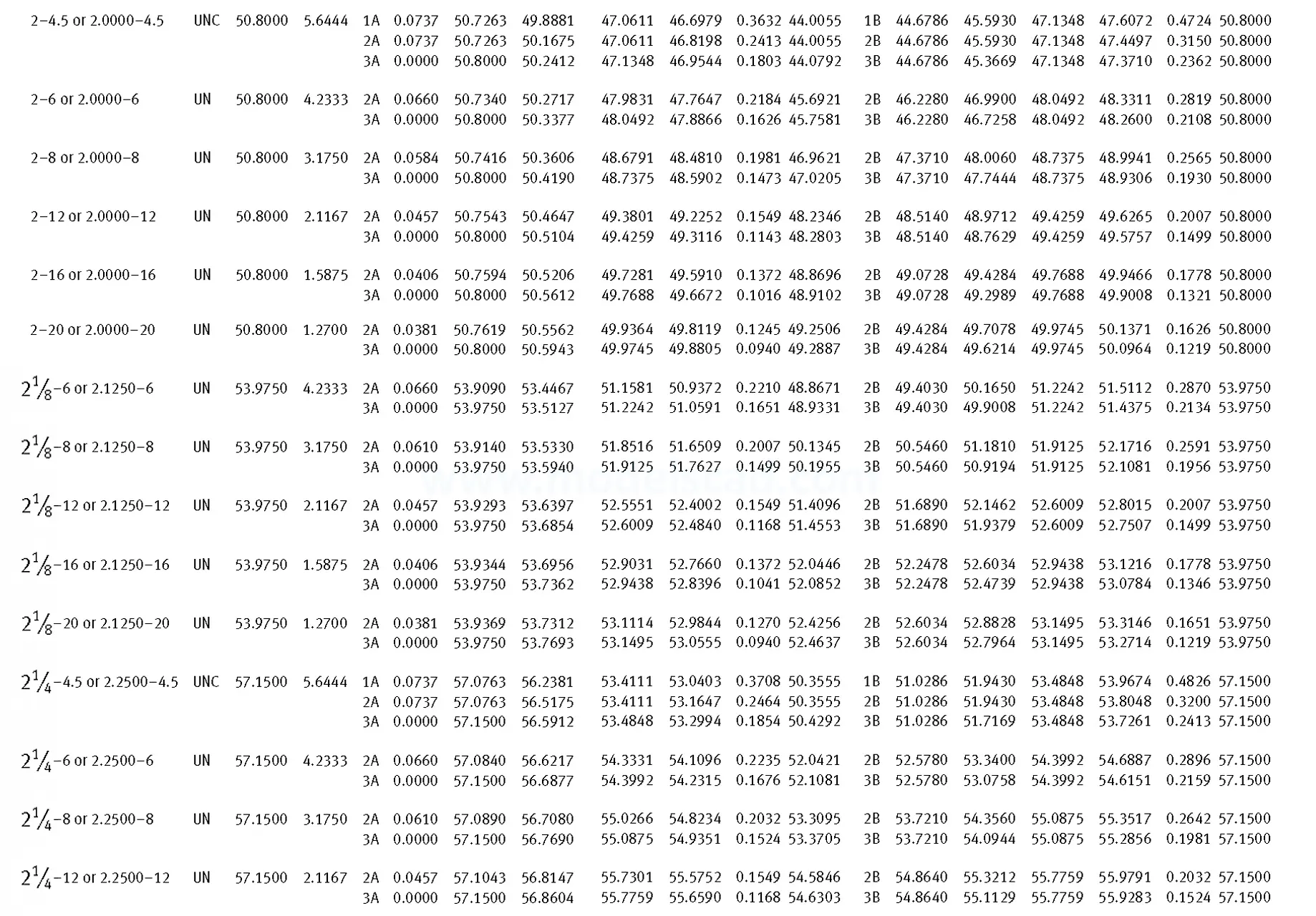
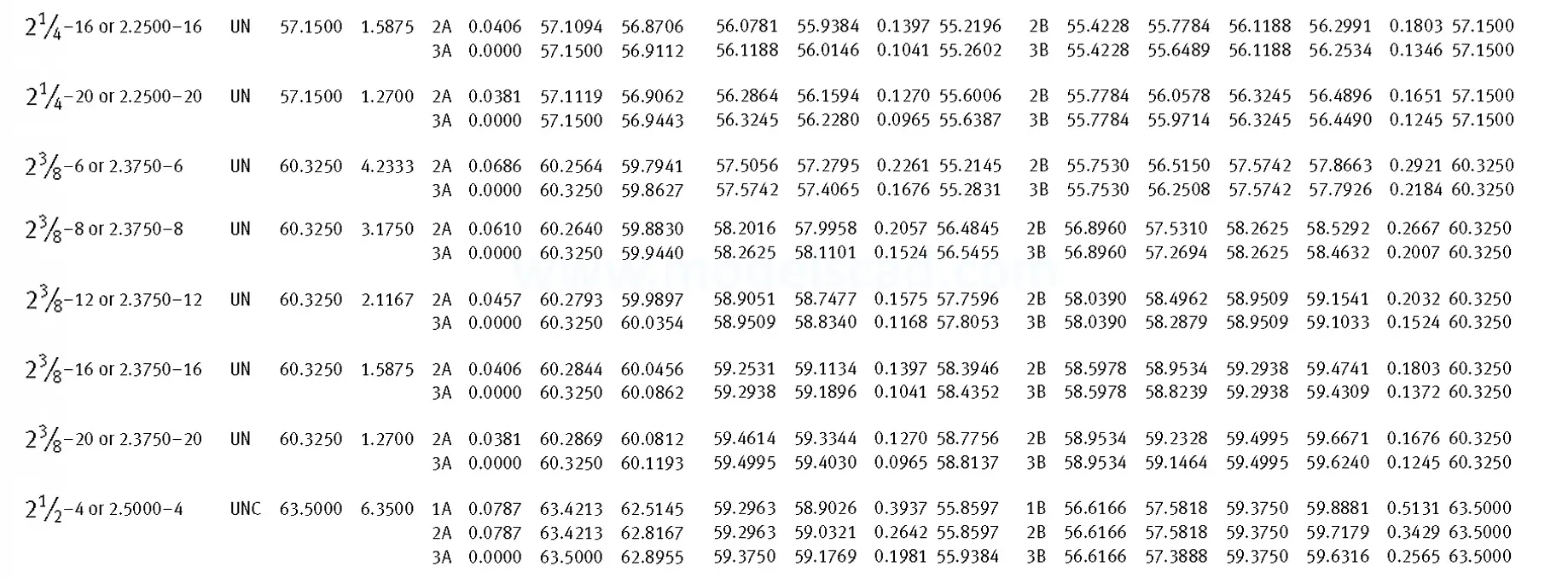
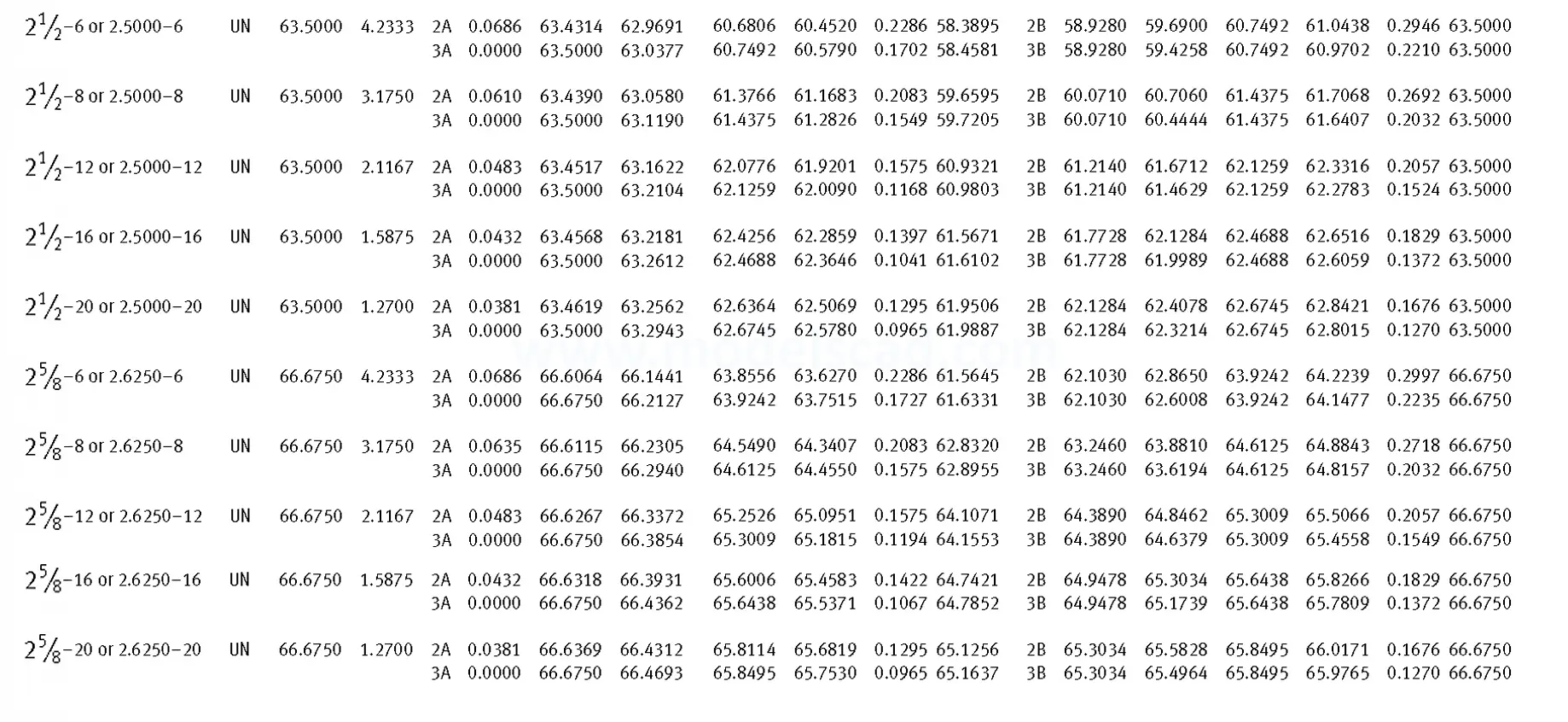
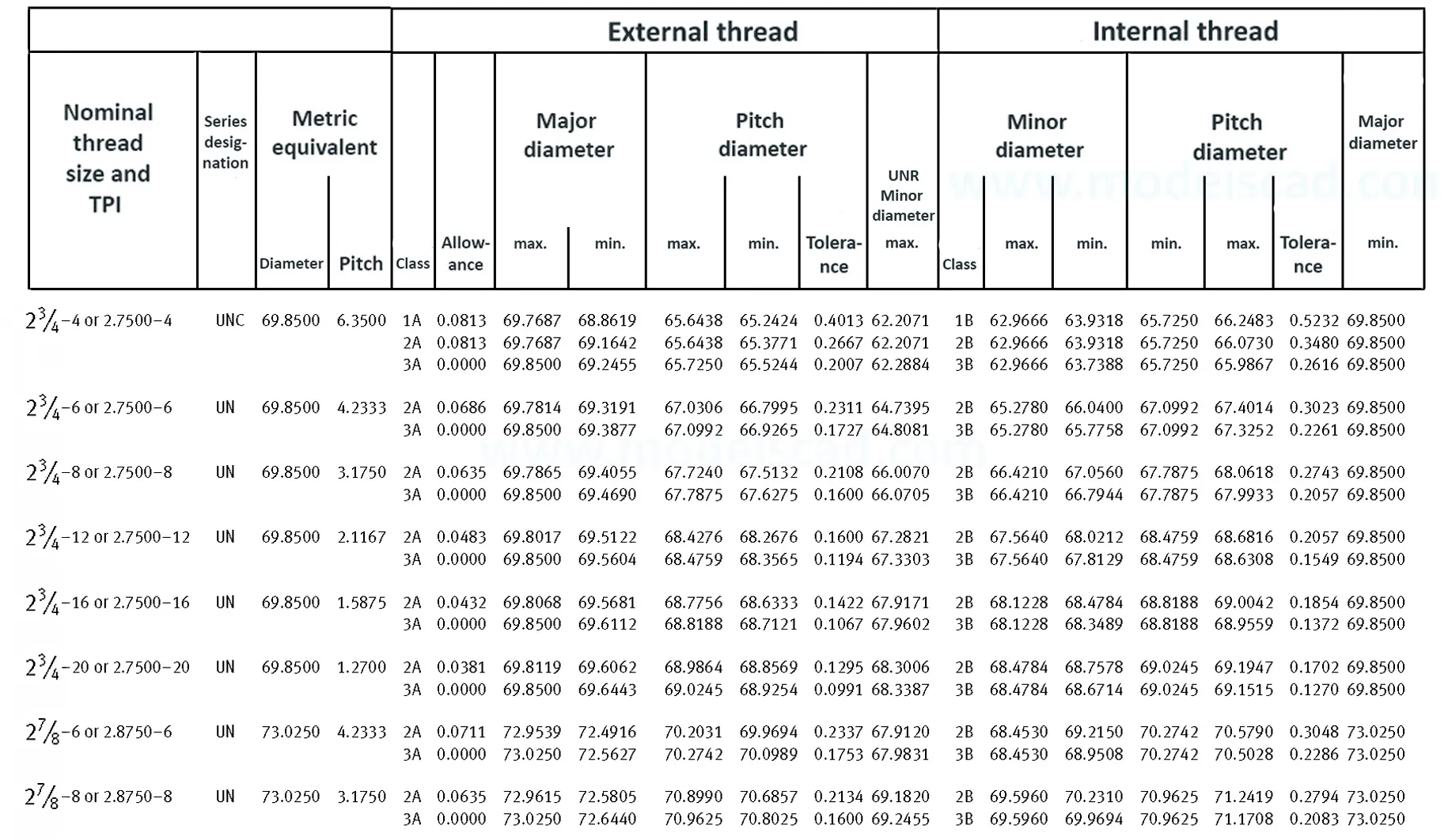
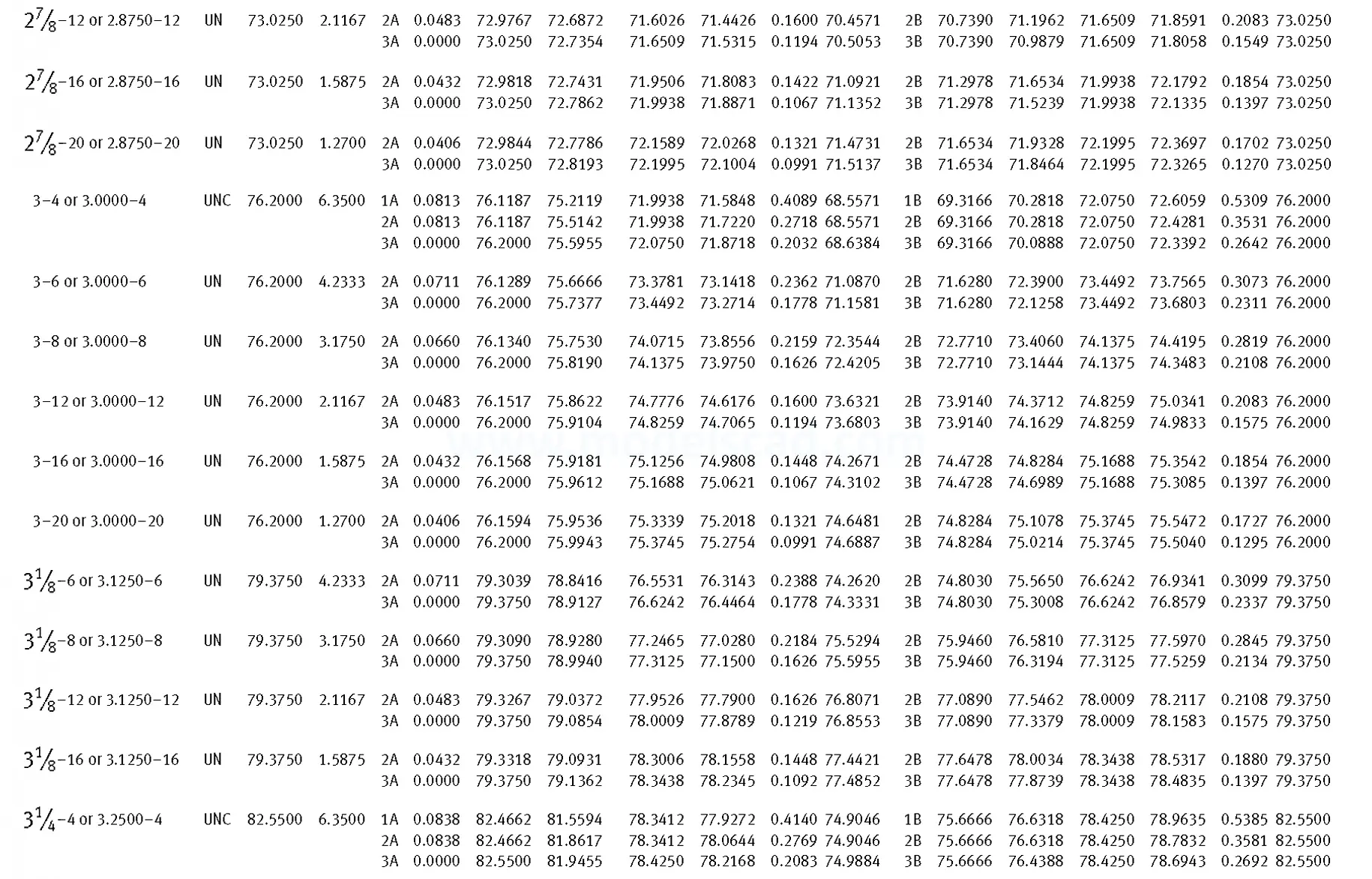
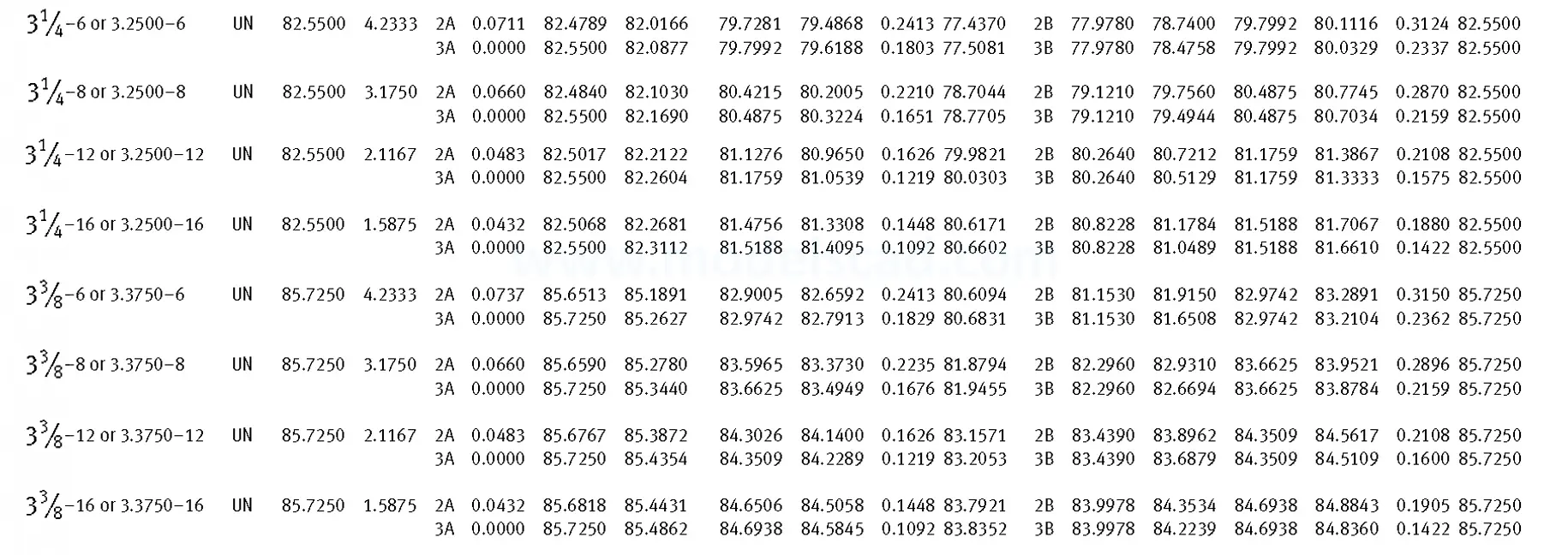
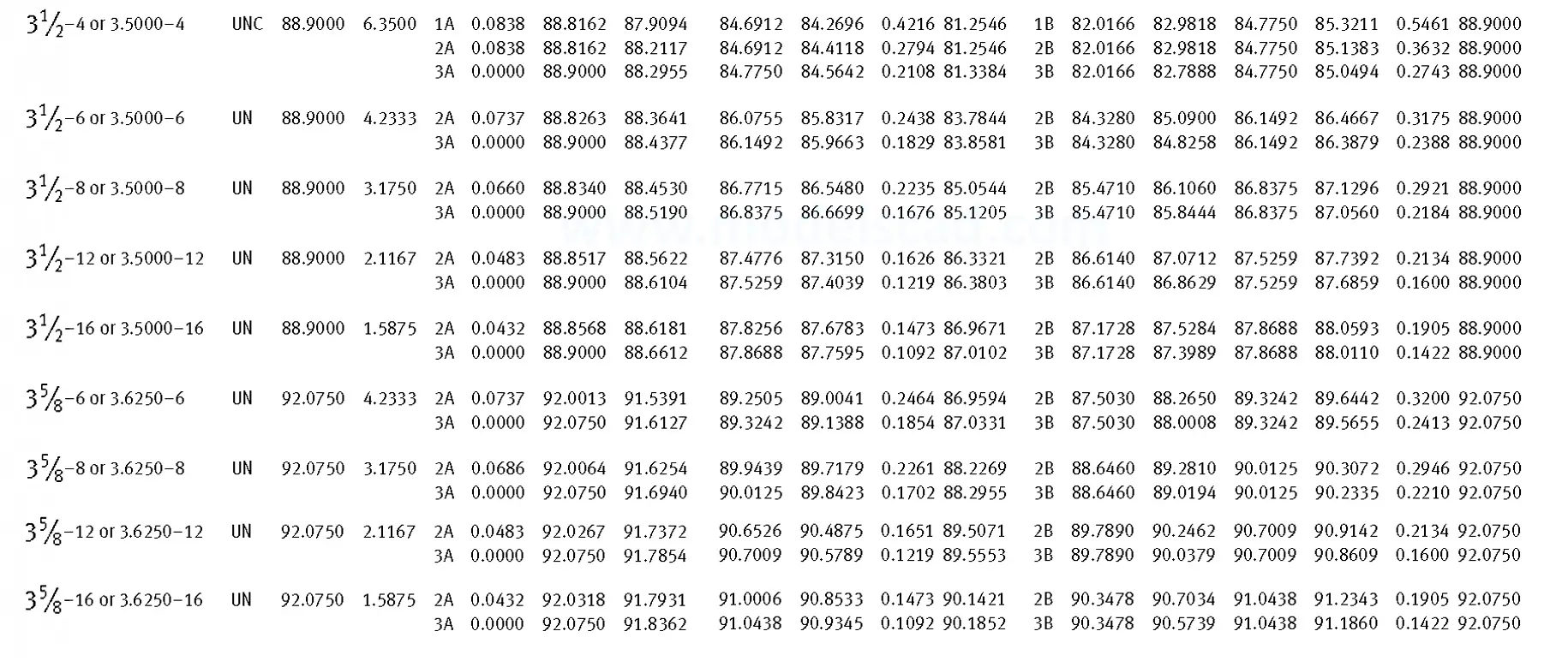
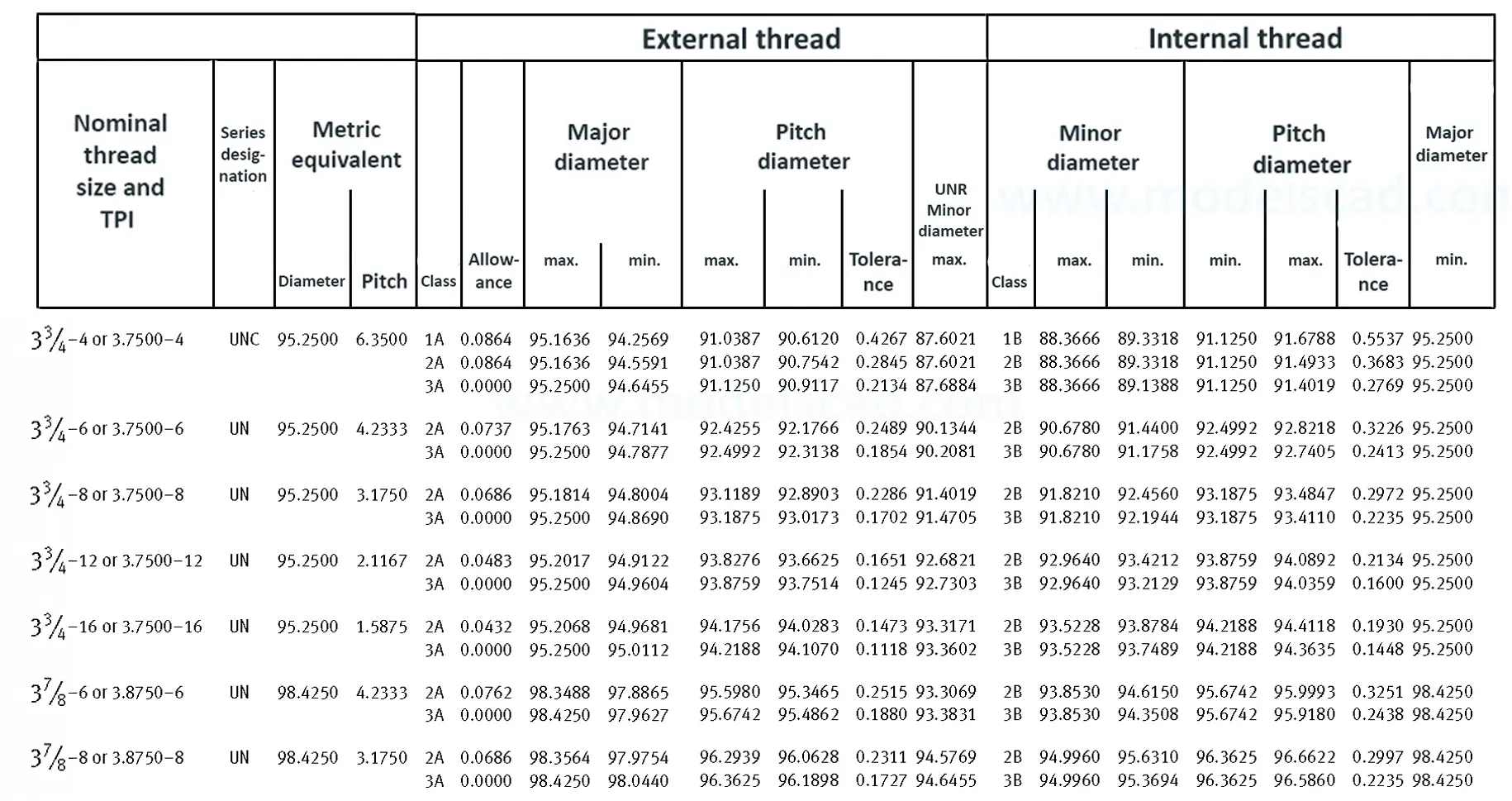
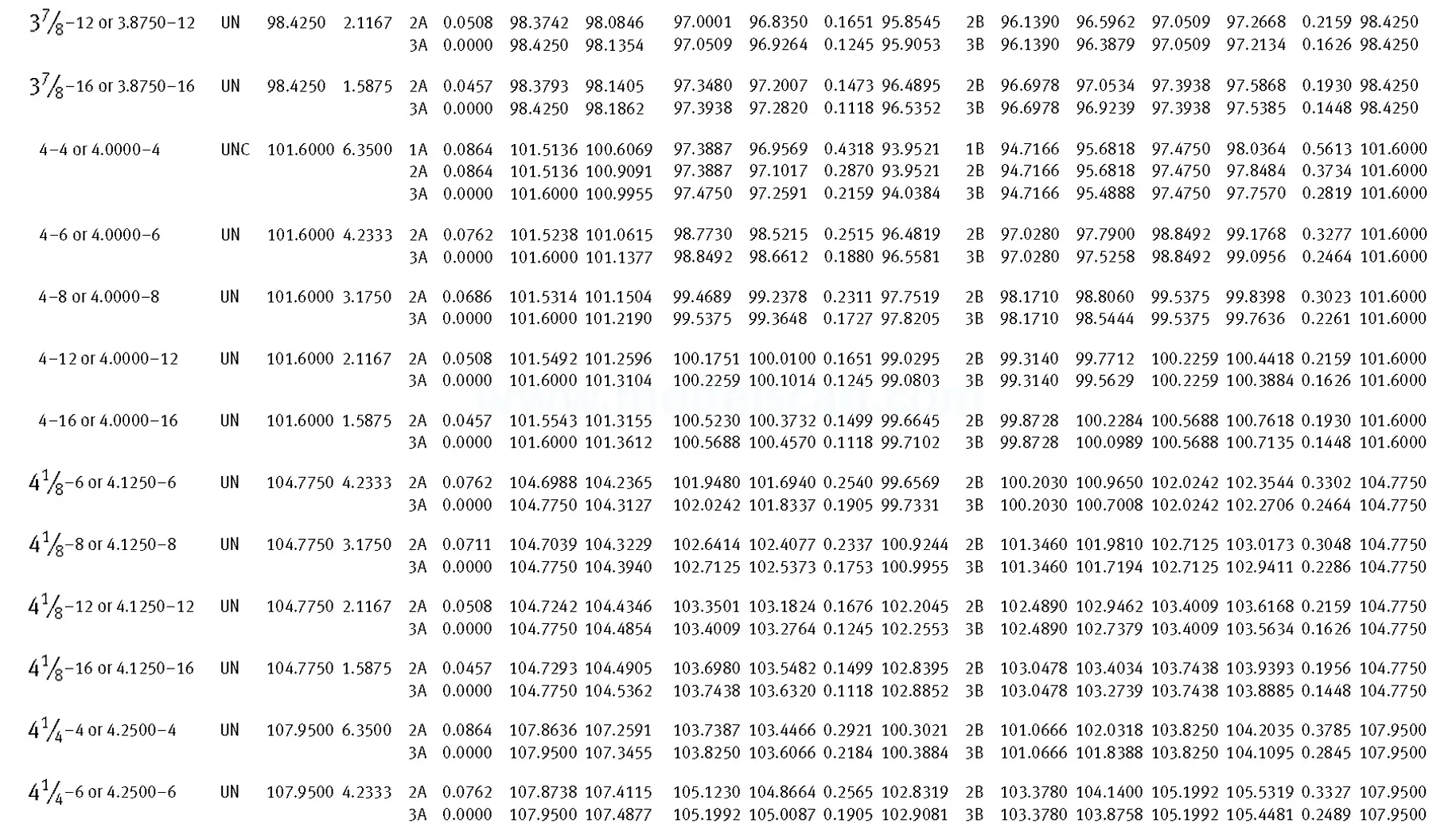
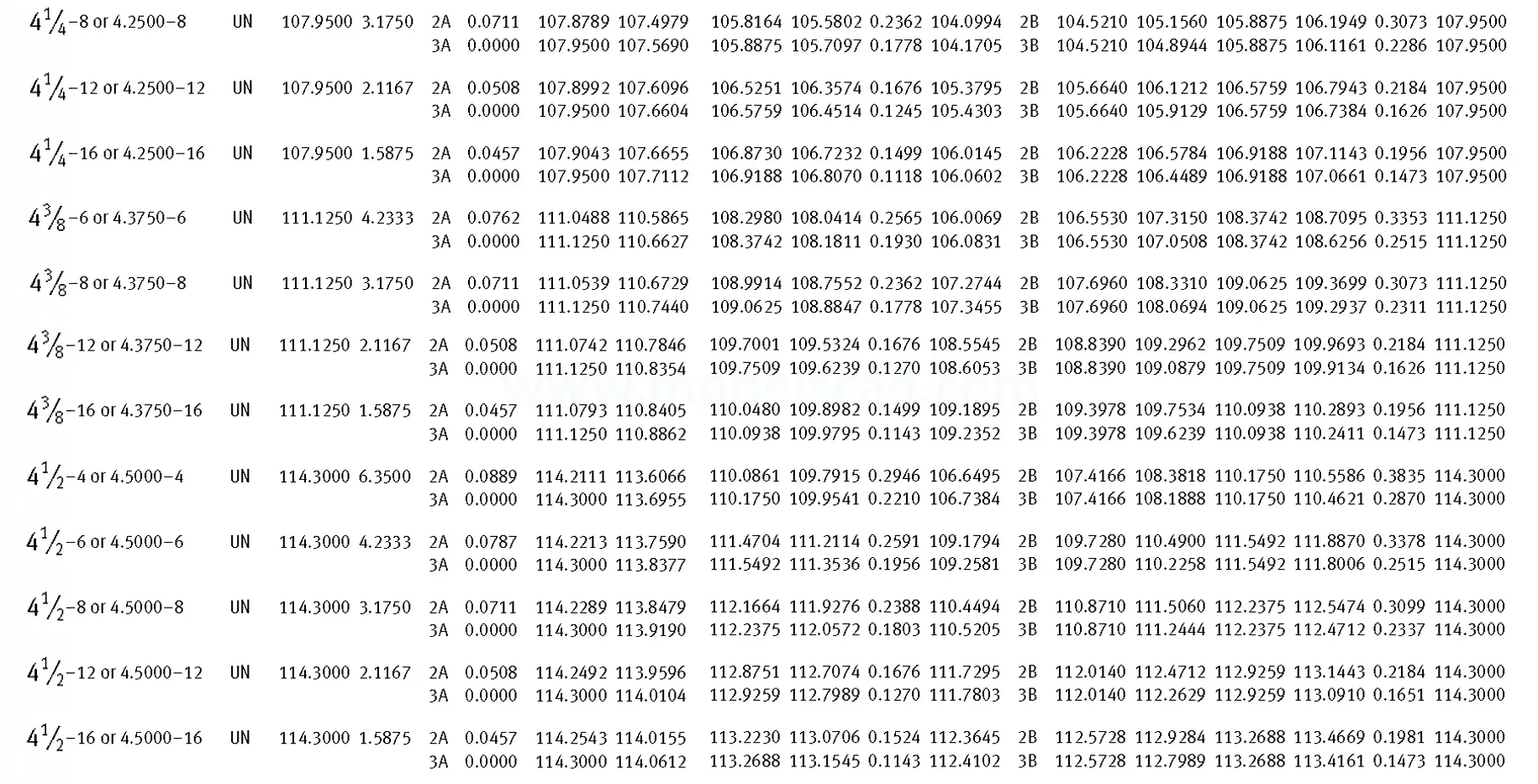
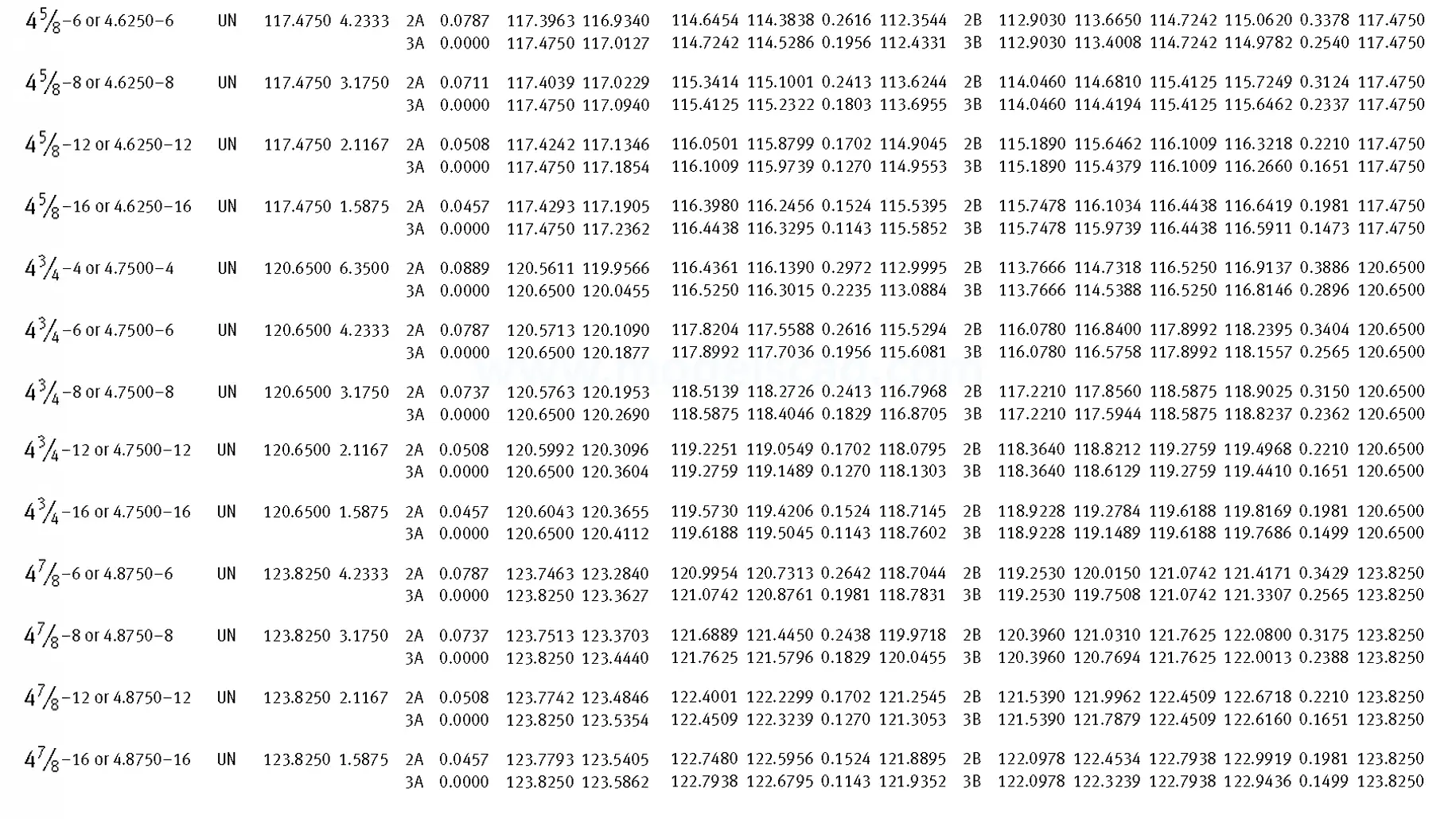
This Standard remained virtually unchanged from 1958 to 1995, while the use of miniature threads diminished considerably due to electronic components, replacing many of the mechanical devices used in instrumentation. There still remains, however, an active use of miniature screw threads in spacecrafts and aircrafts, as components are miniaturized for weight considerations.
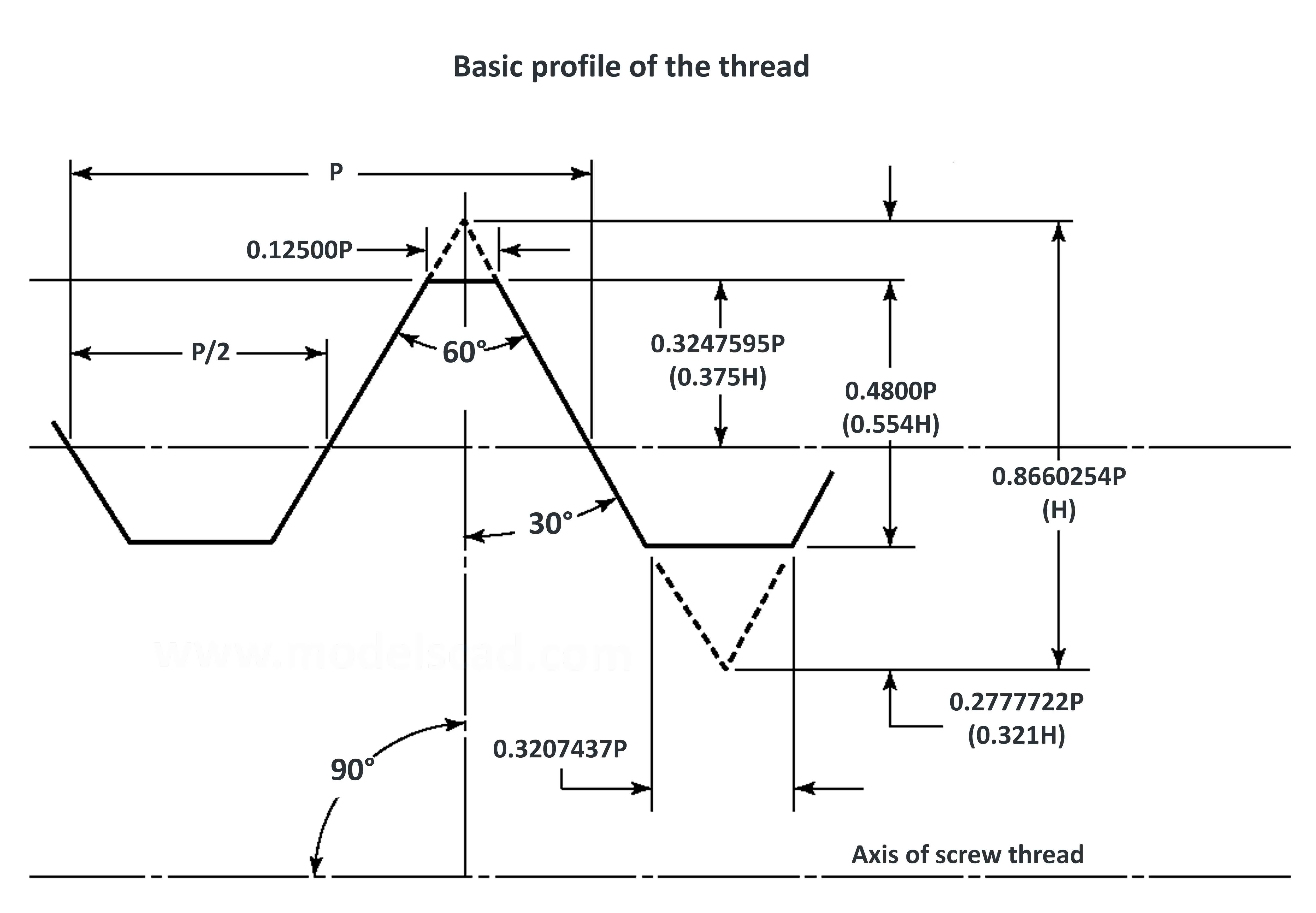
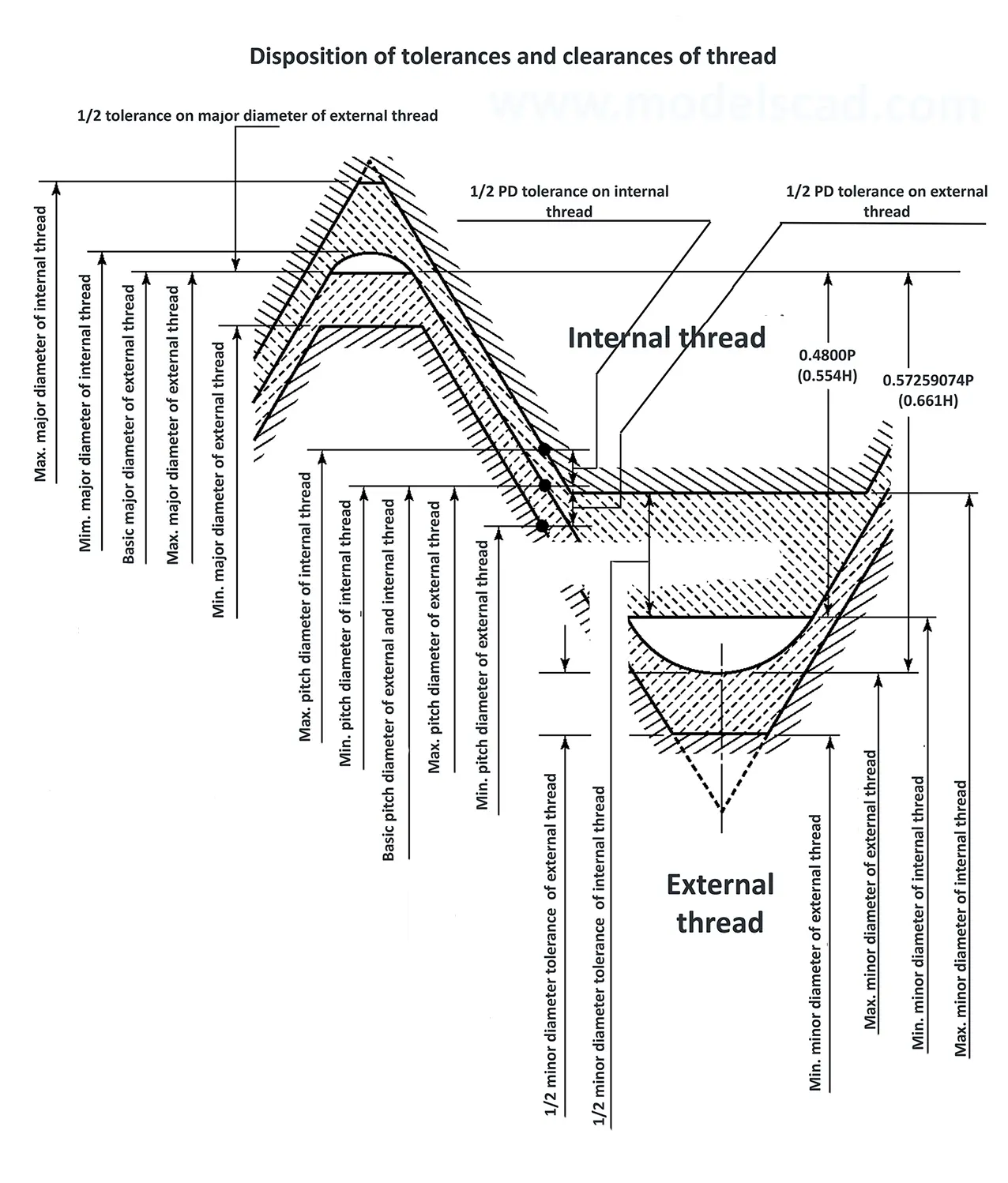
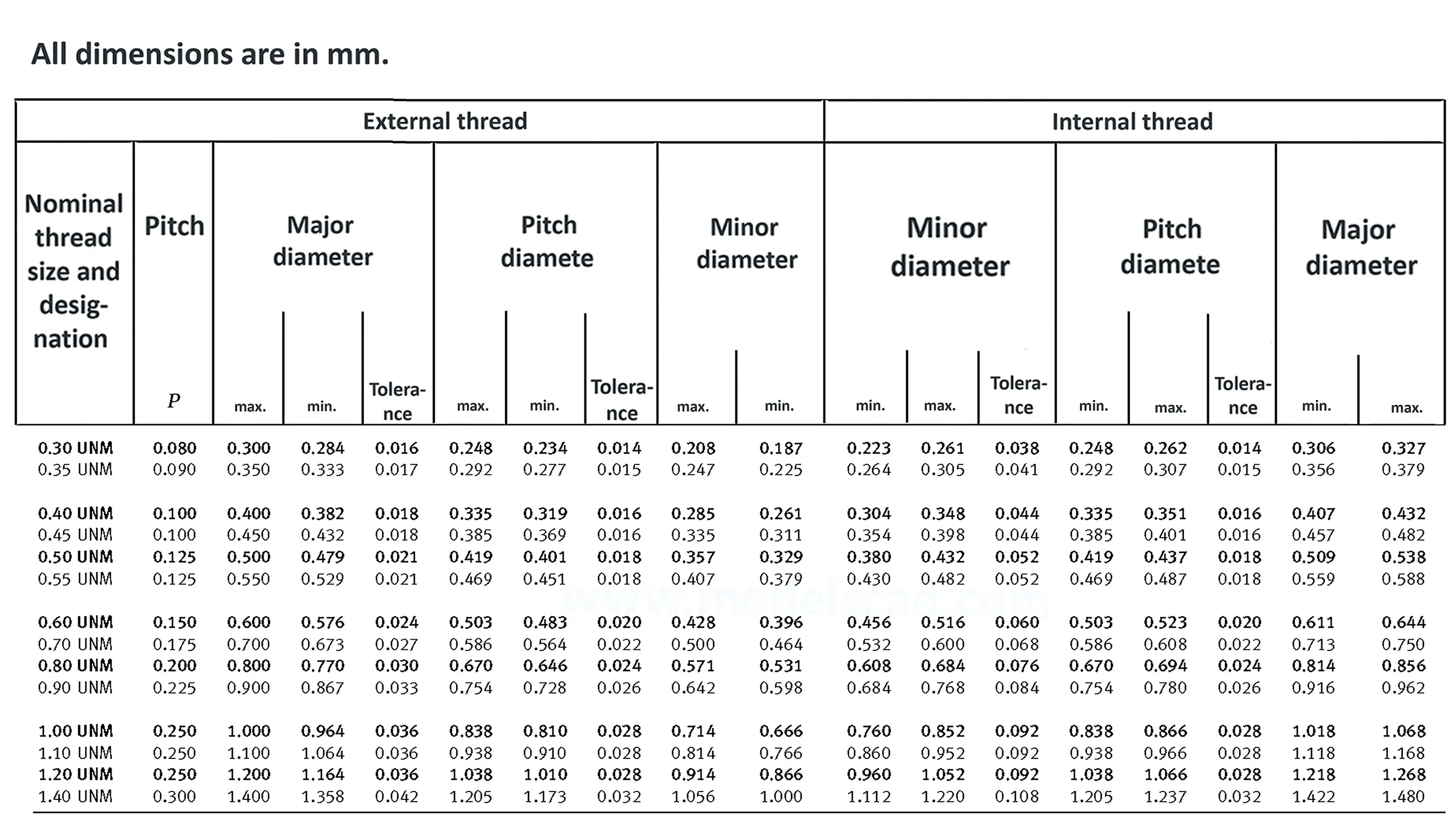
Thread is used for special purposes. The flank angle is 60°.
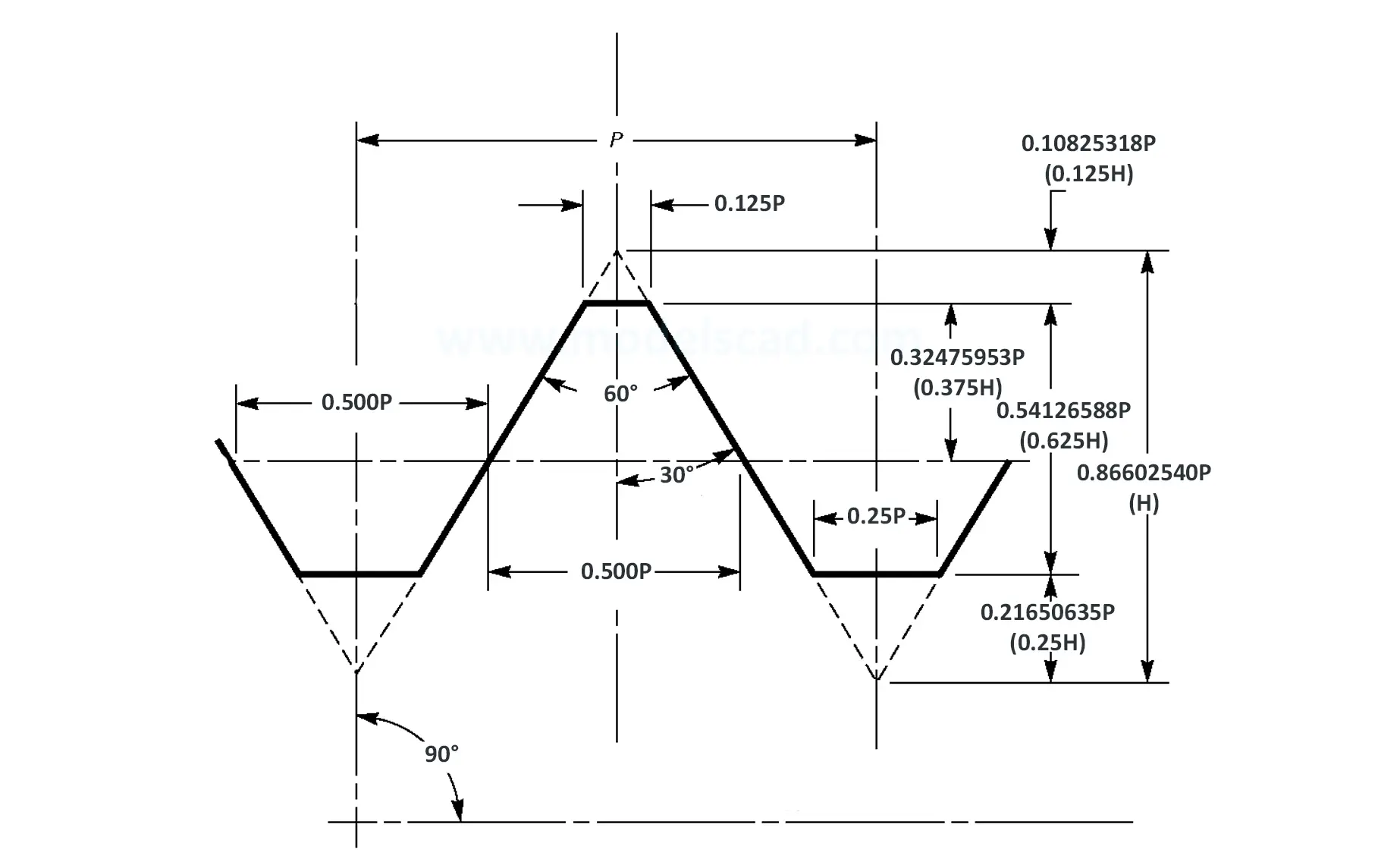
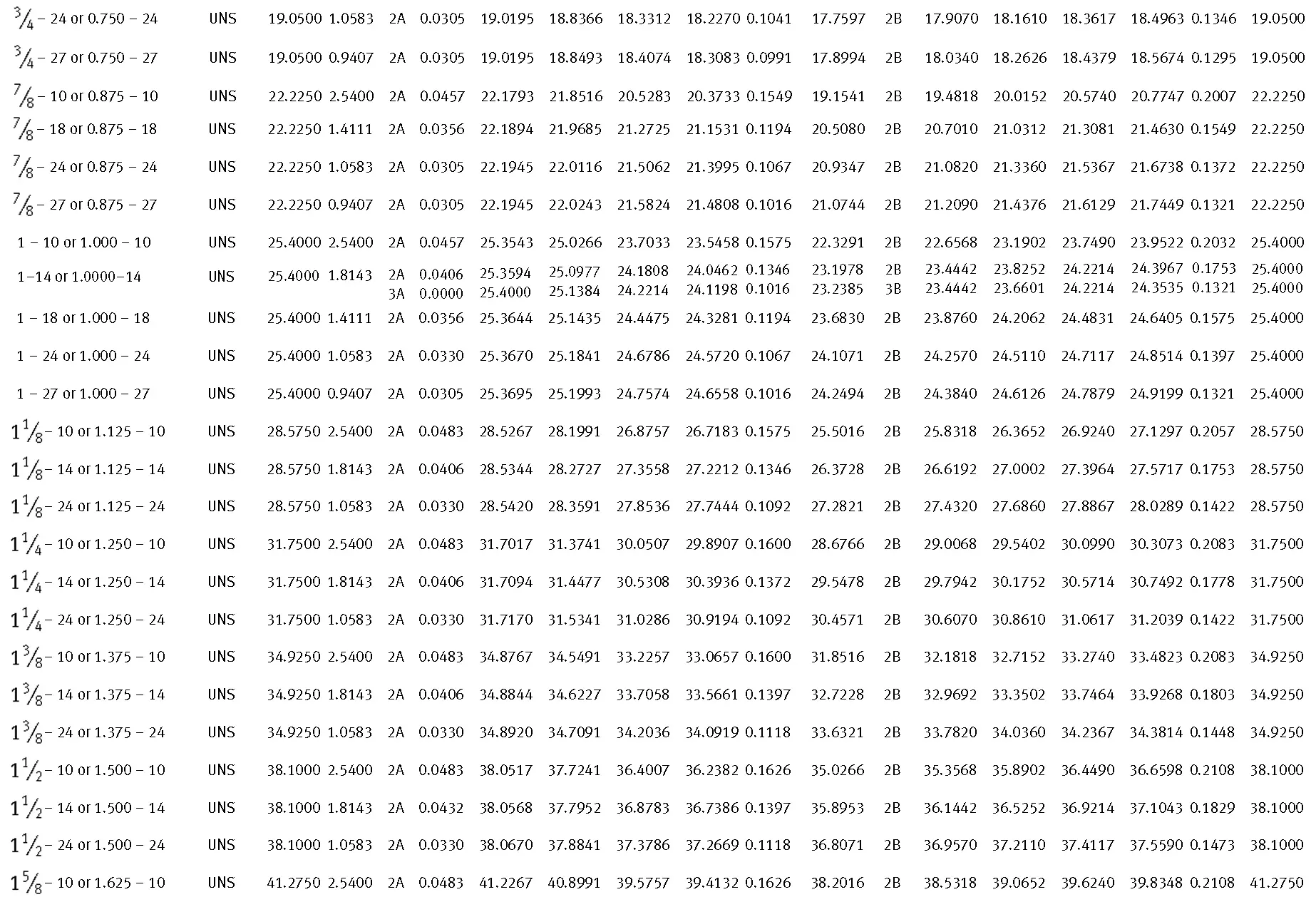
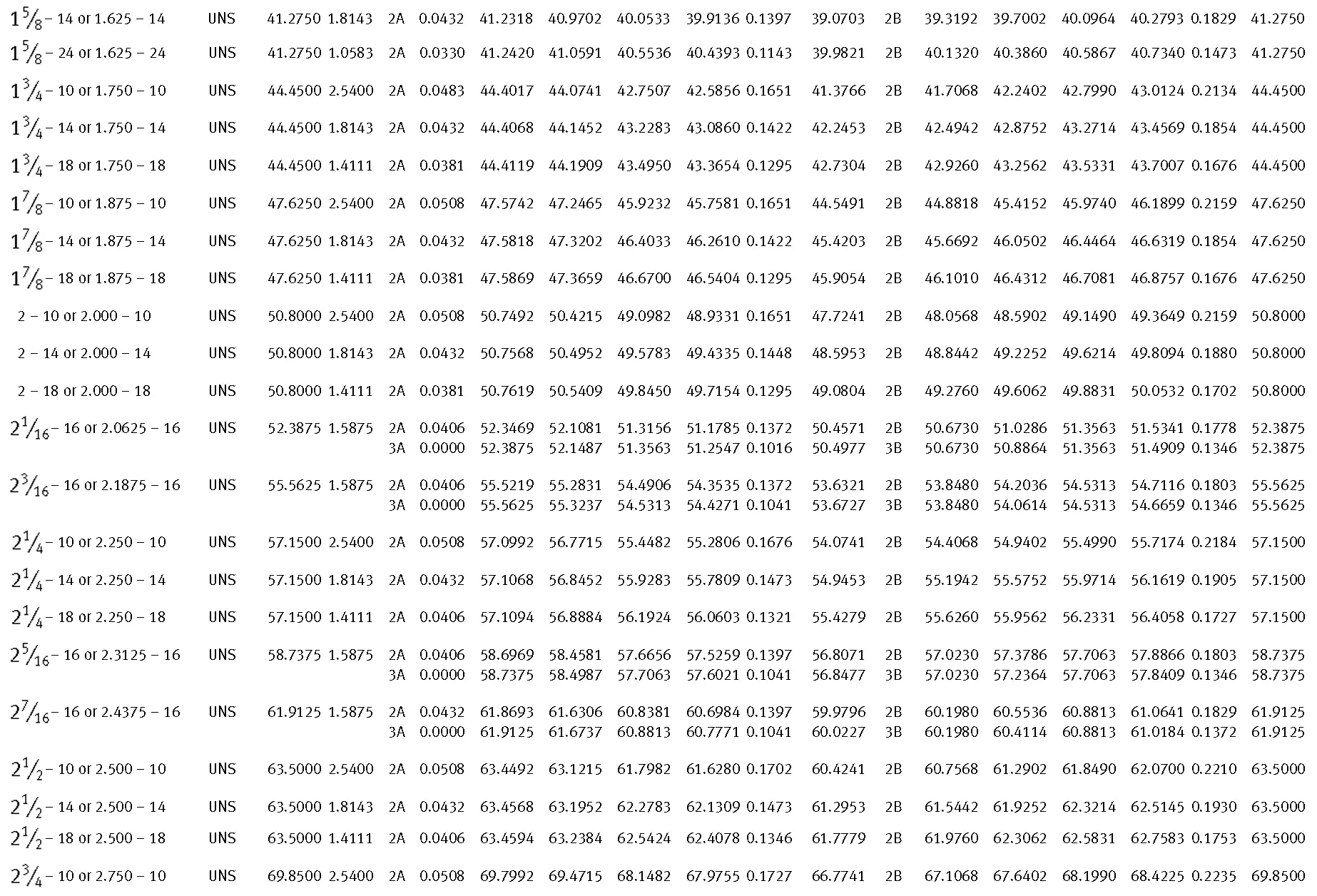
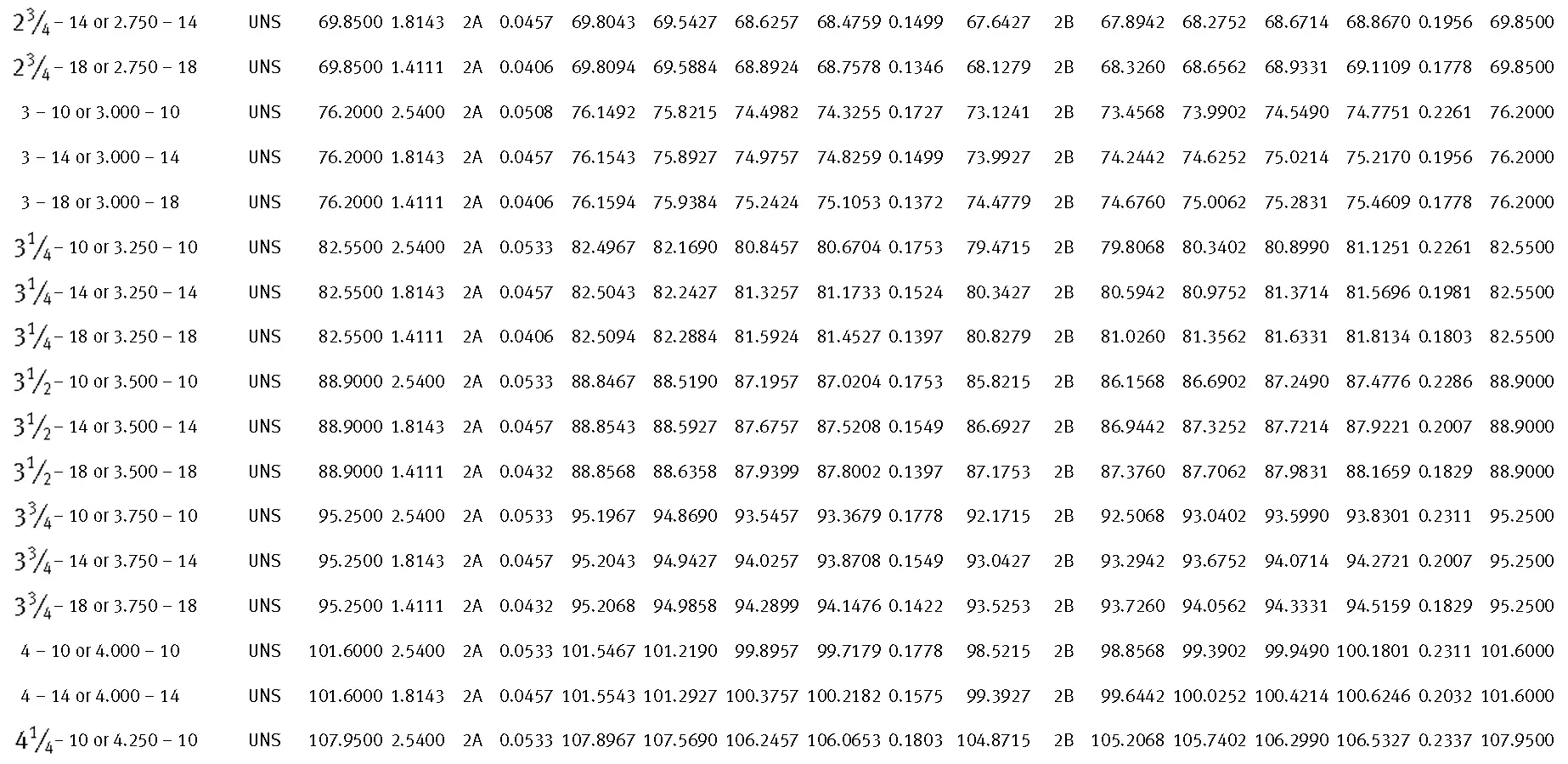
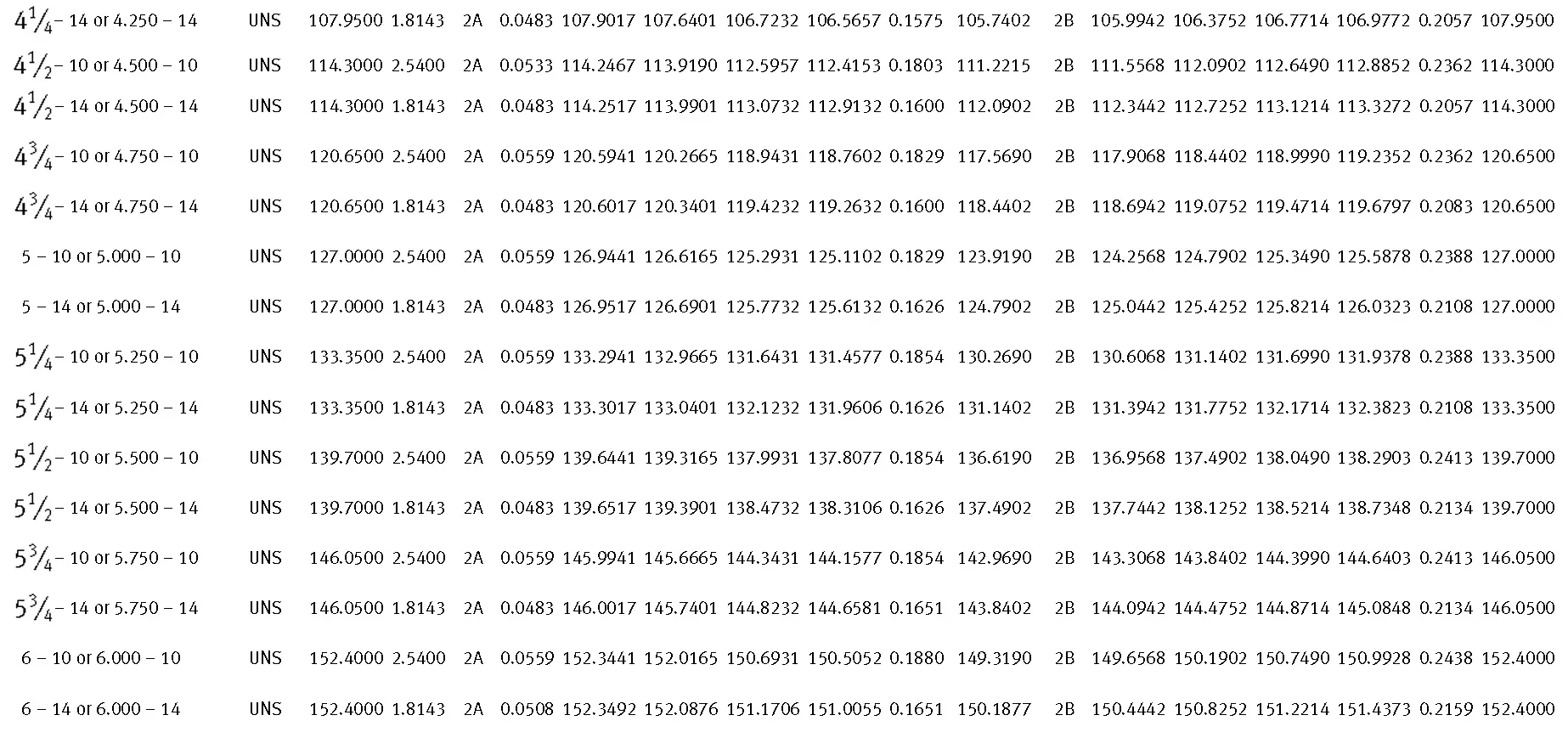
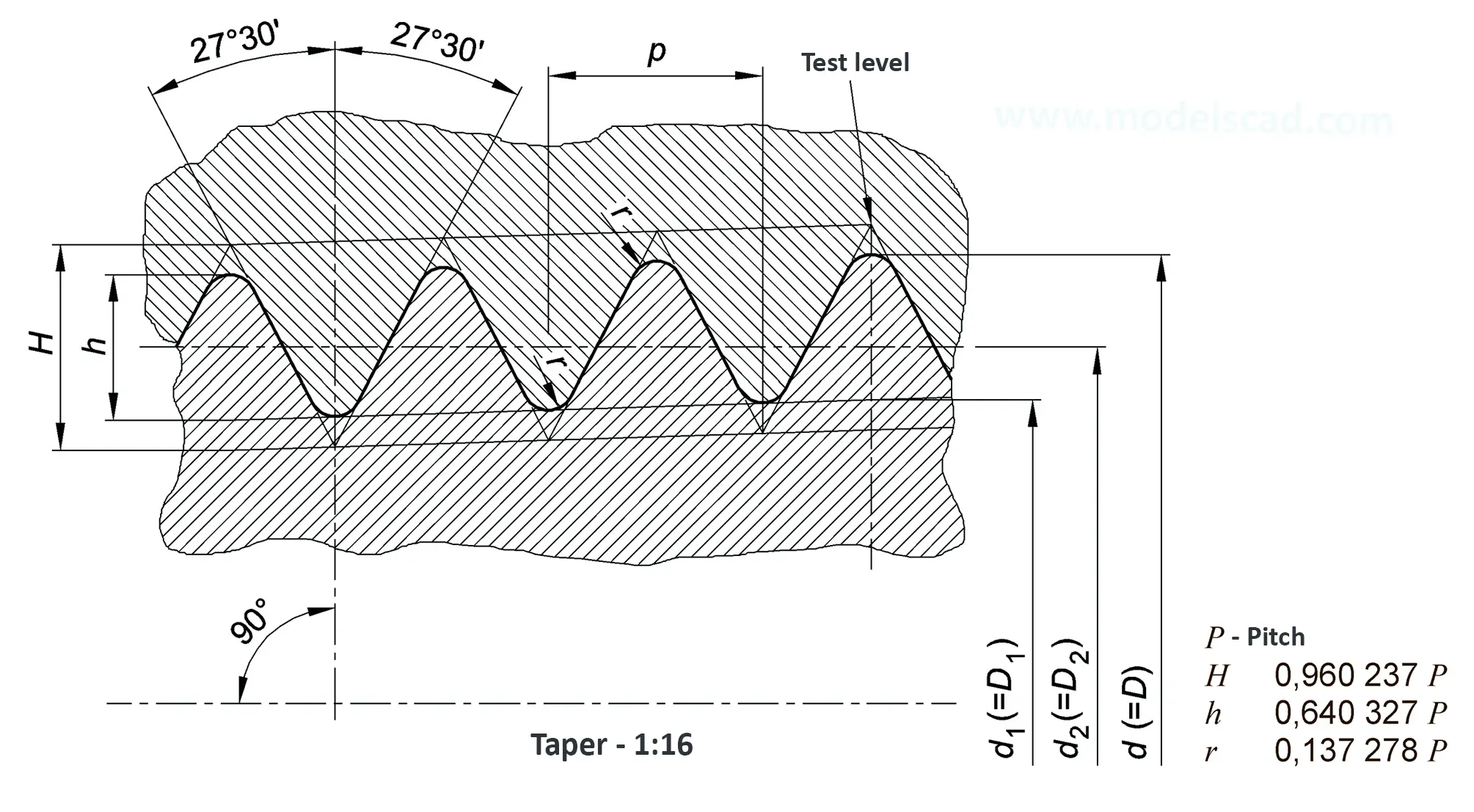
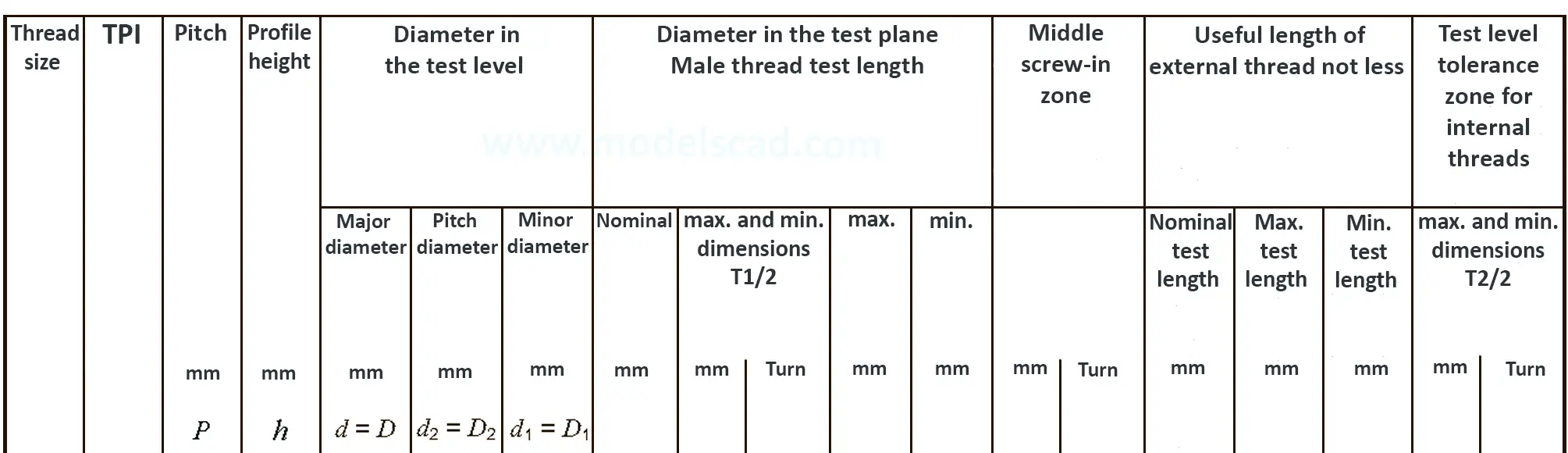
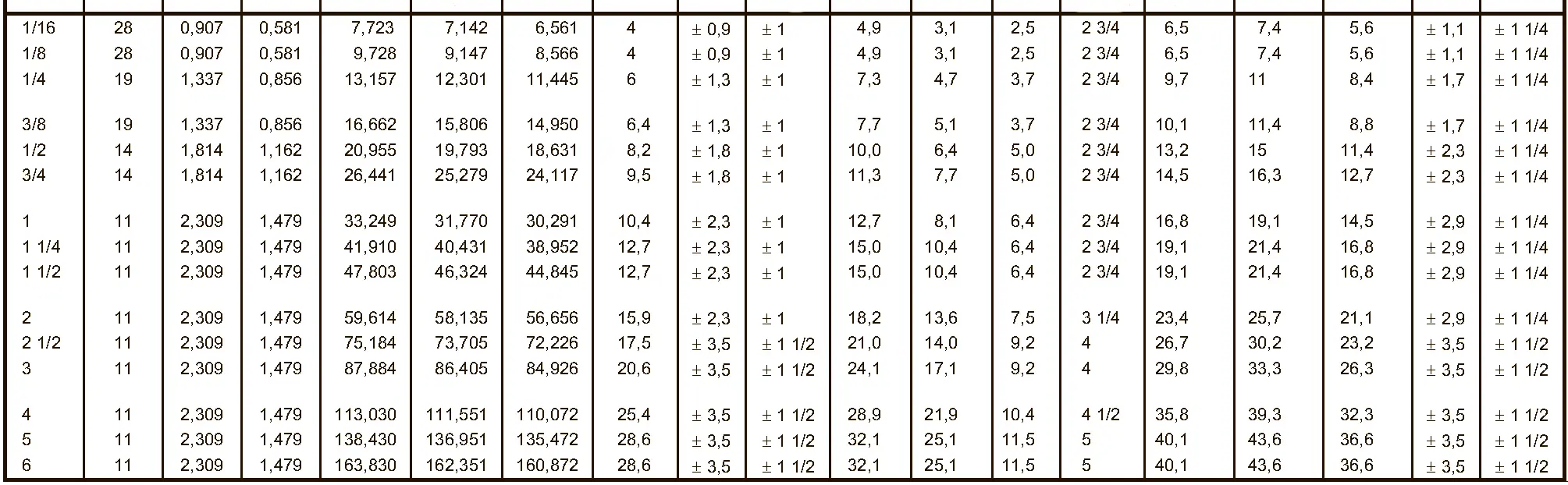
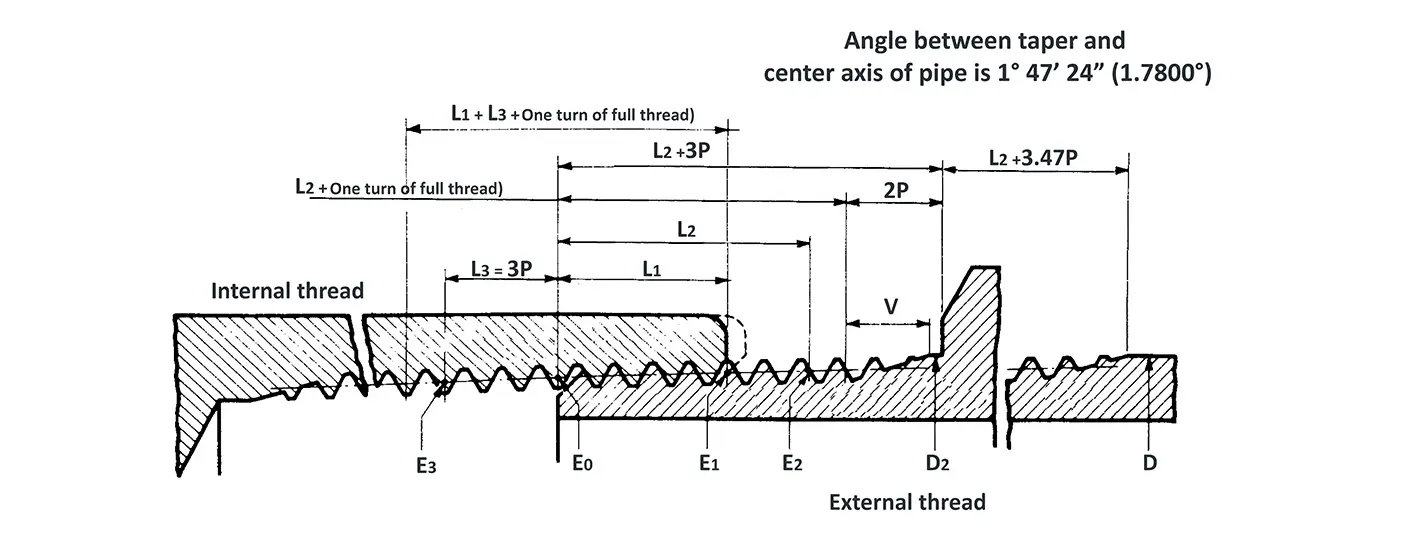
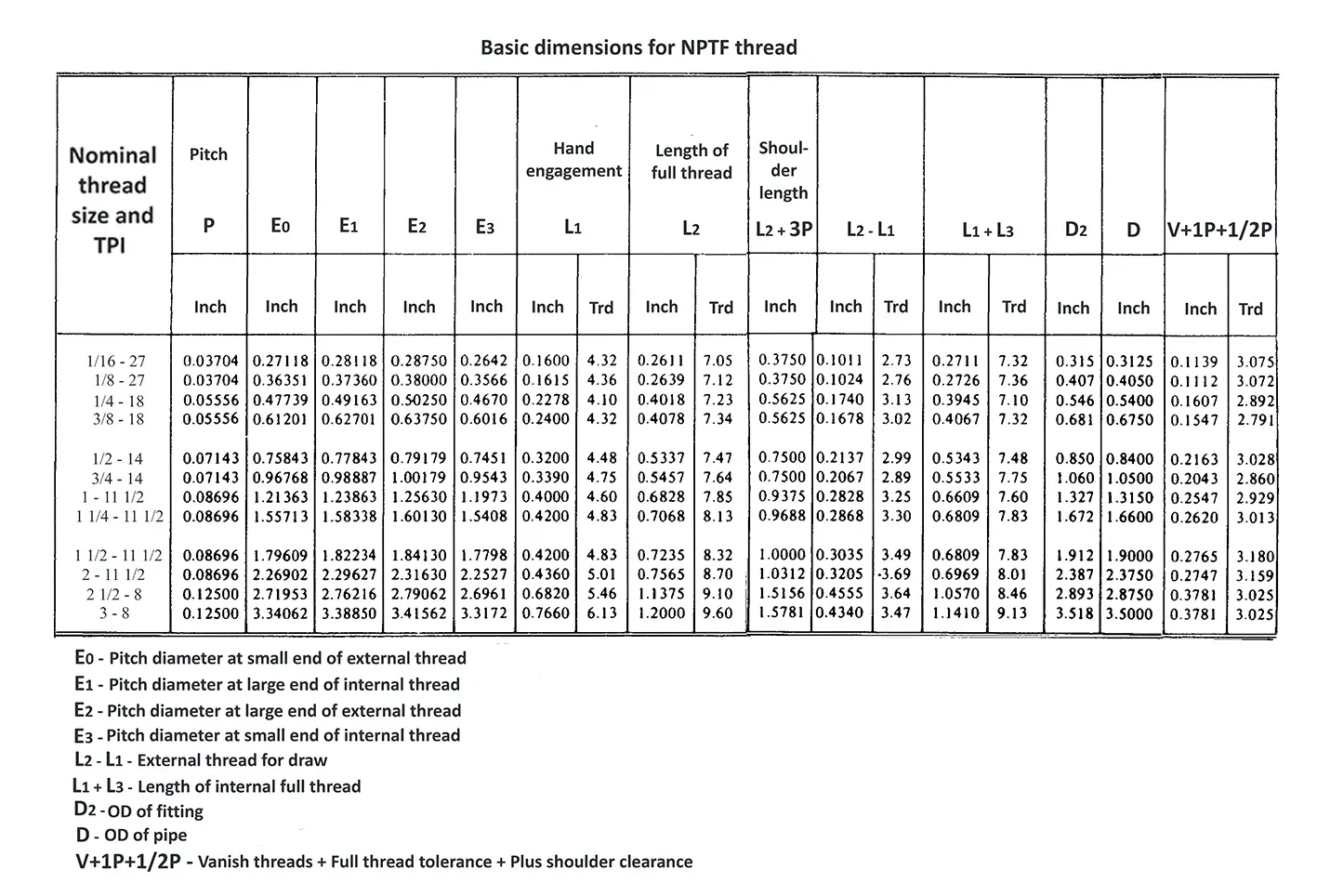
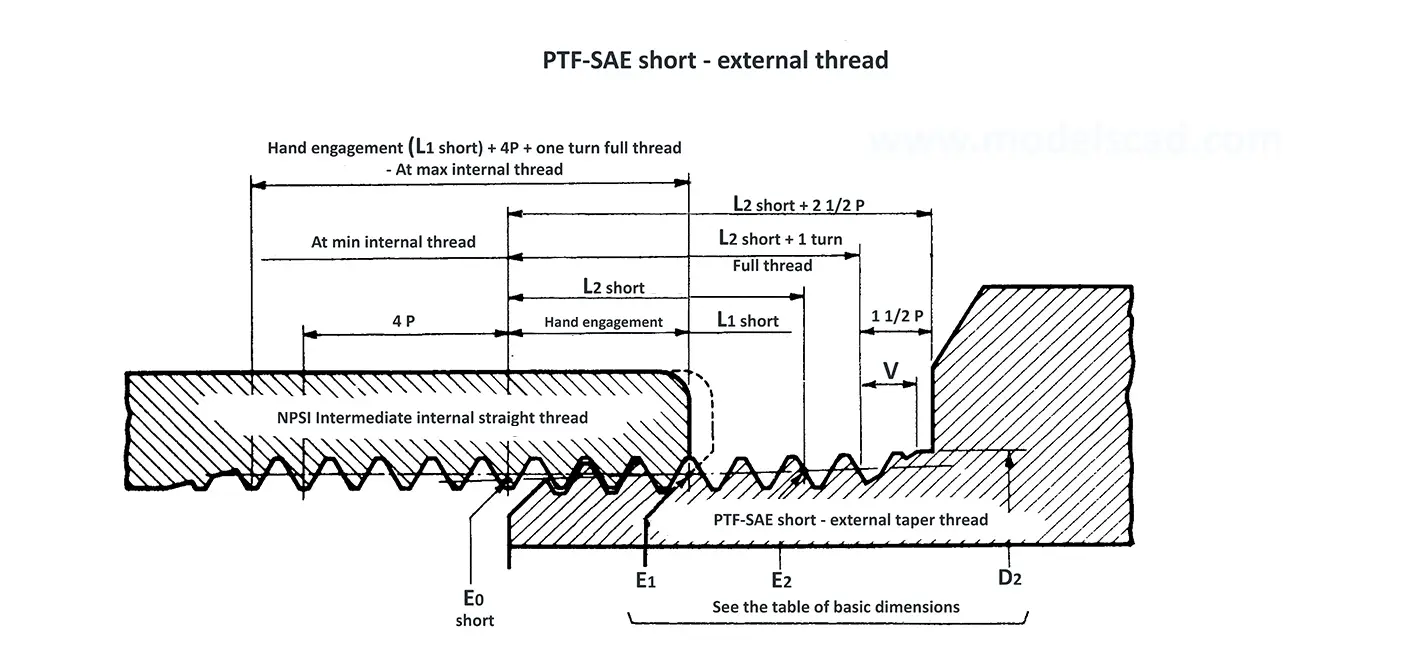
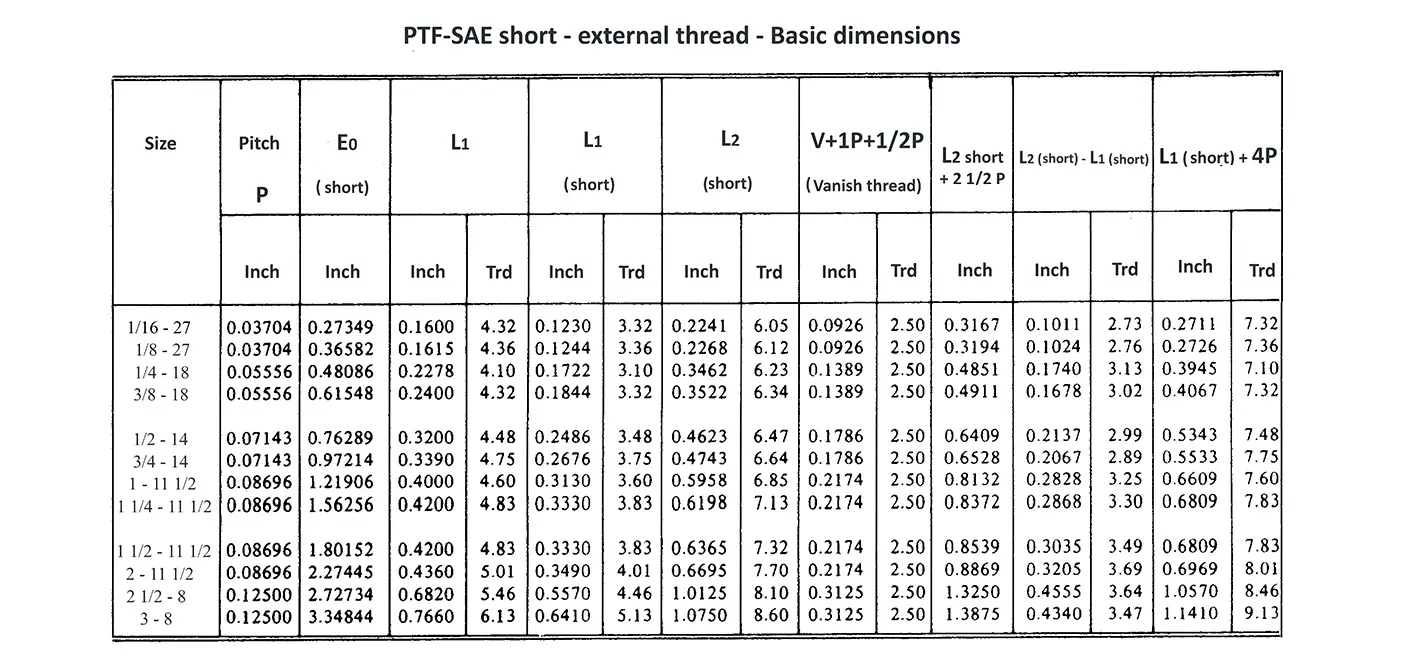
American taper pipe thread. Thread taper (1:16), profile flank angle is 60°.
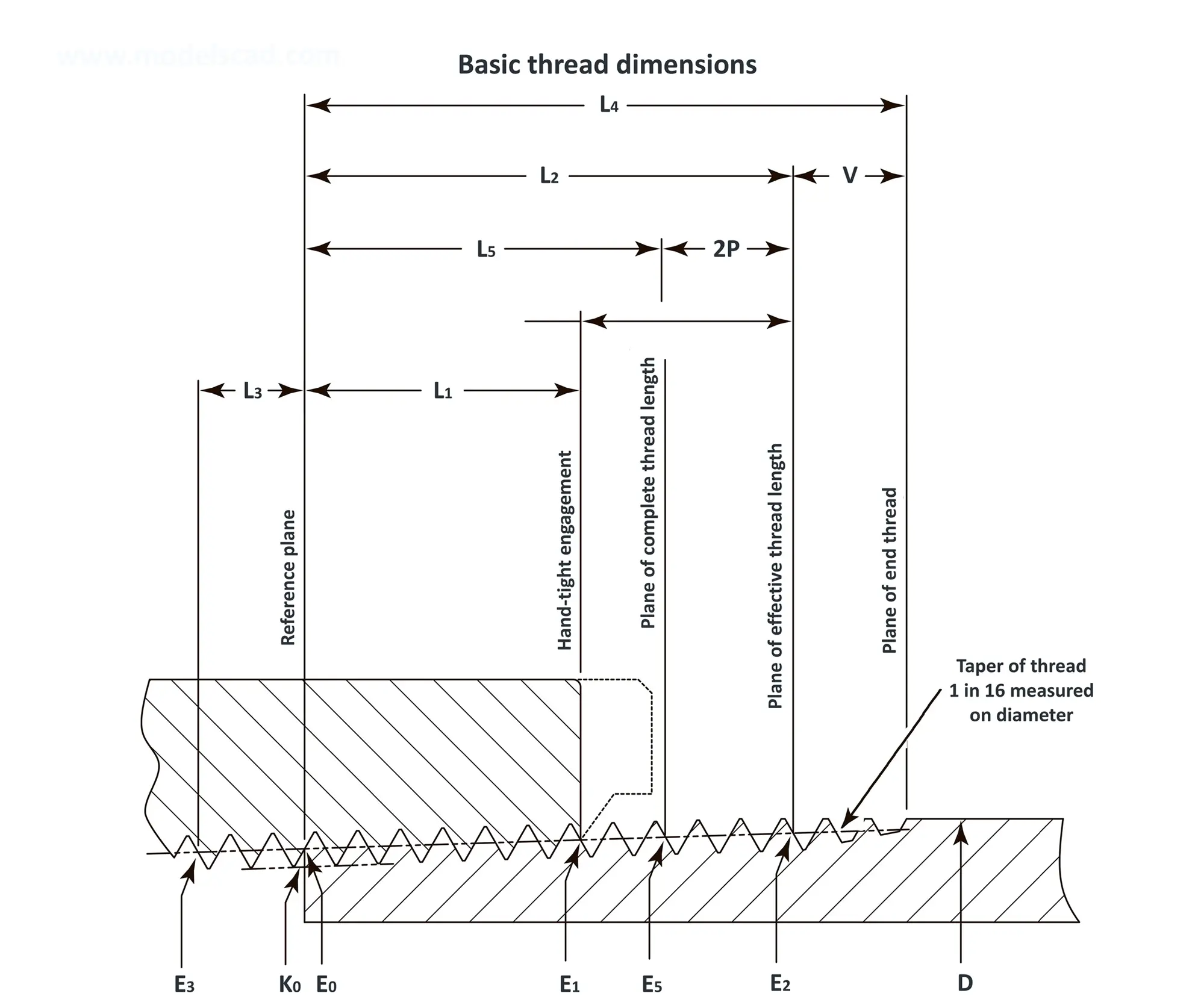
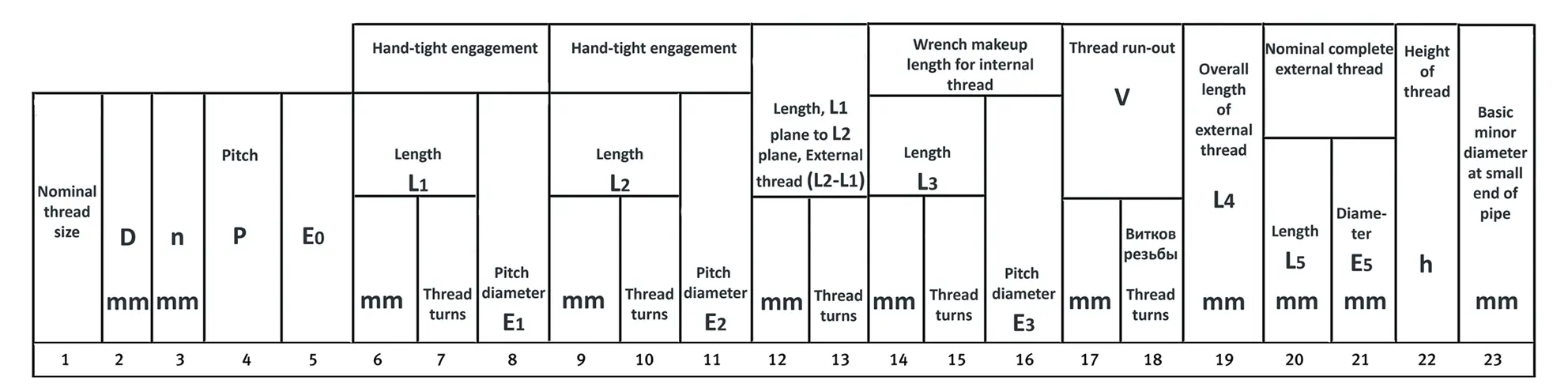
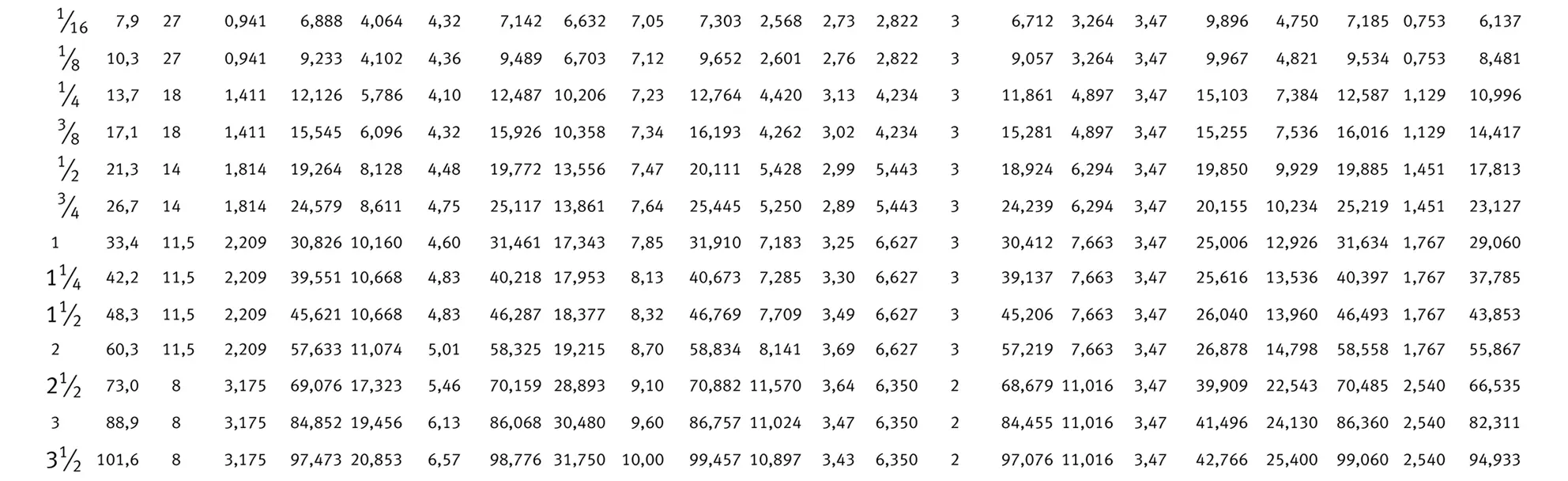
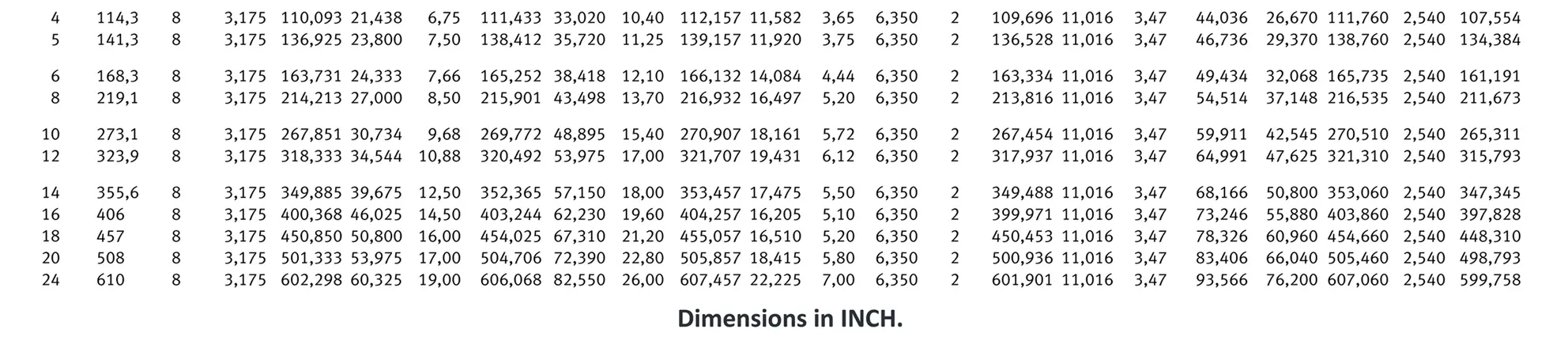
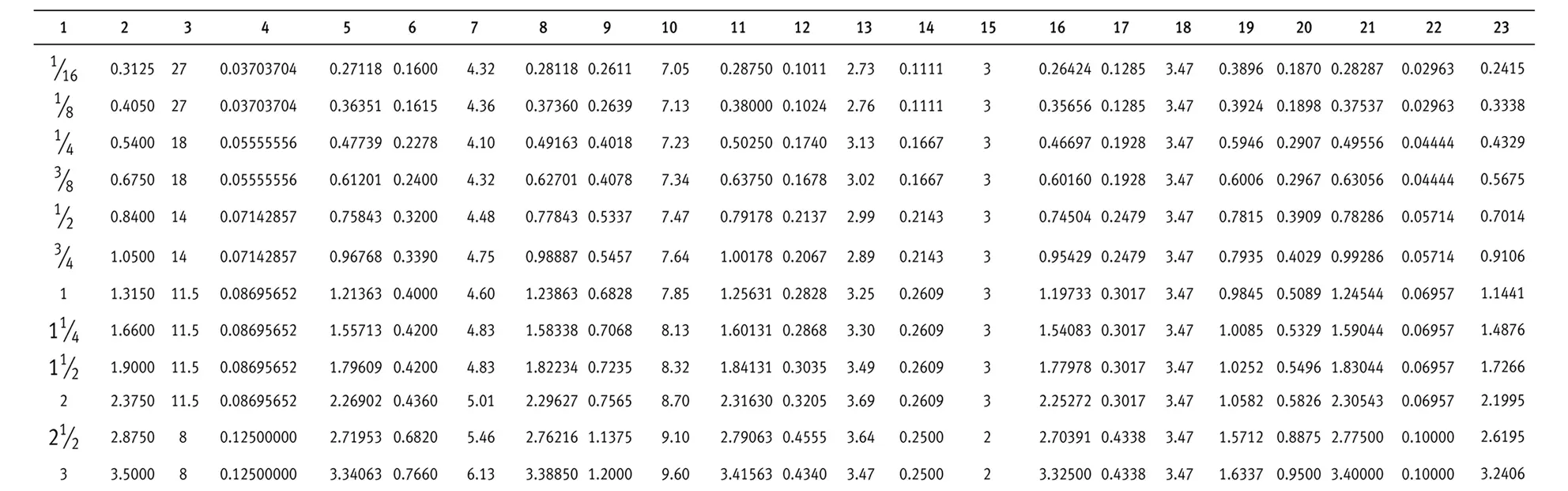
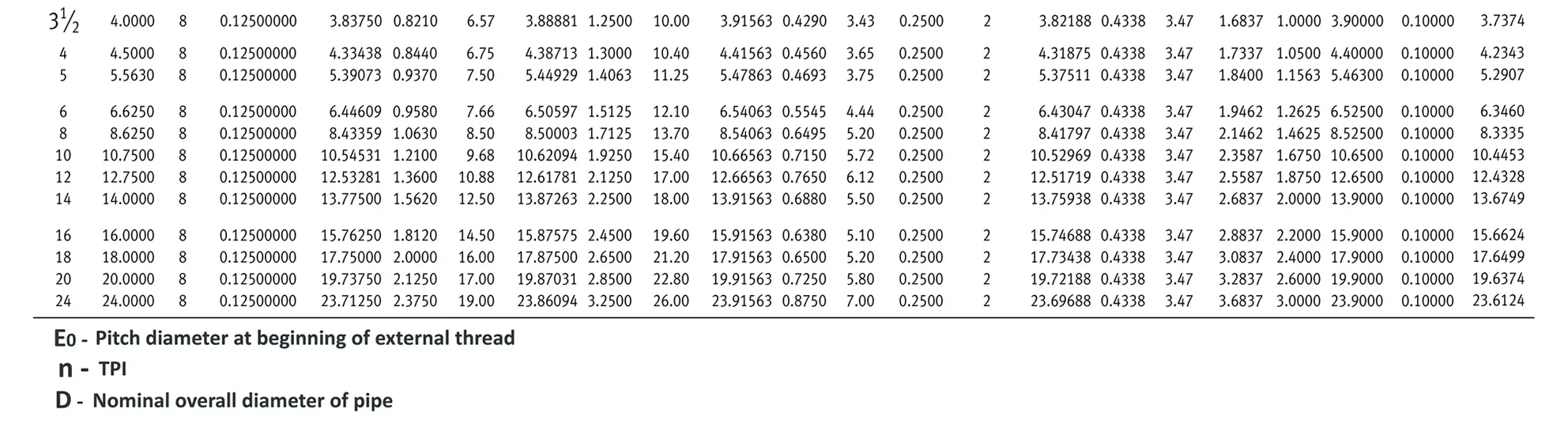
American taper pipe thread for dryseal joint without sealant compound. The flank angle is 60°.
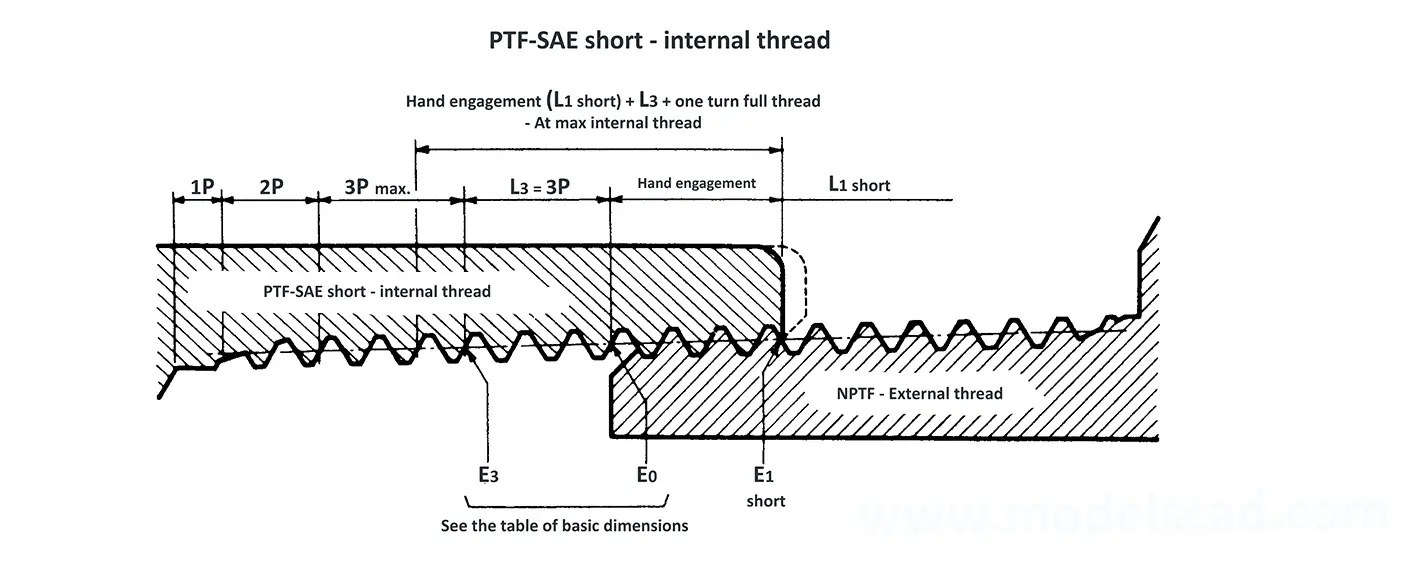
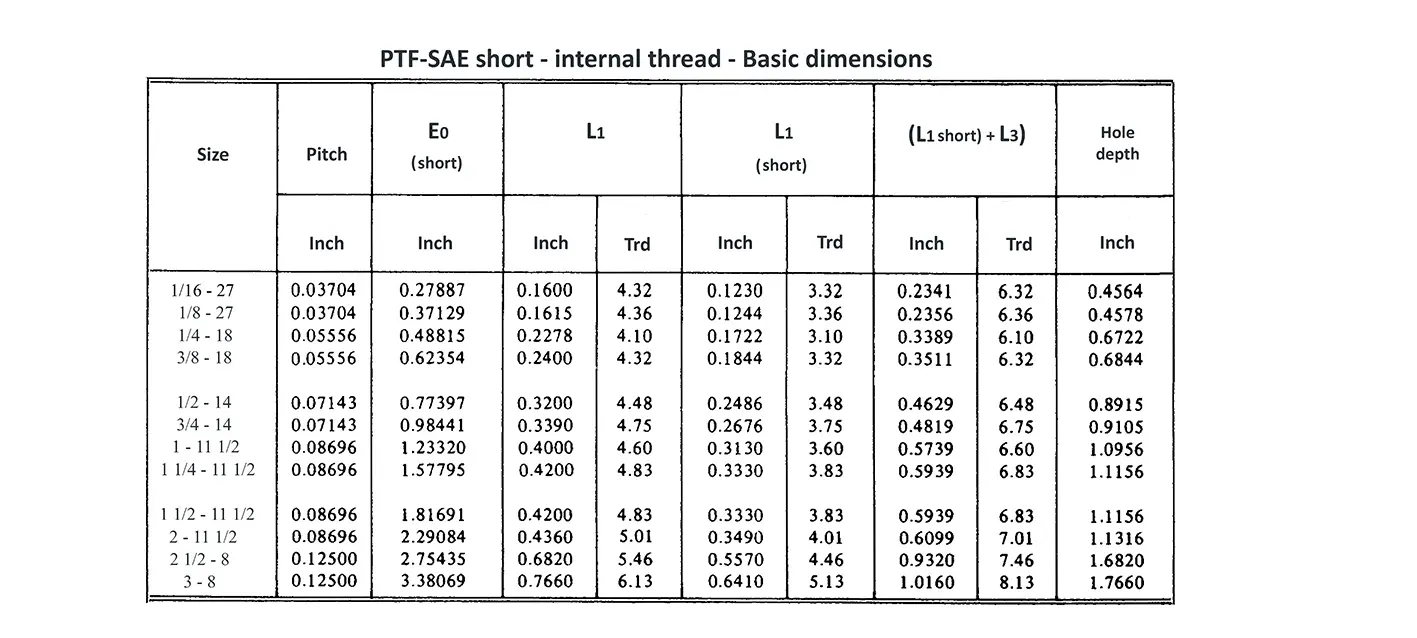
Acme screw threads ANSI ASME B1.5 provides for two main applications of given threads: general purpose threads and centralizing threads. The flank angle is 29°.
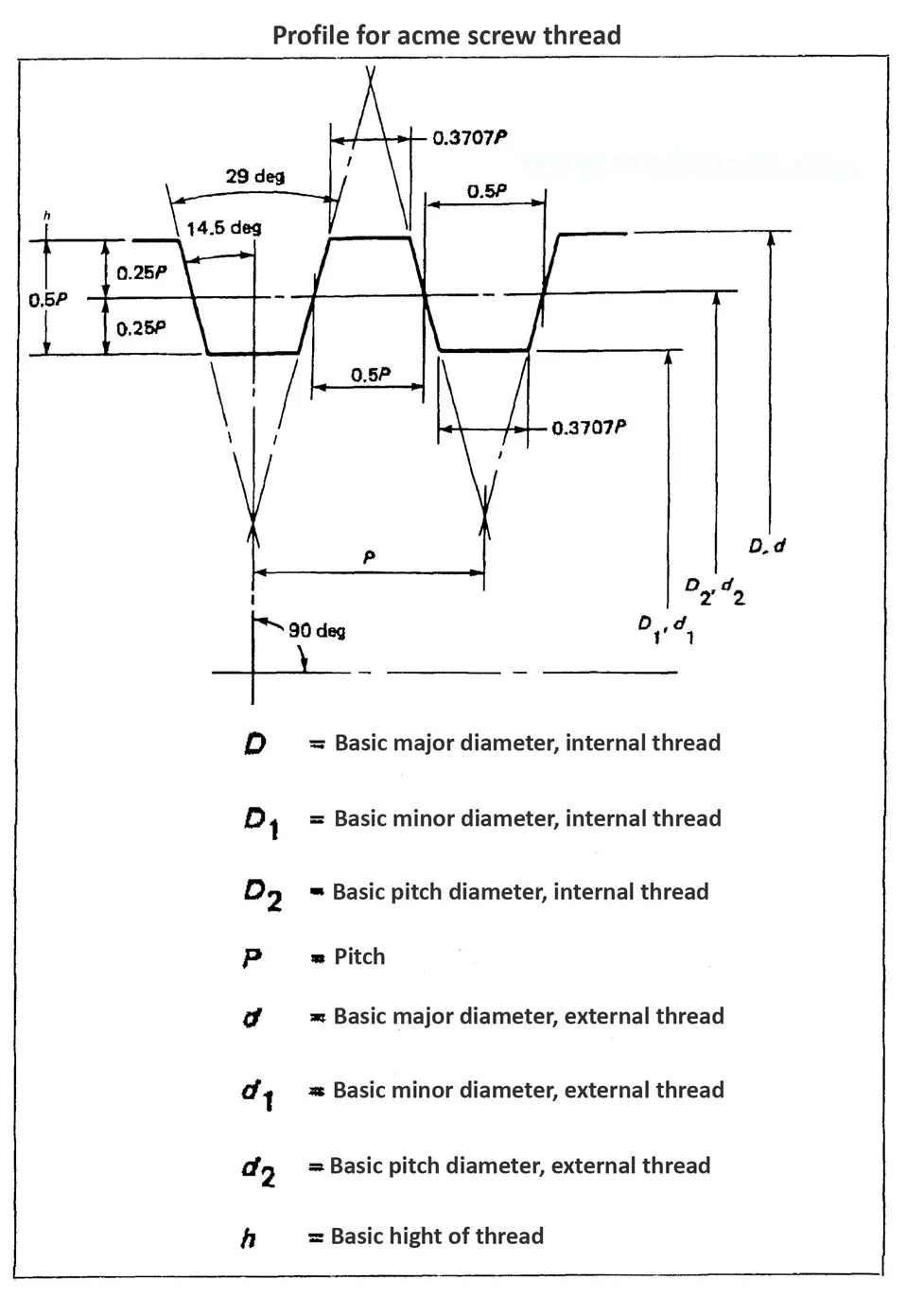
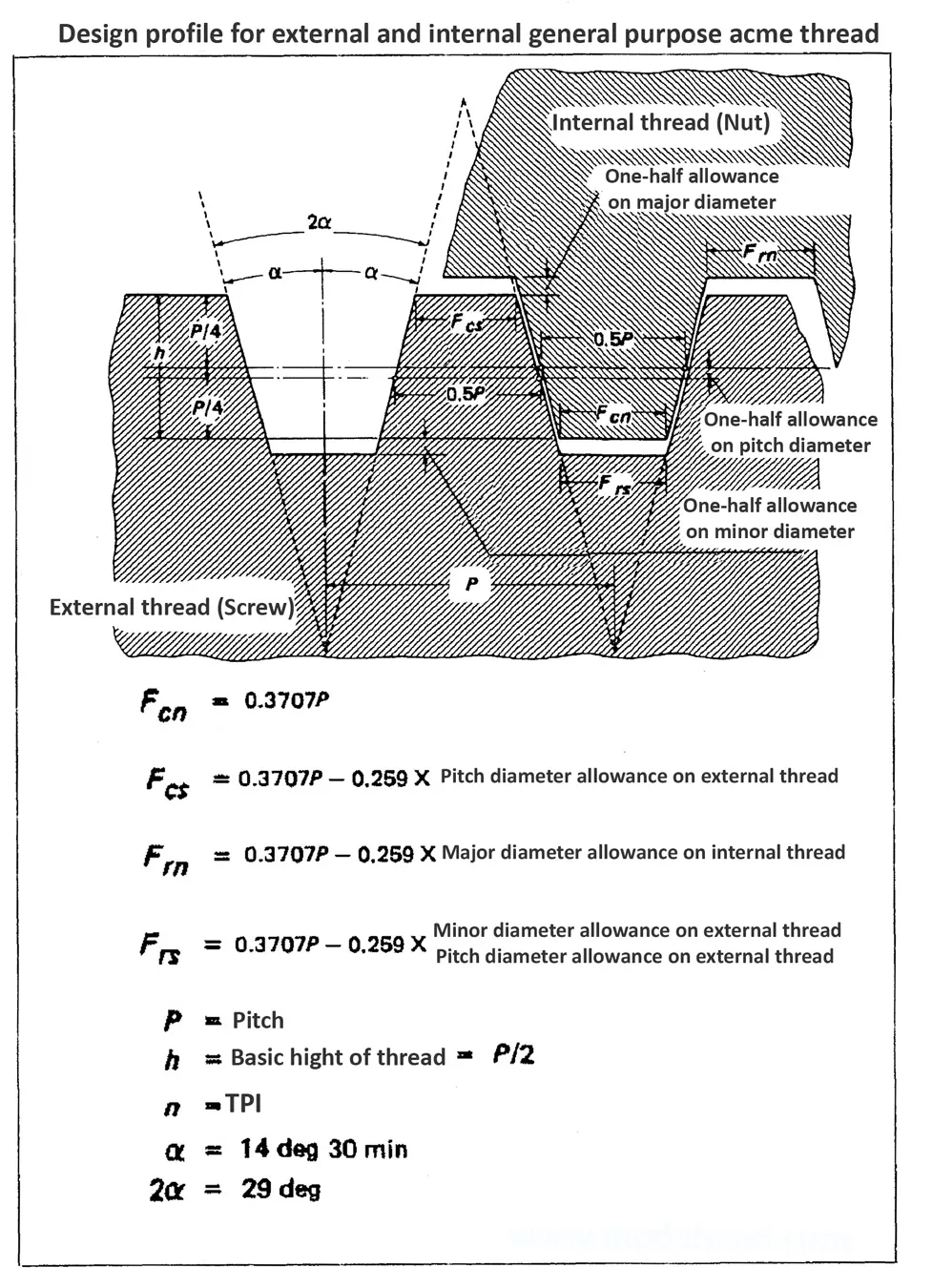
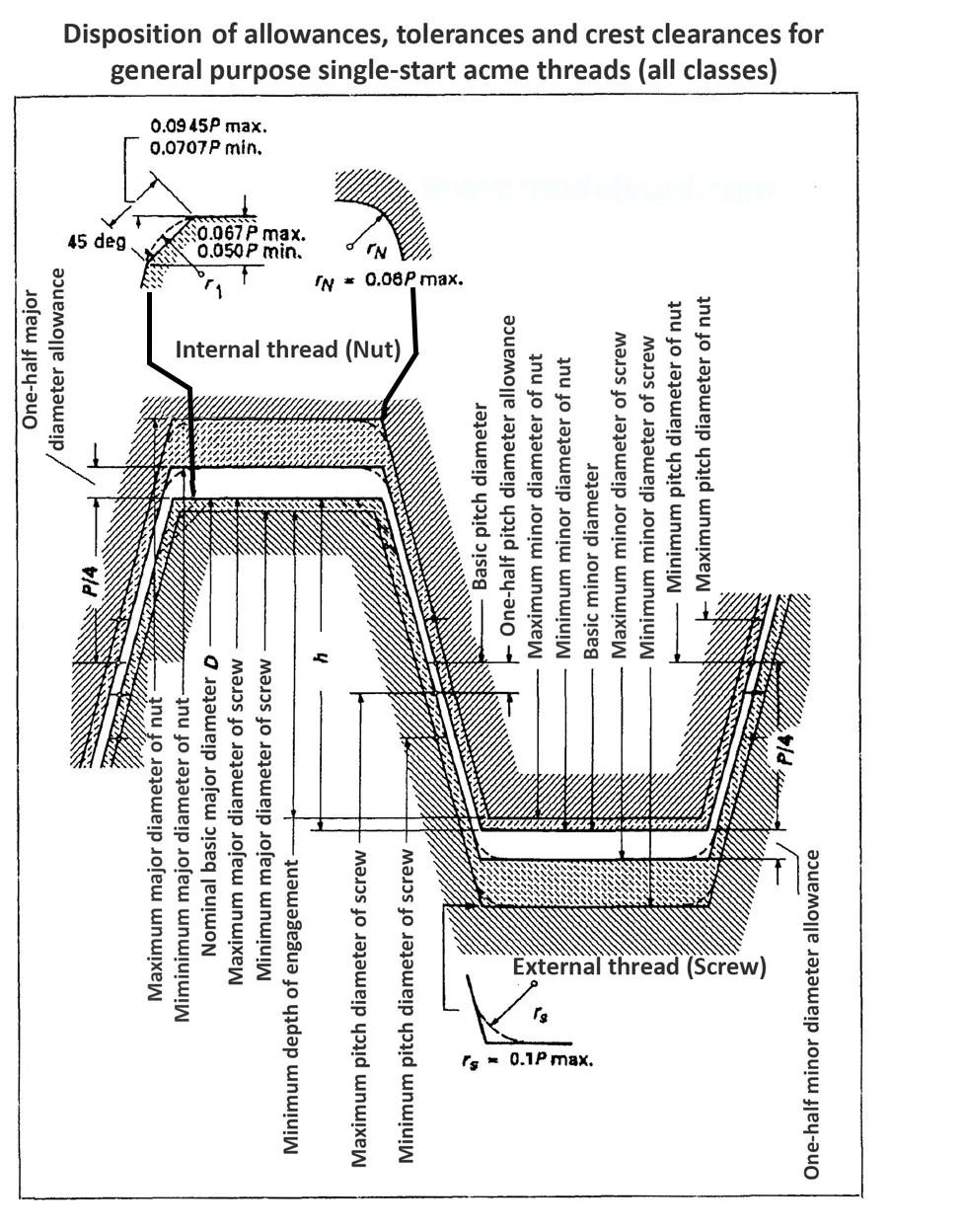
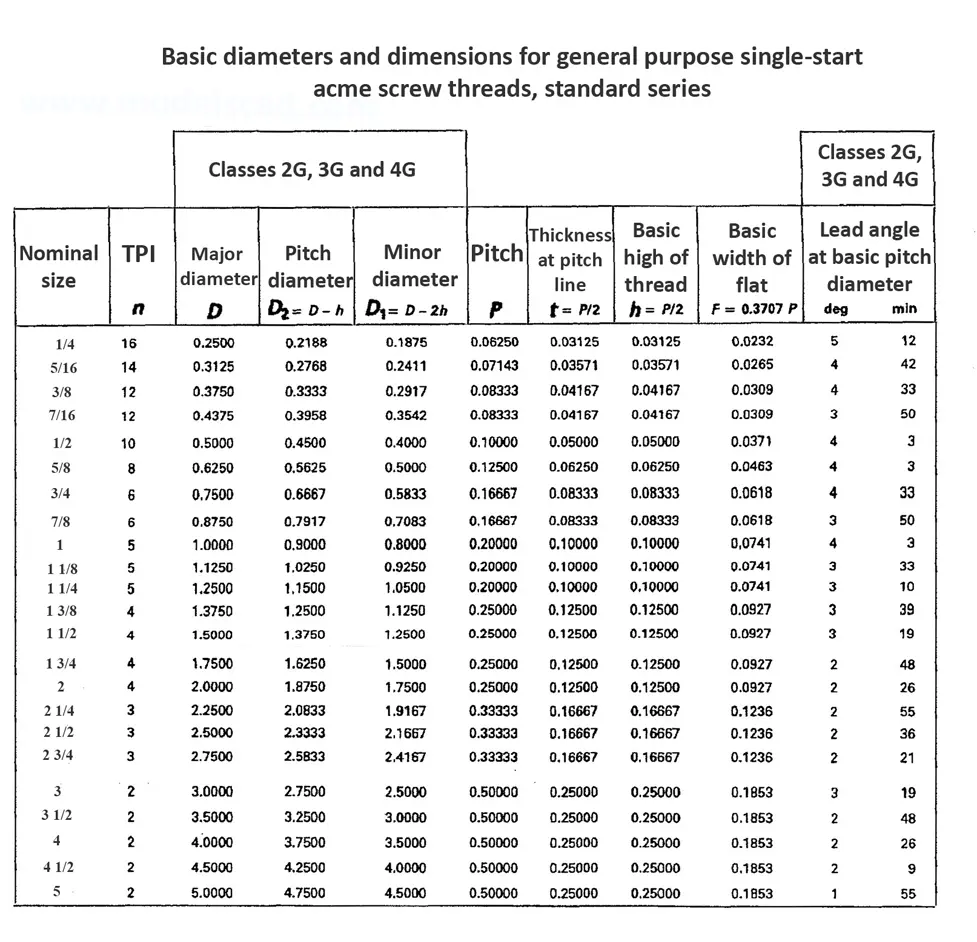
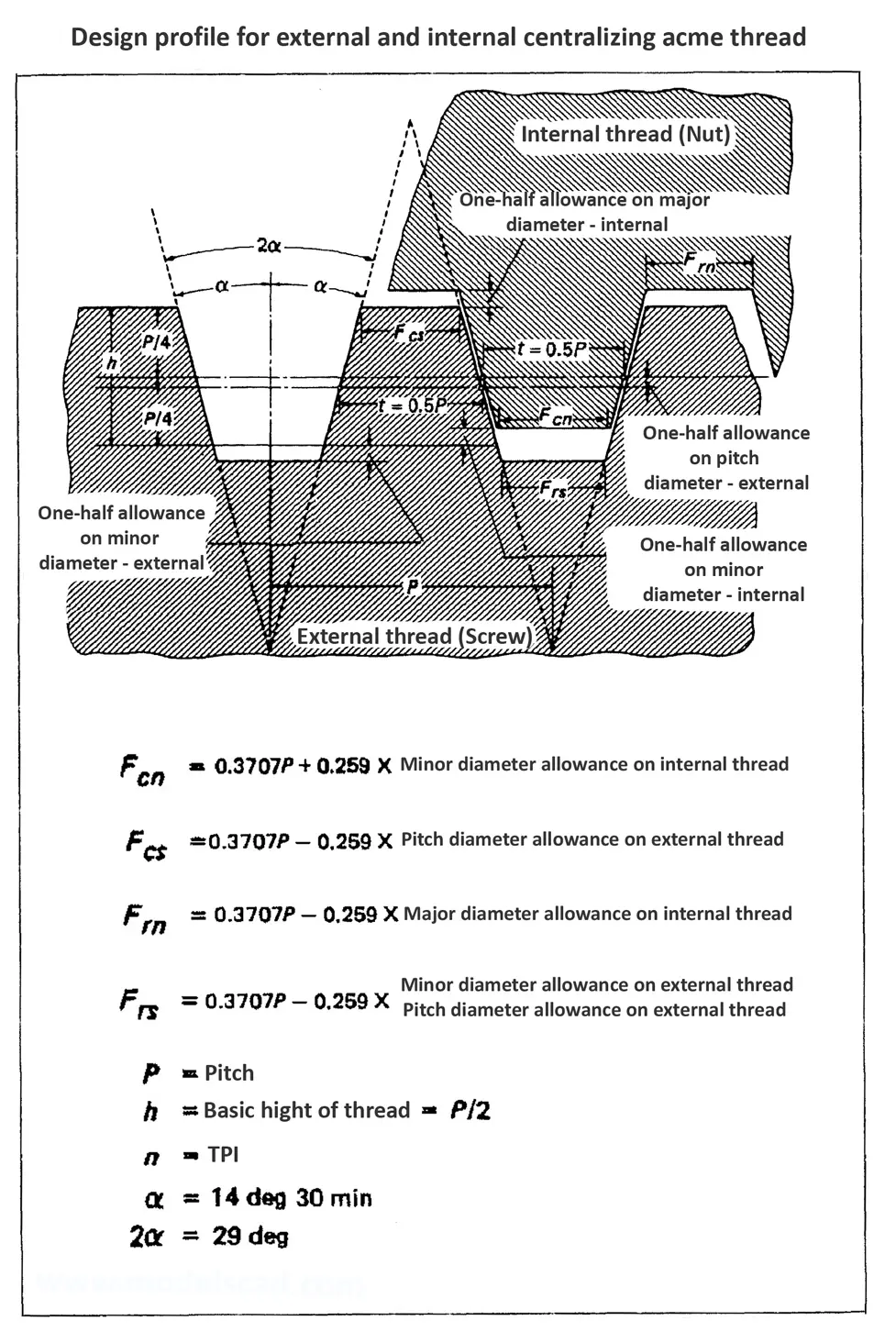
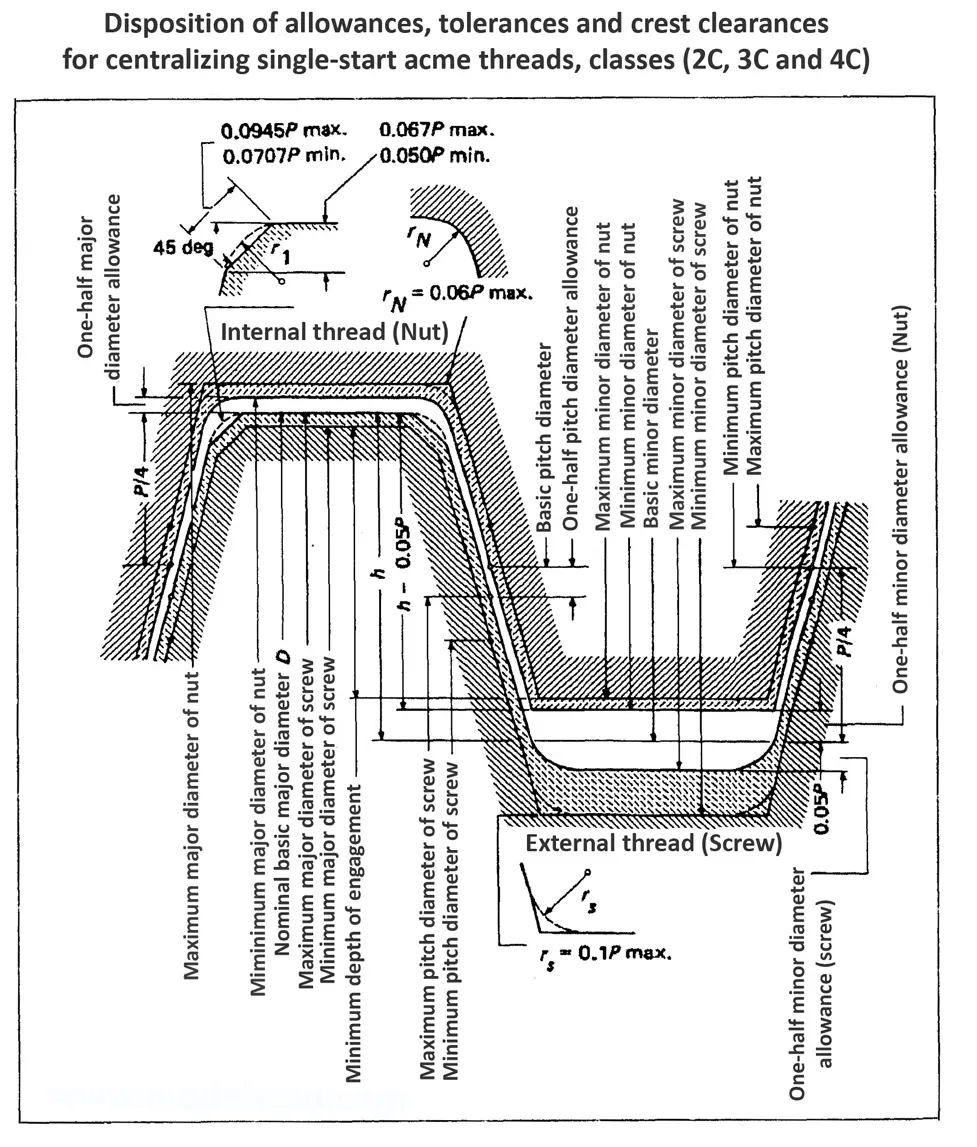
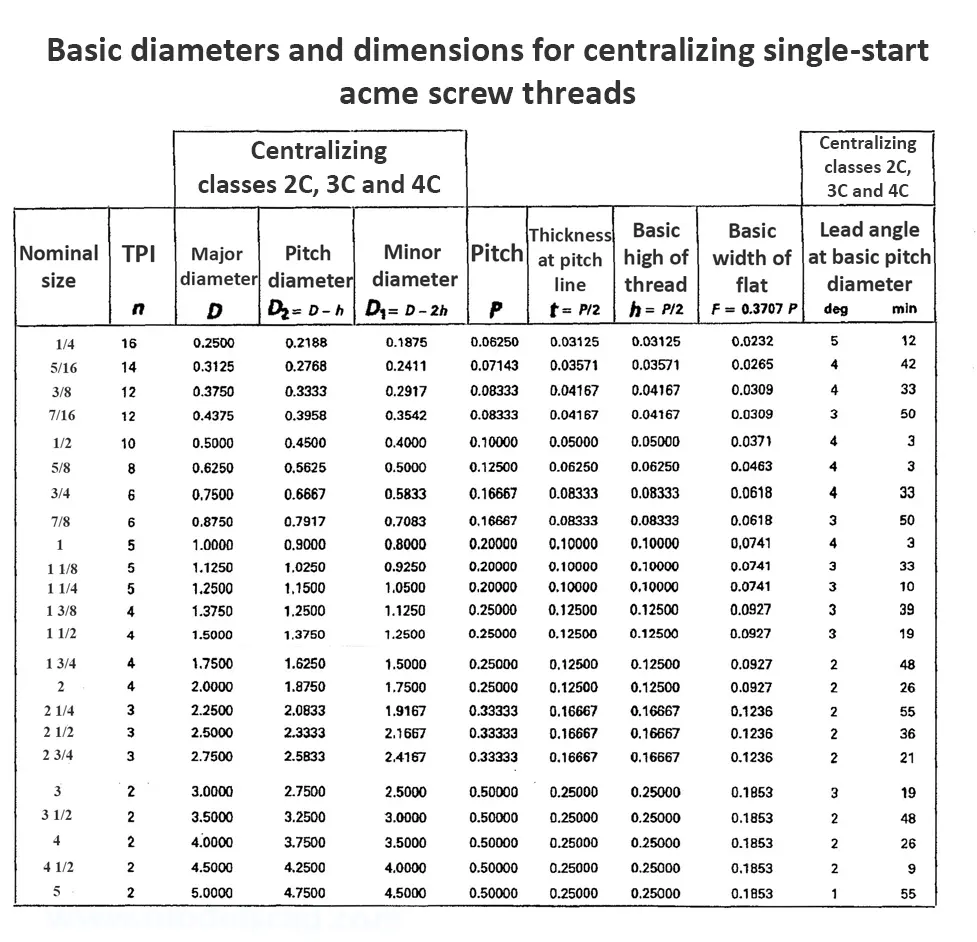
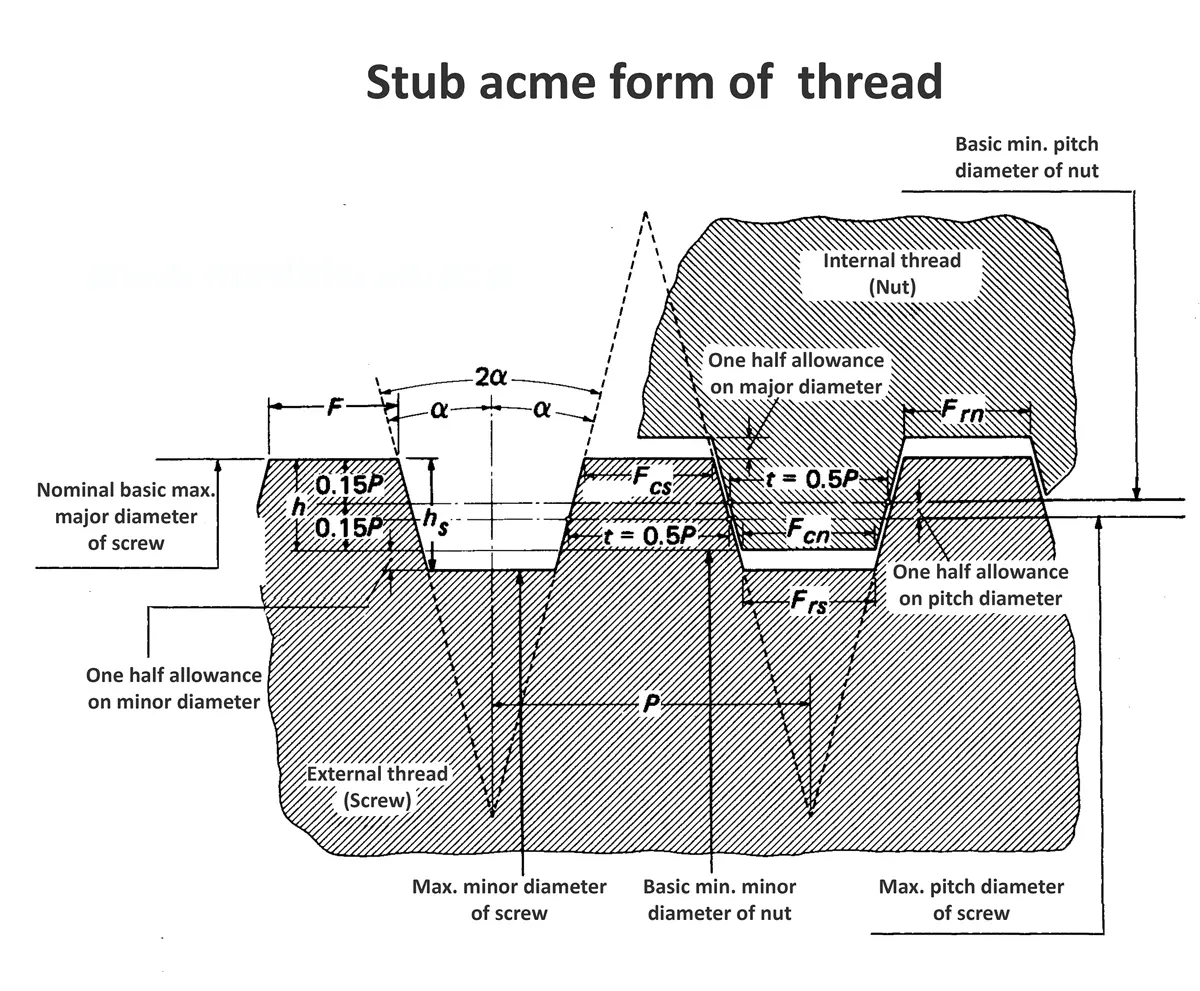
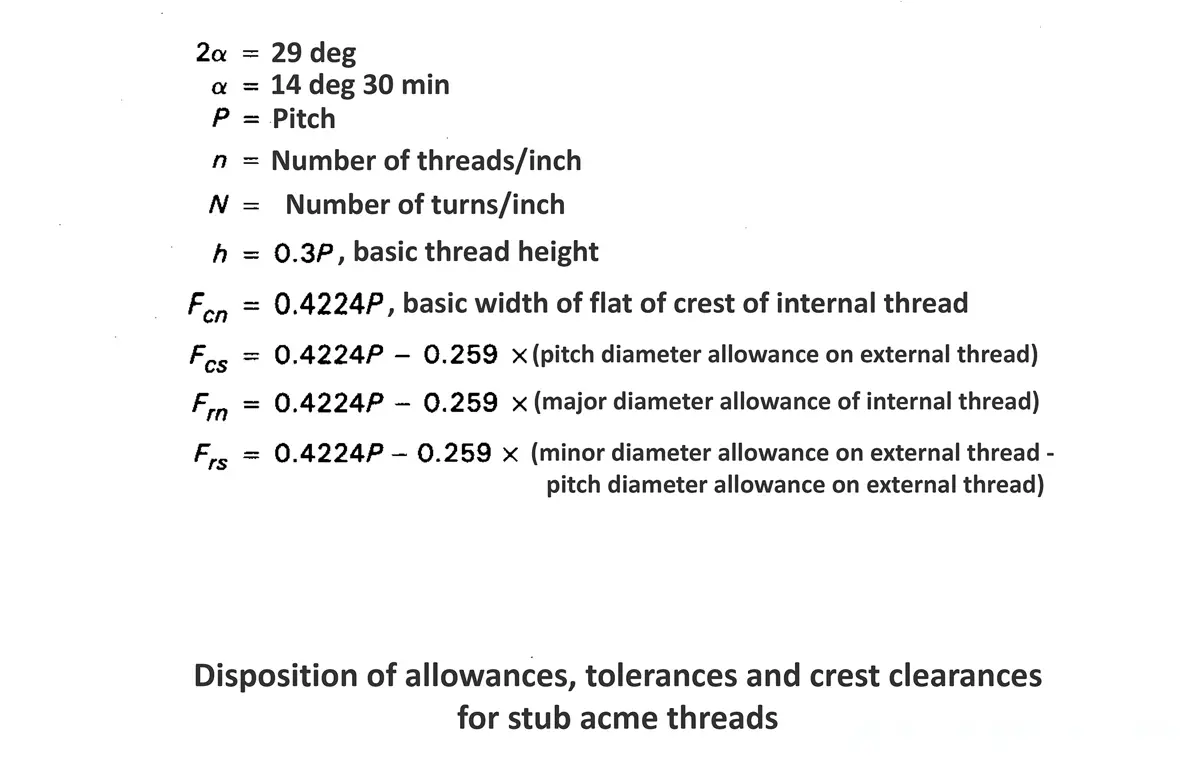
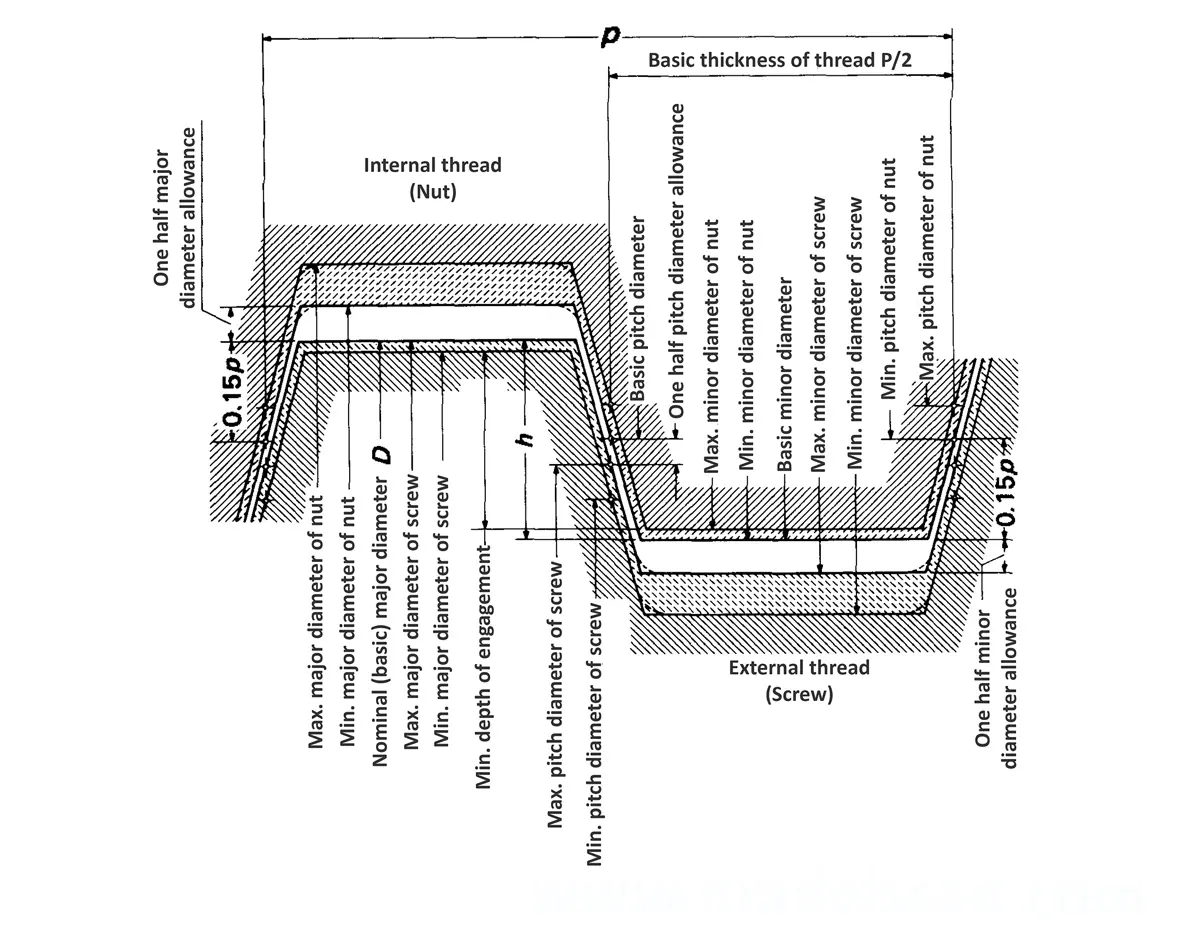
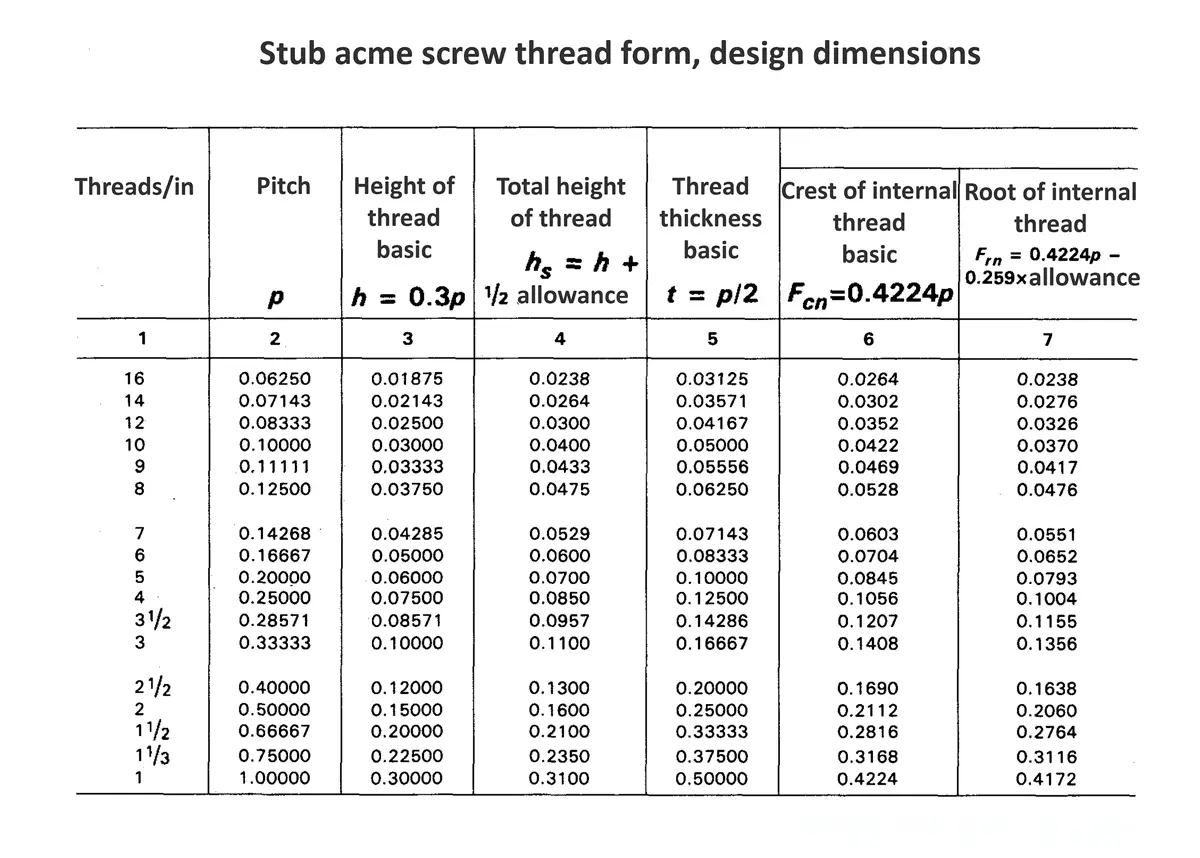
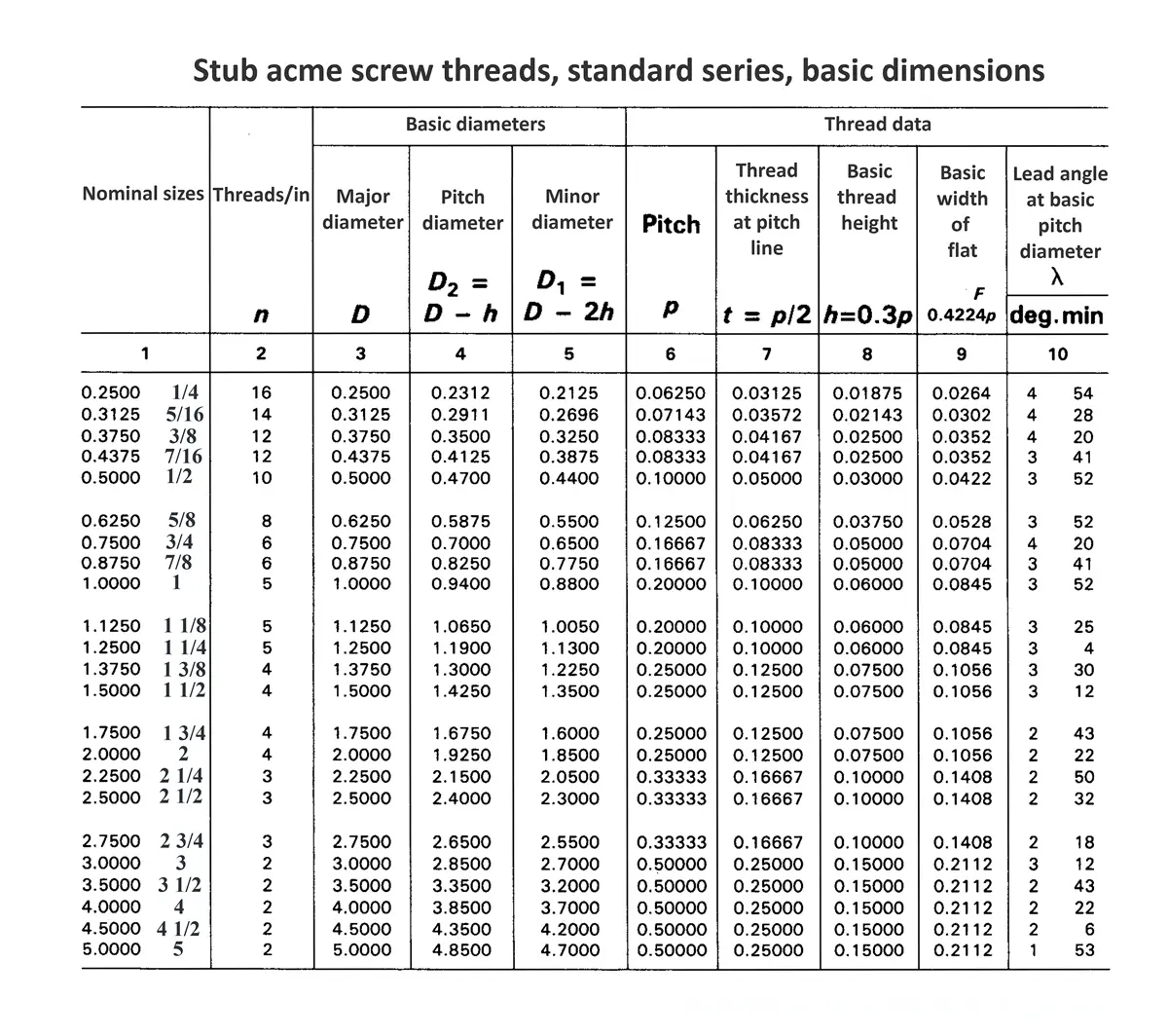
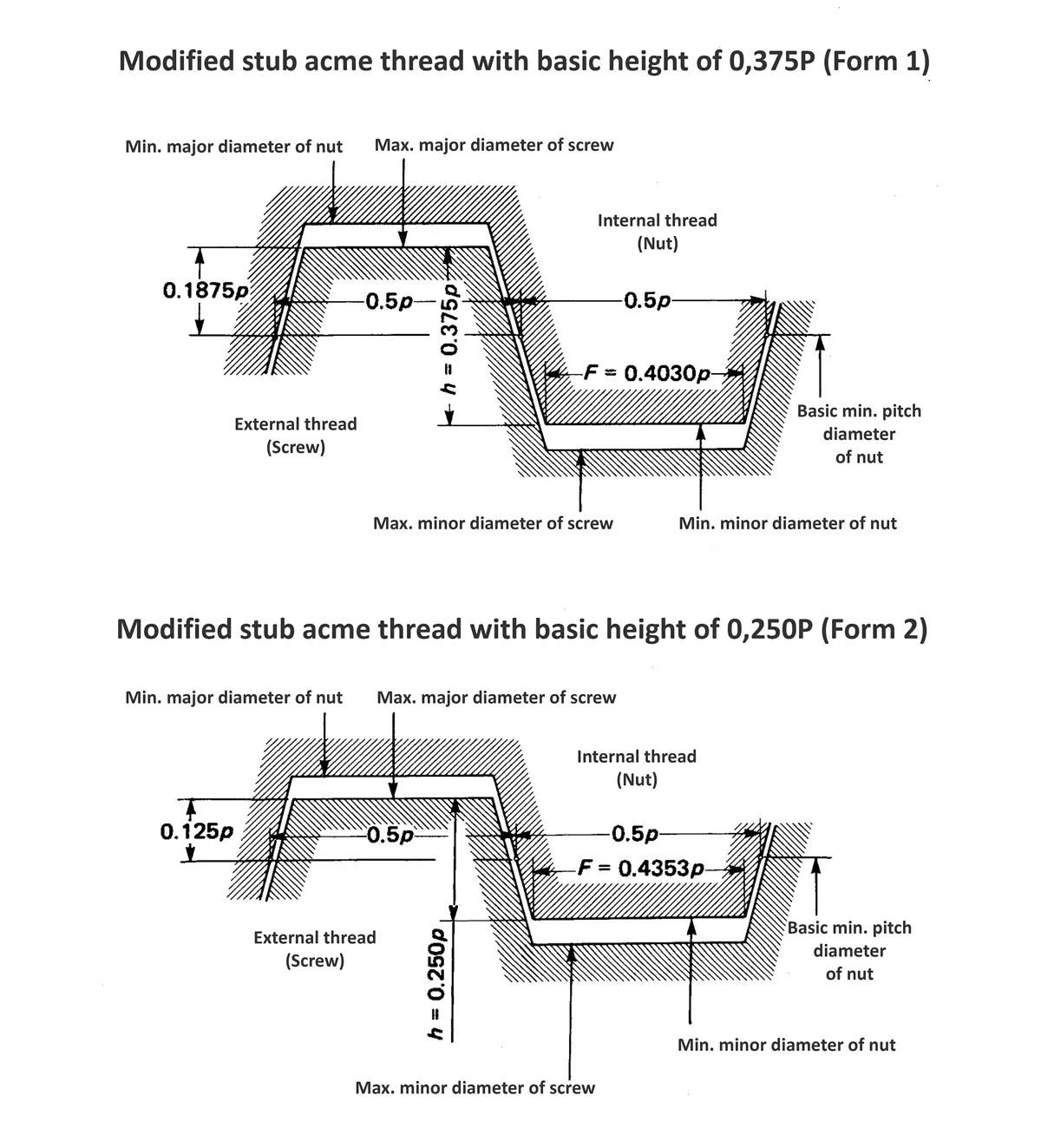
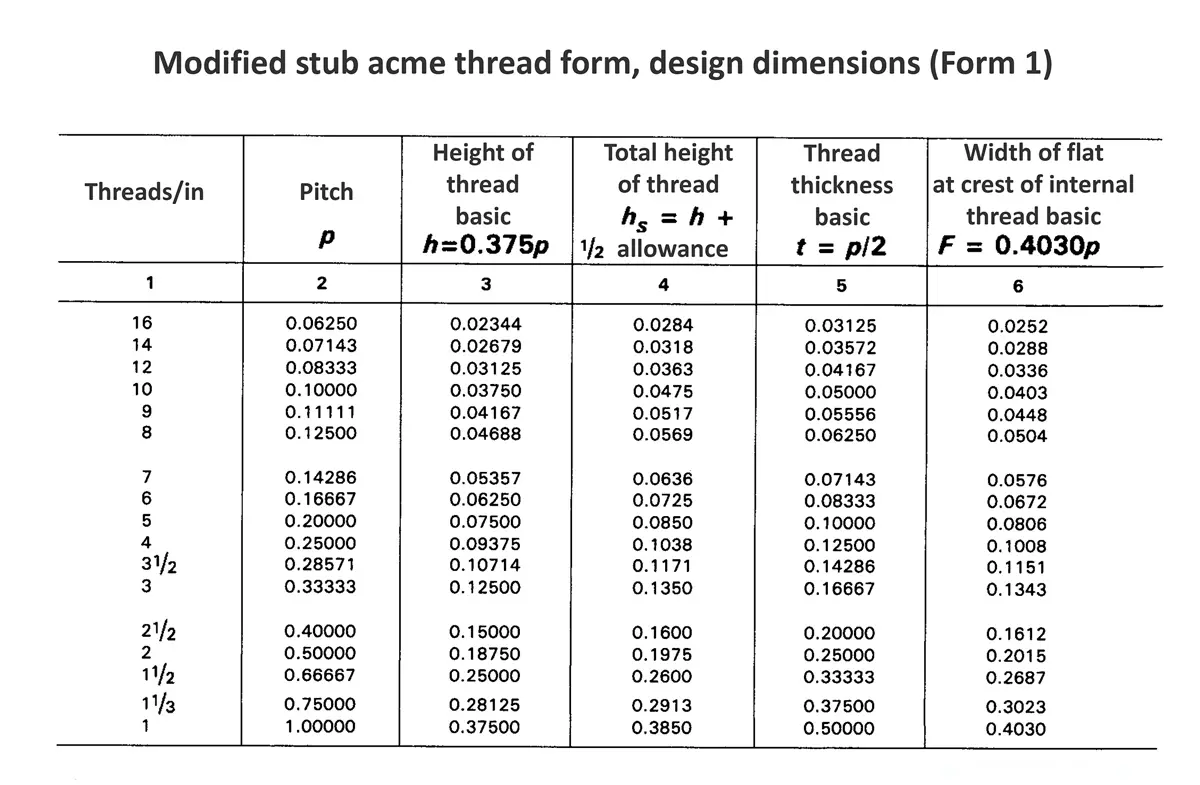
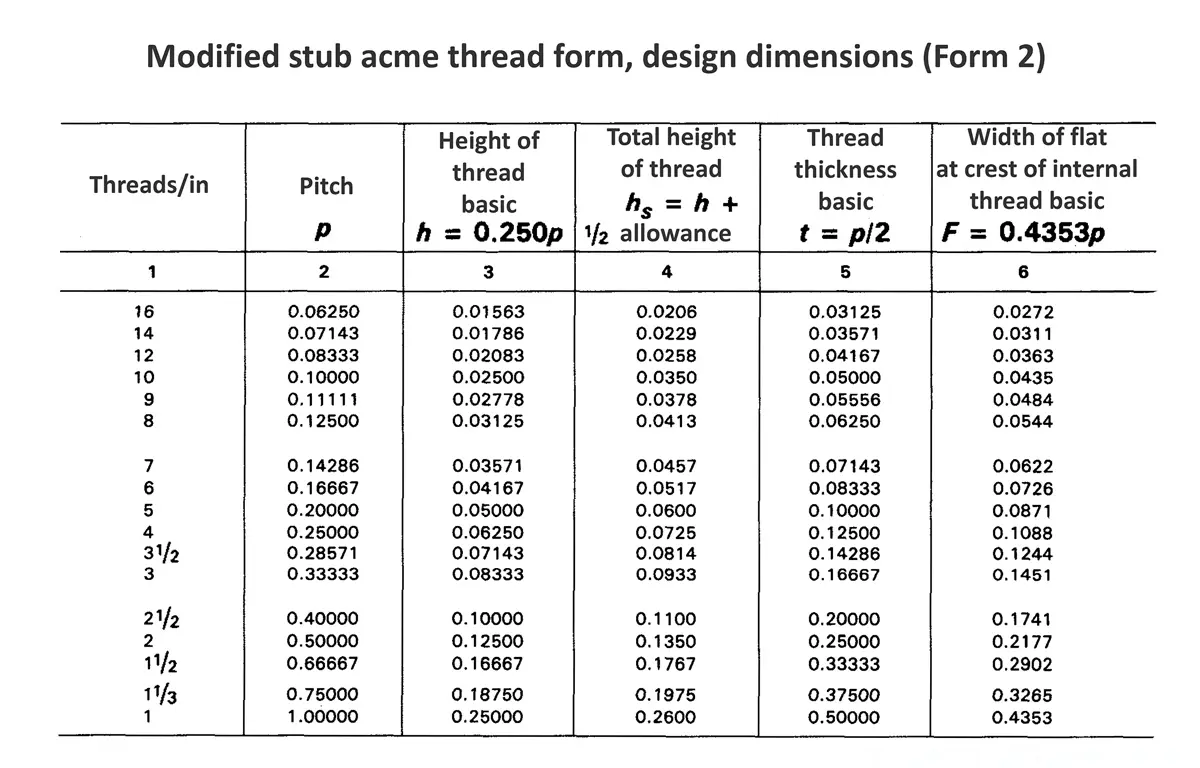
Acme screw threads were intended to replace square threads and a variety of threads of other forms used chiefly for the purpose of producing traversing motions on machines, tools, etc. Stub acme screw thread has generally uses where is required a coarse-pitch thread of shallow depth due to mechanical or technical considerations. The flank angle is 29°.
UK standards
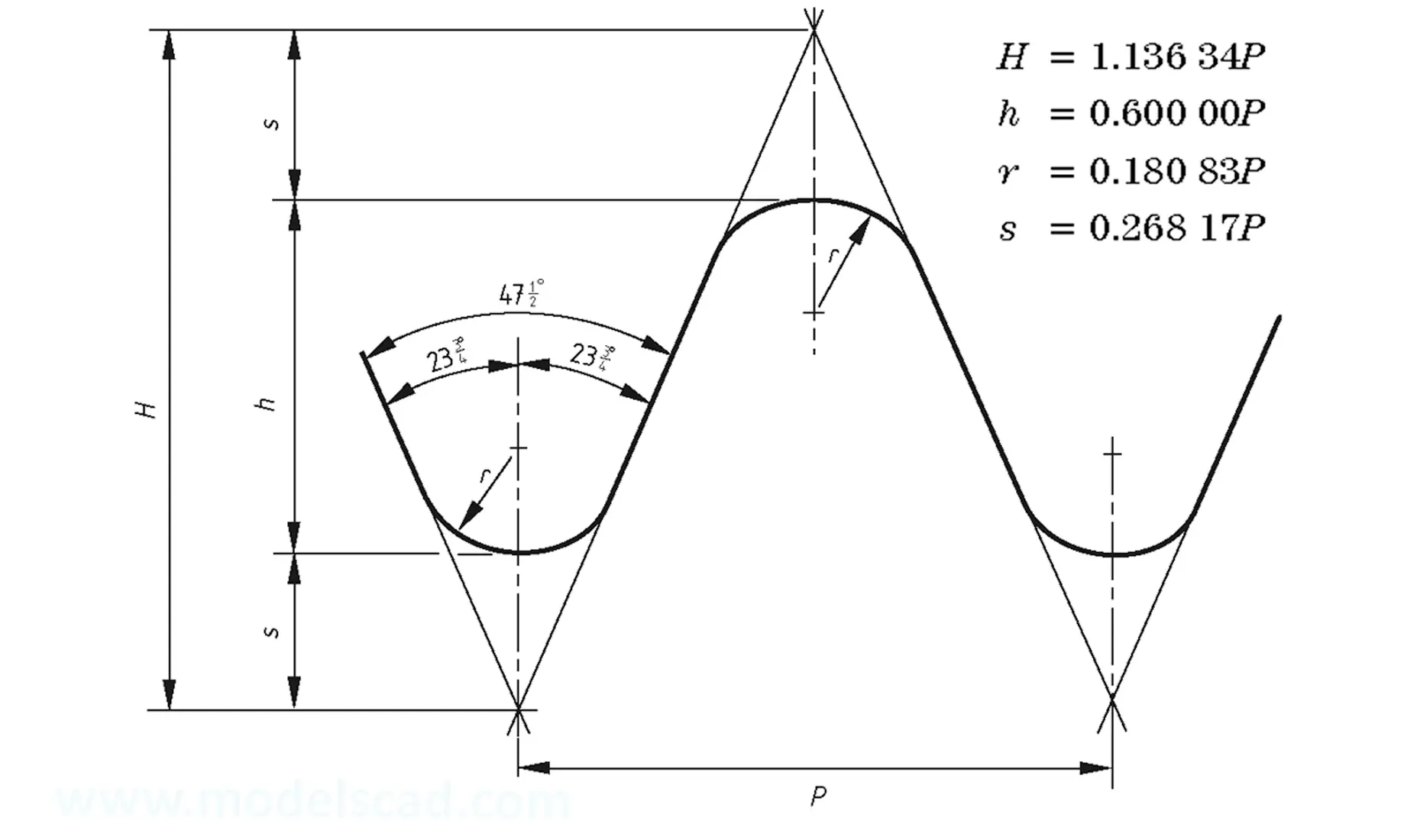
British standard thread BS 93. Used in tools, profile angle 47.5°. Has been replaced by coarse and fine ISO threads.
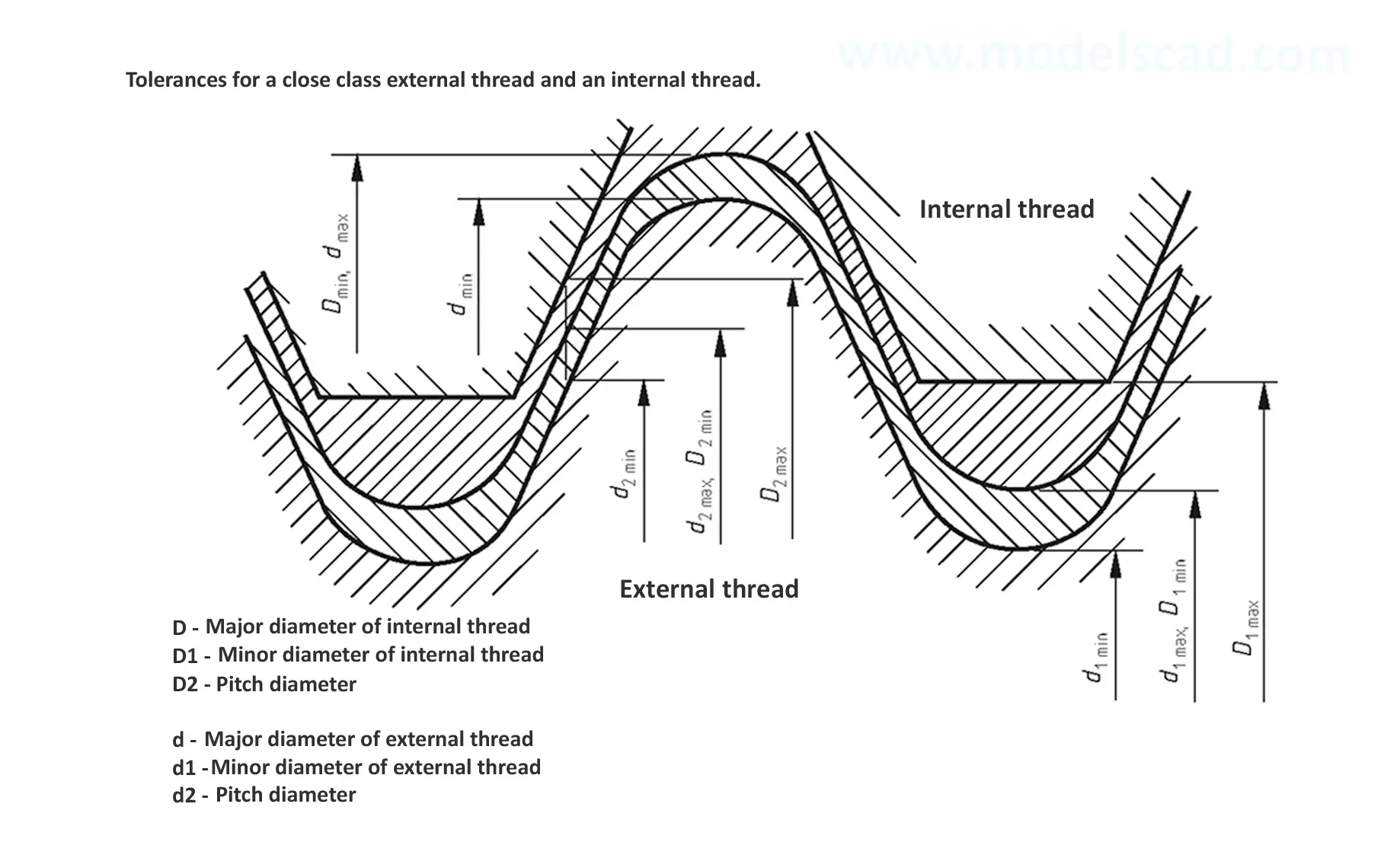
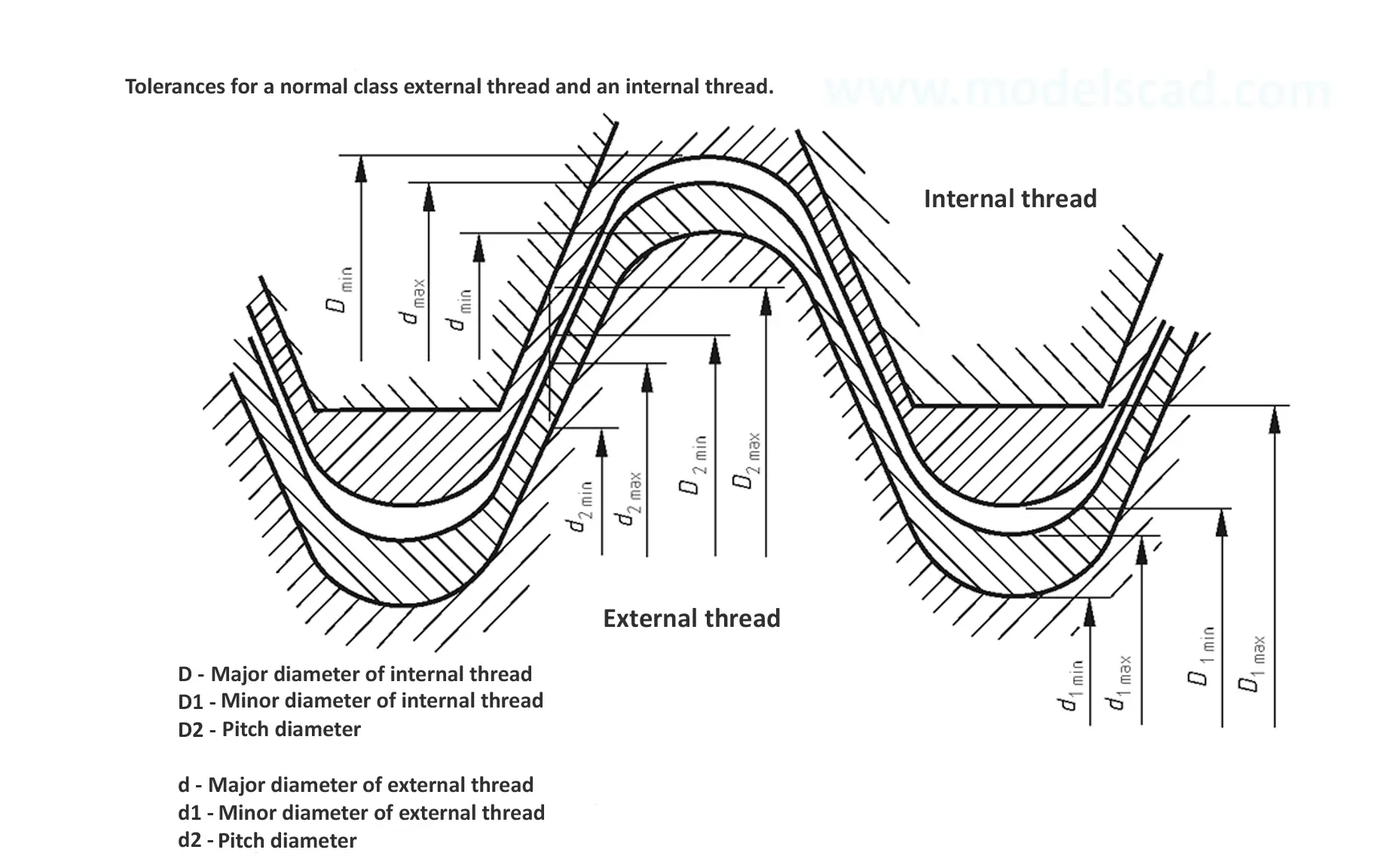
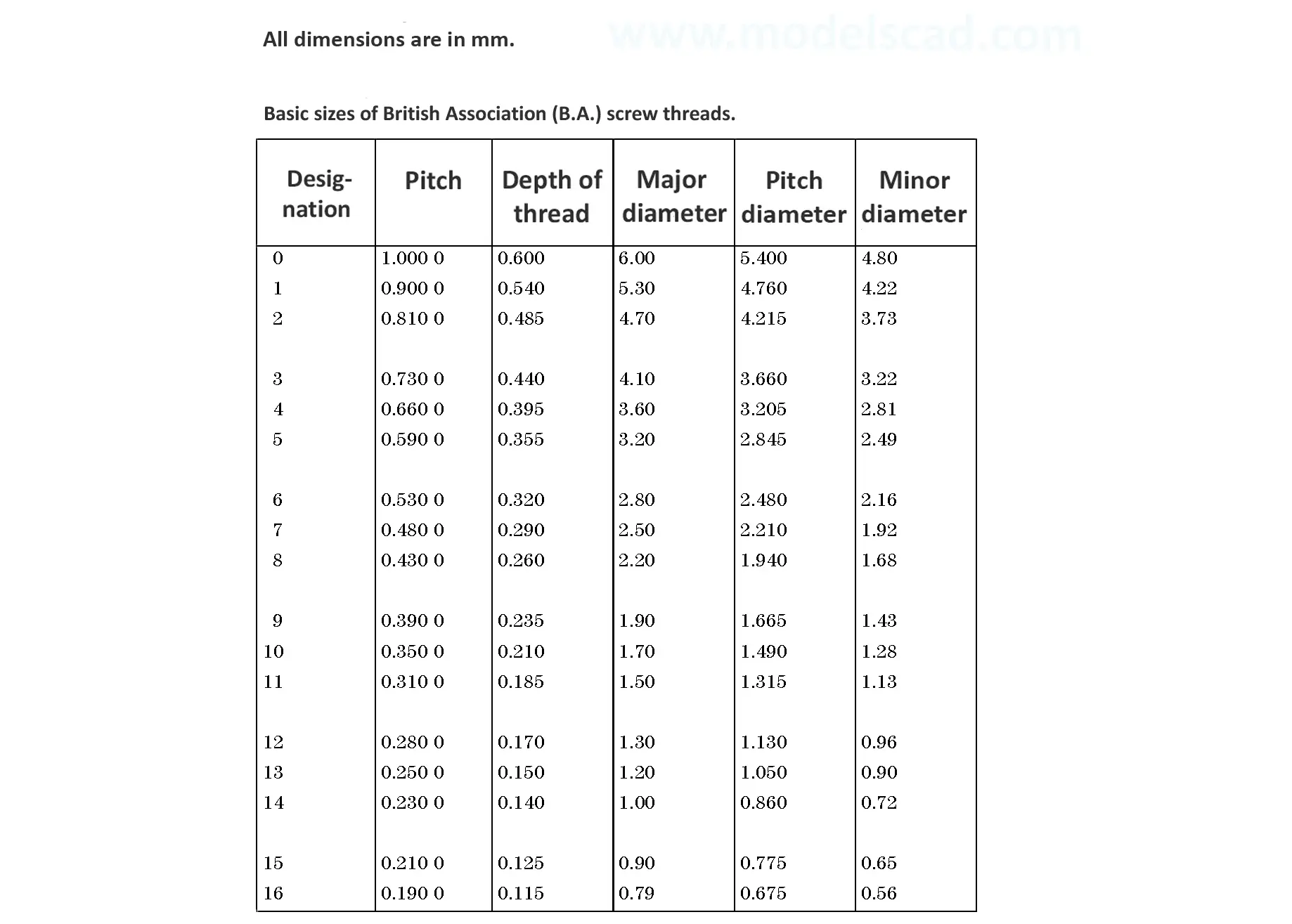
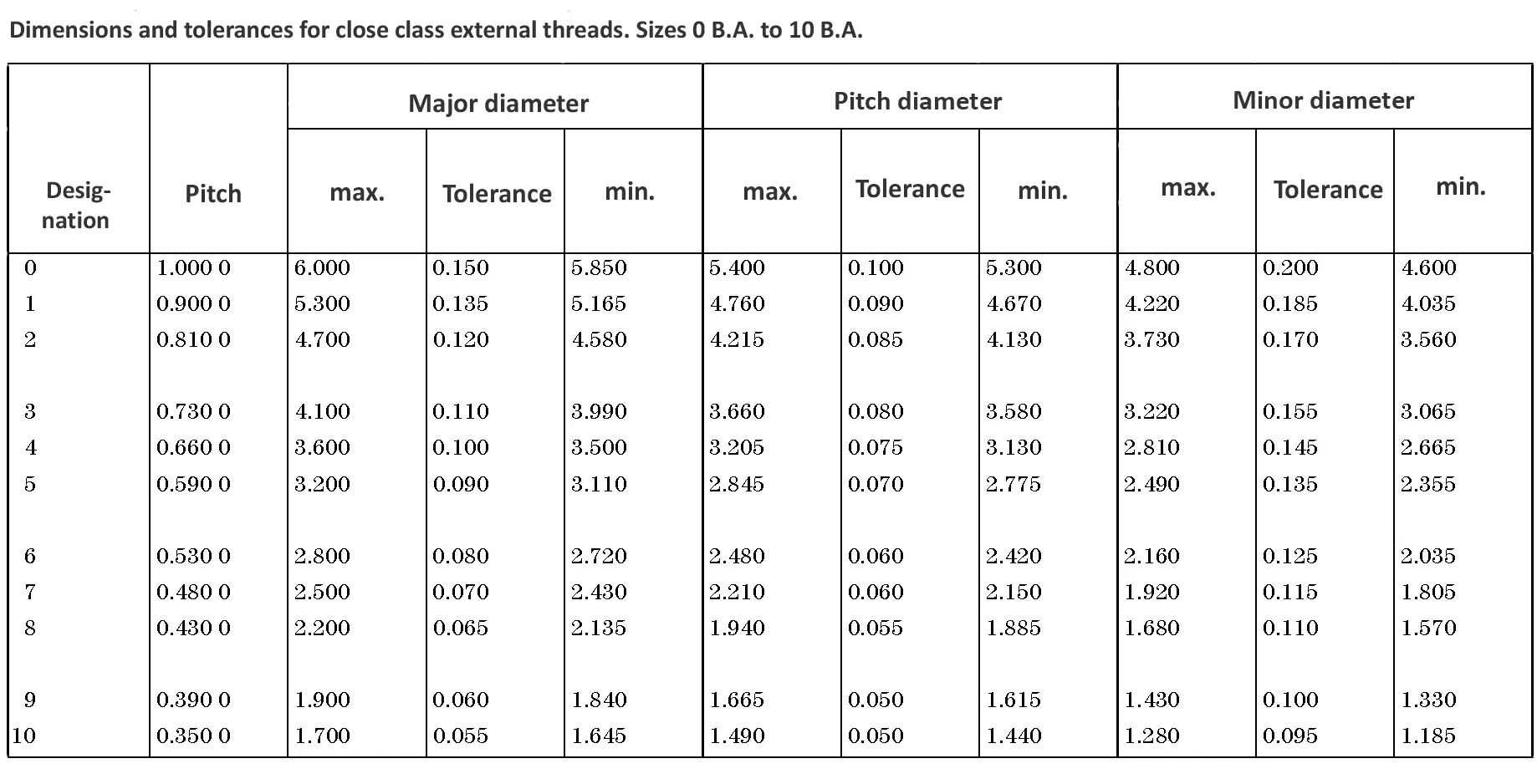
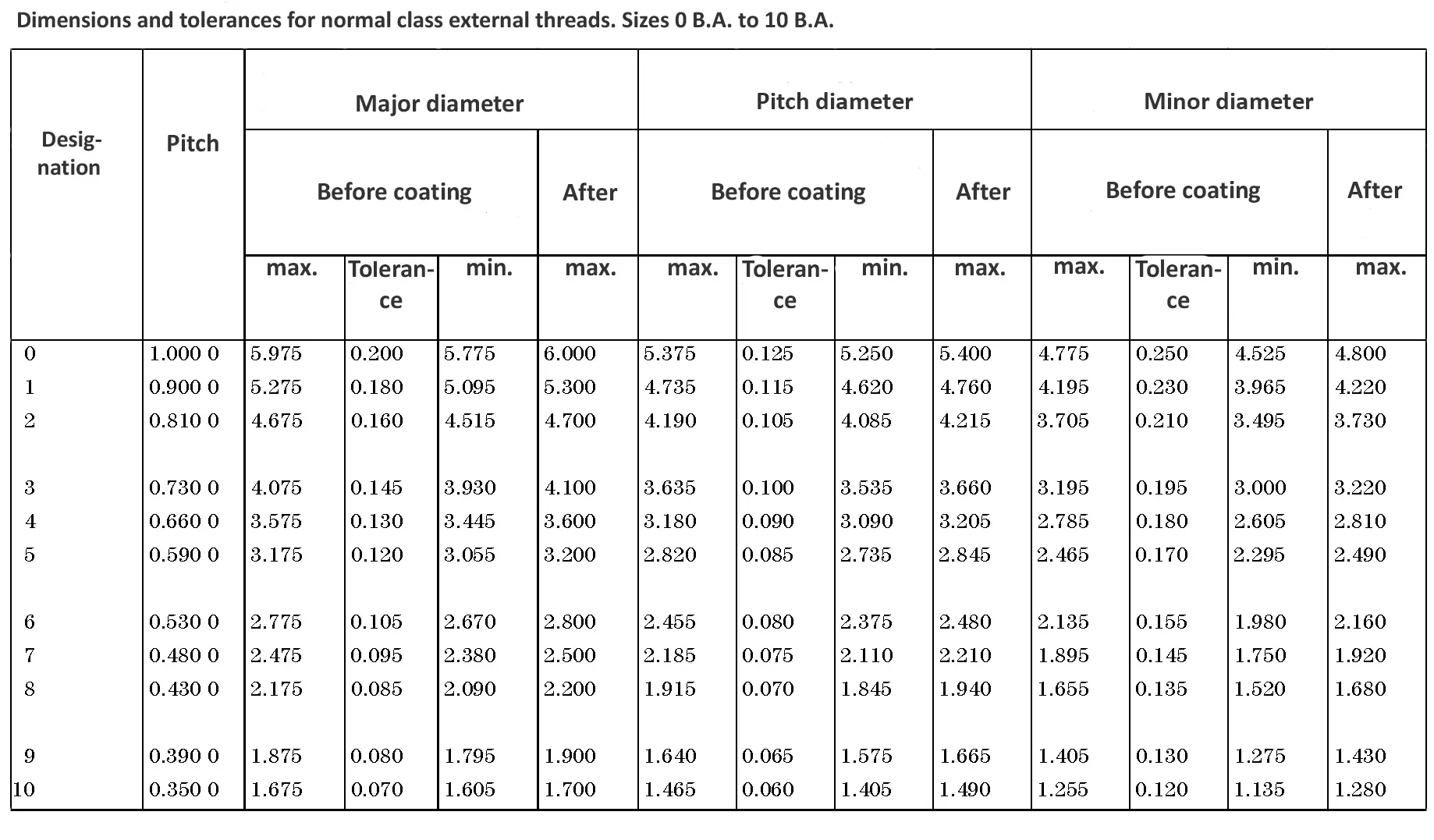
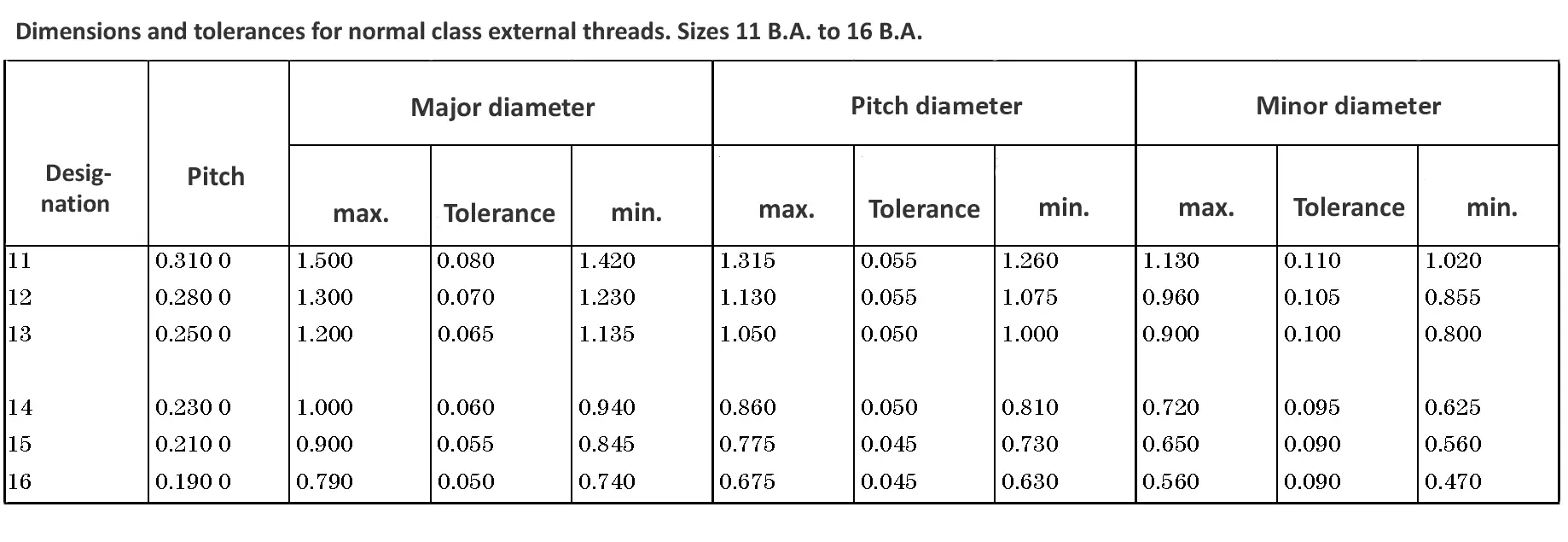
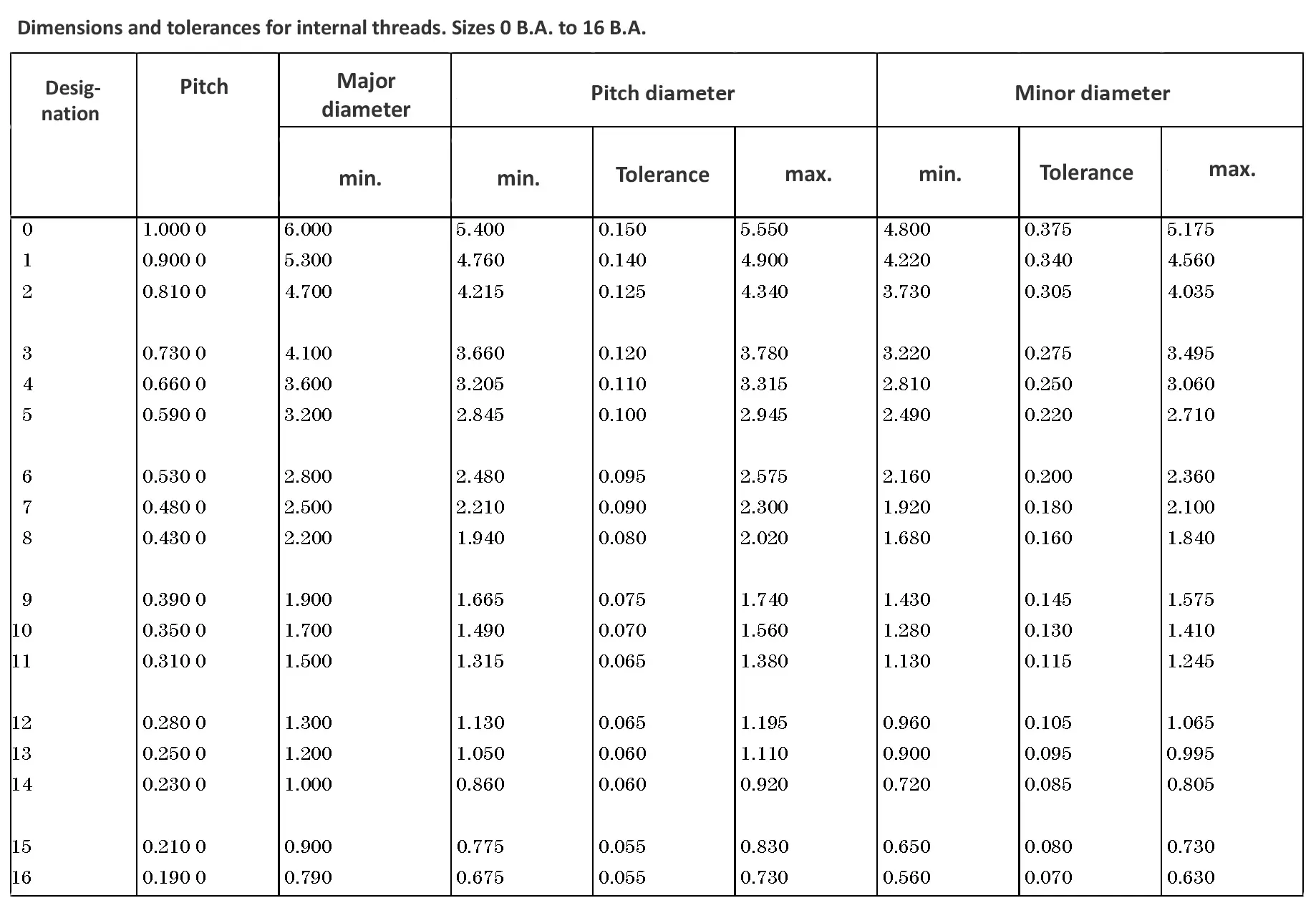
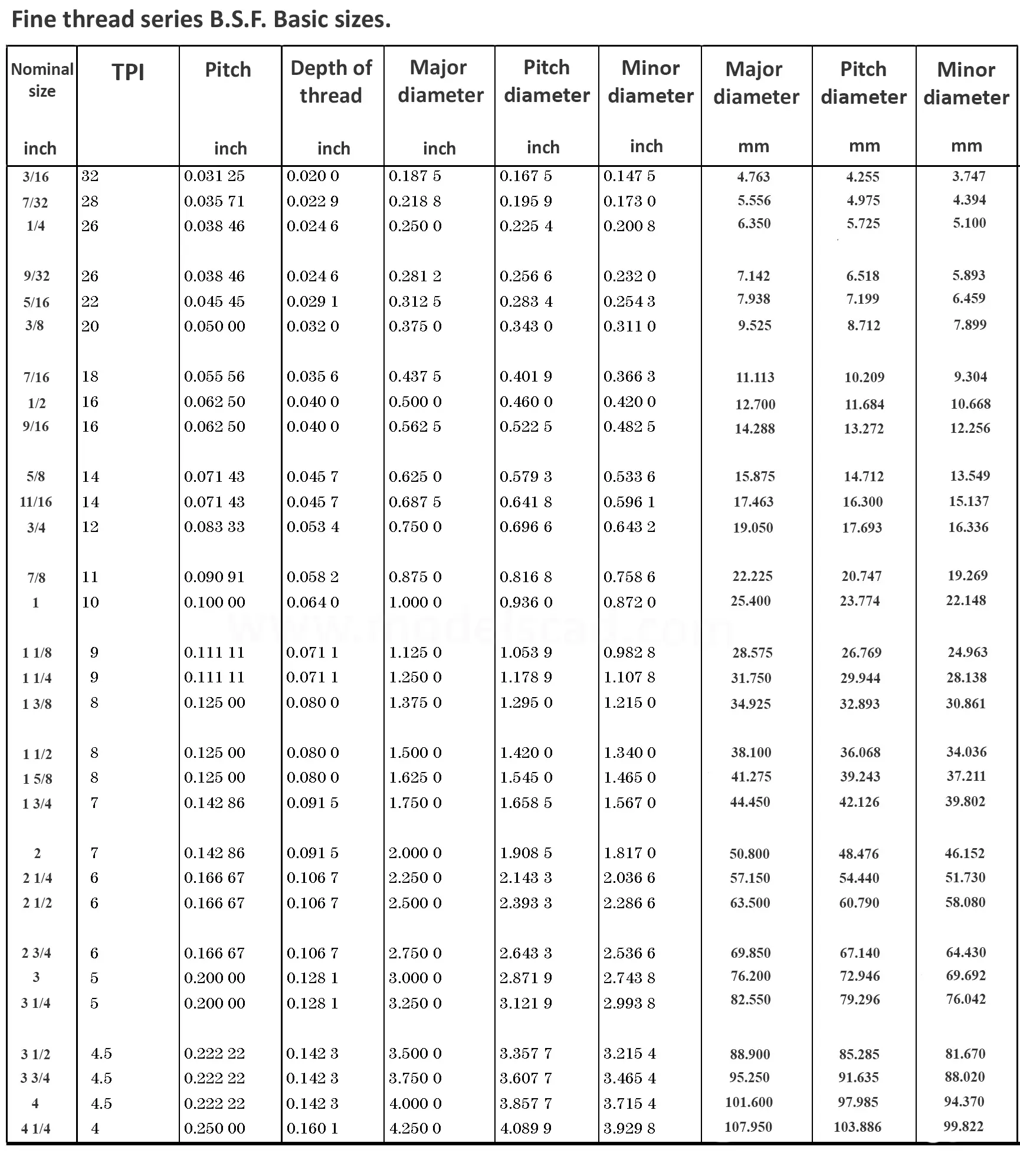
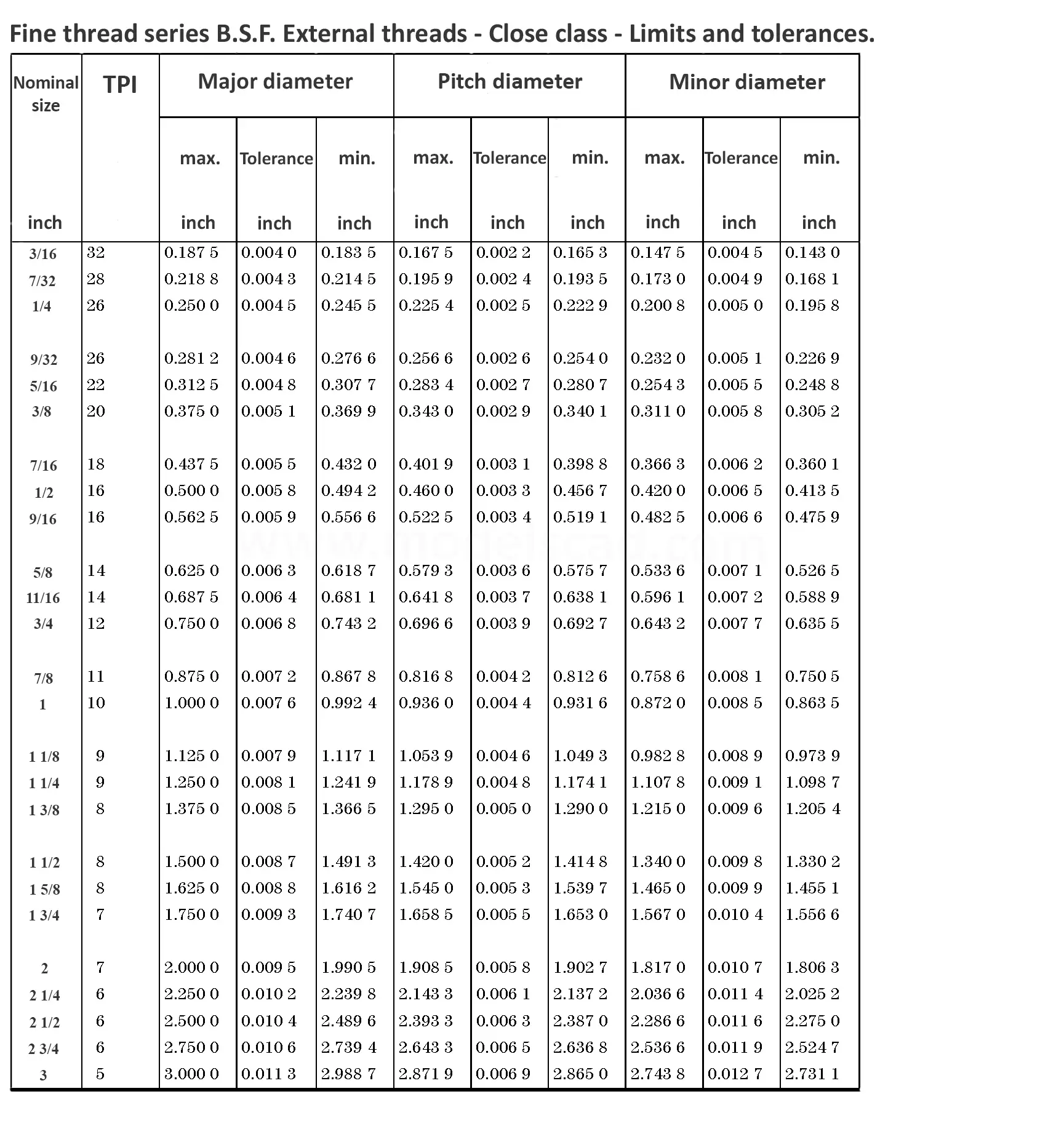
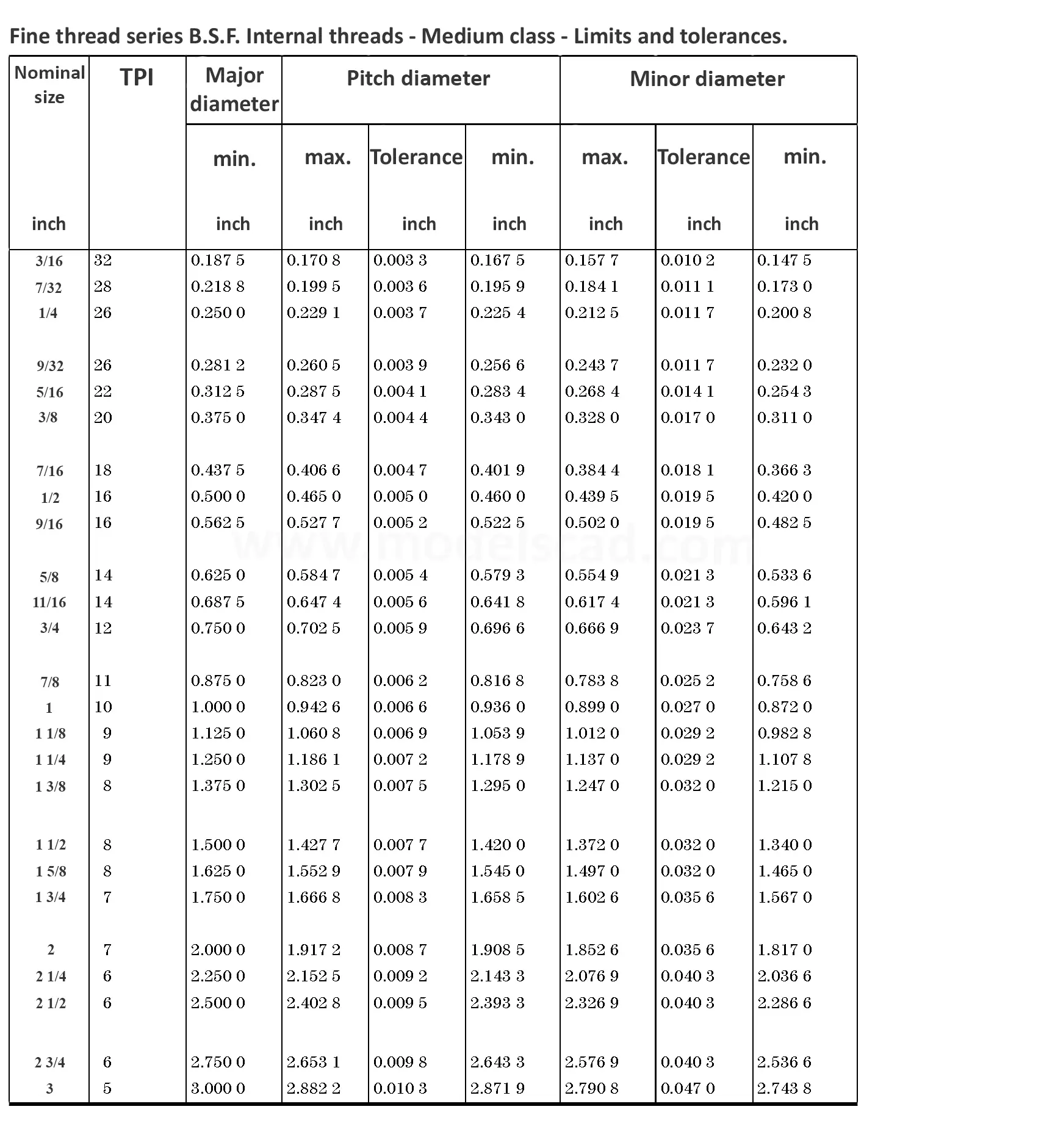
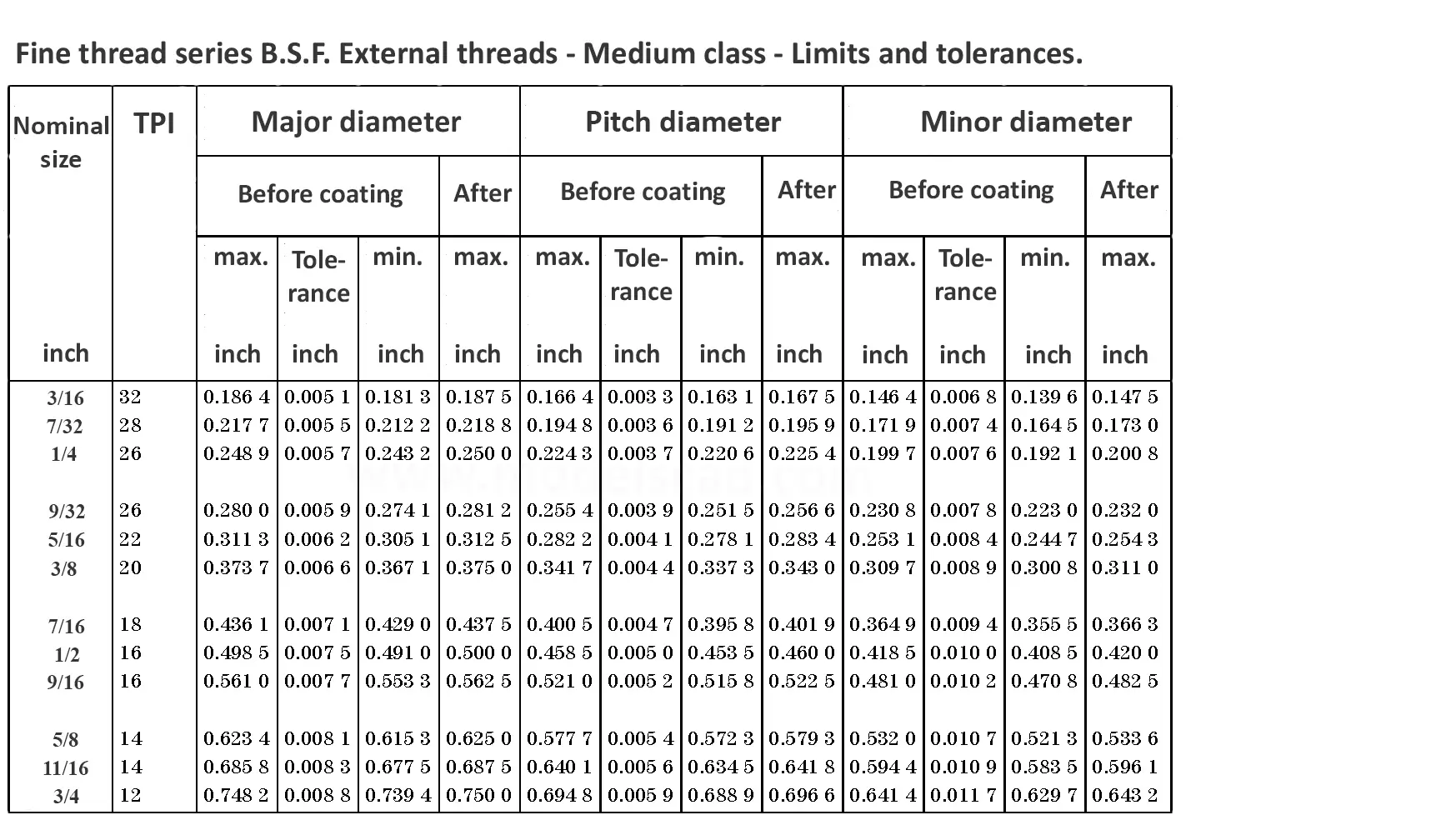
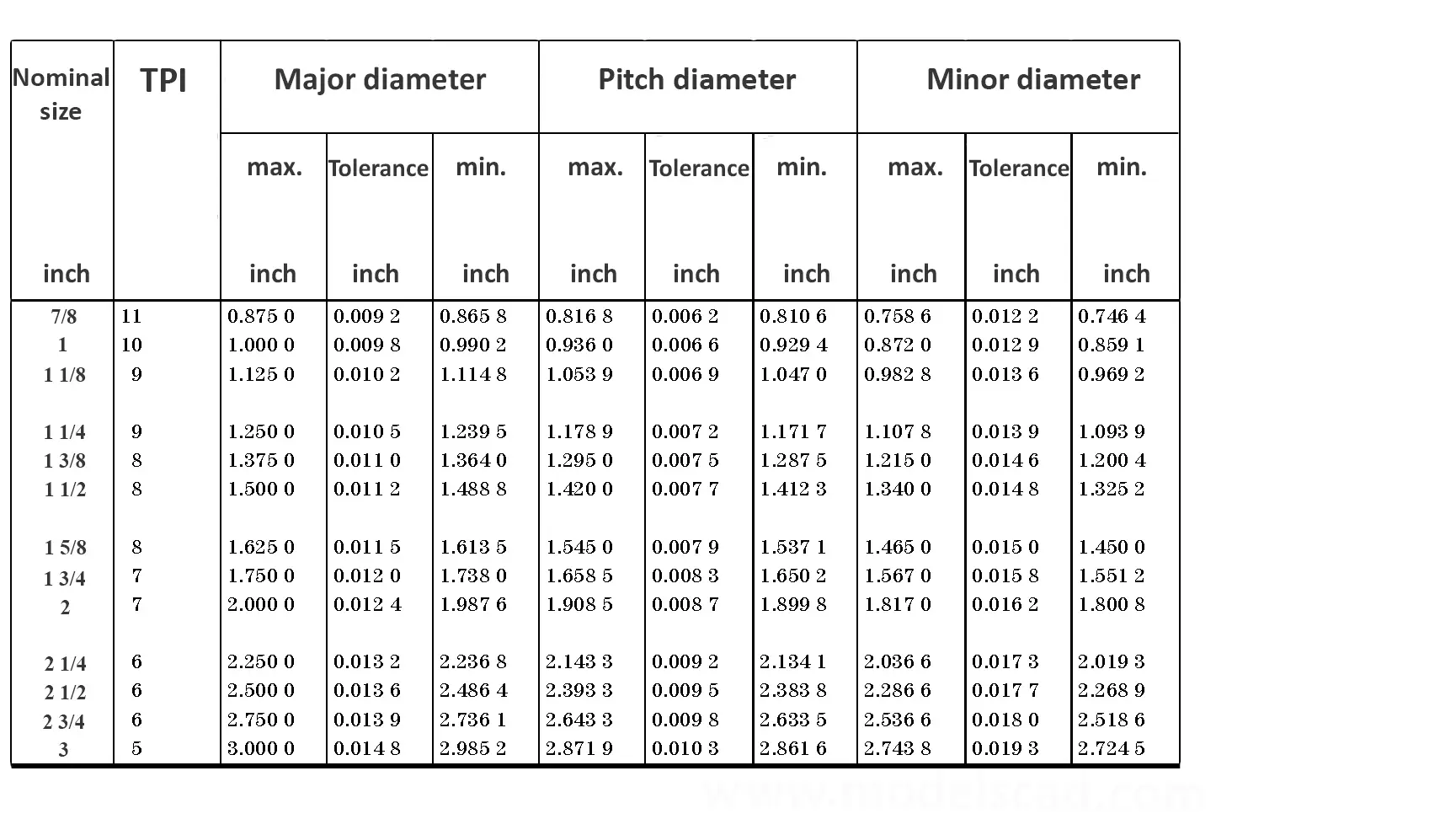
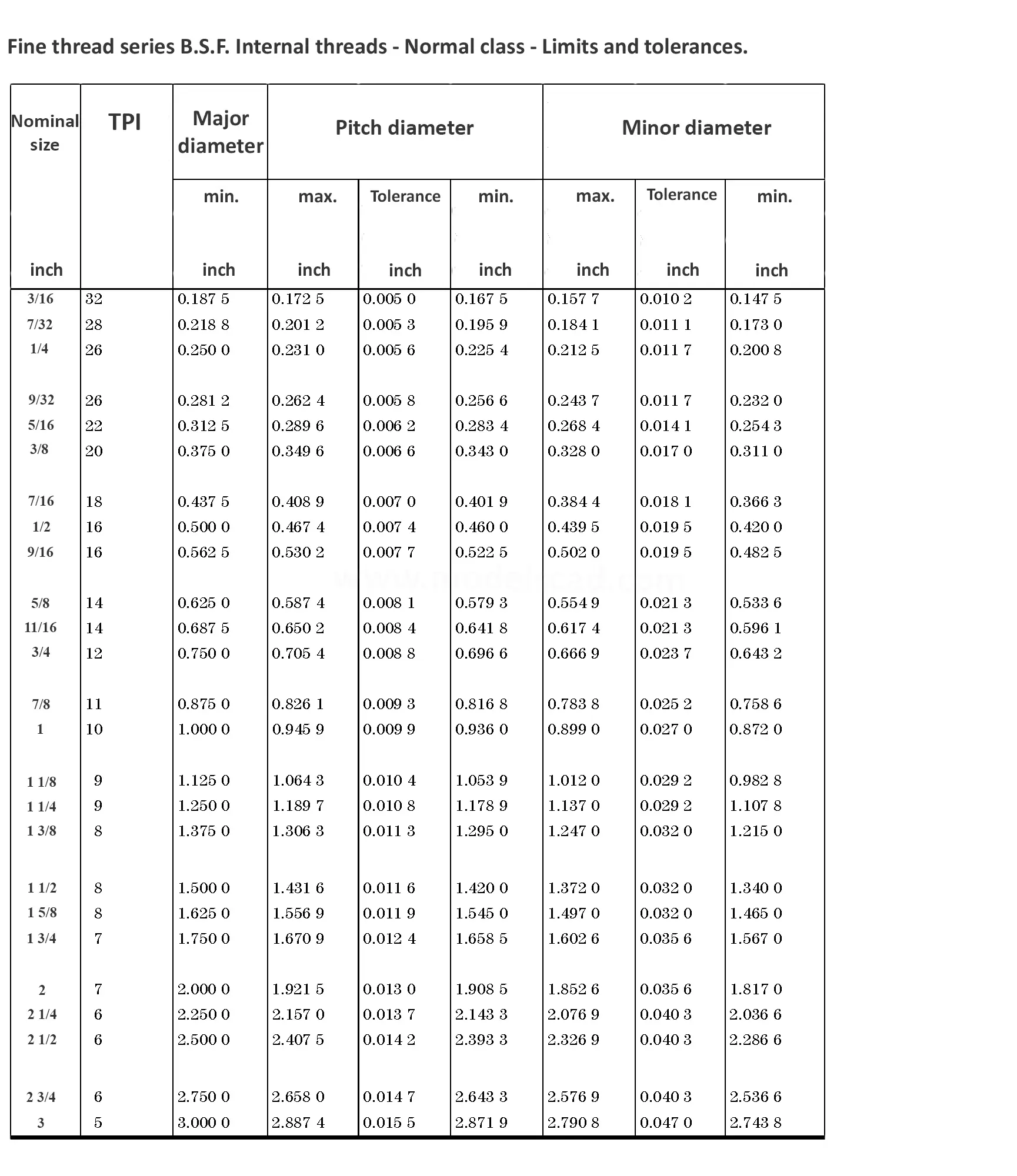
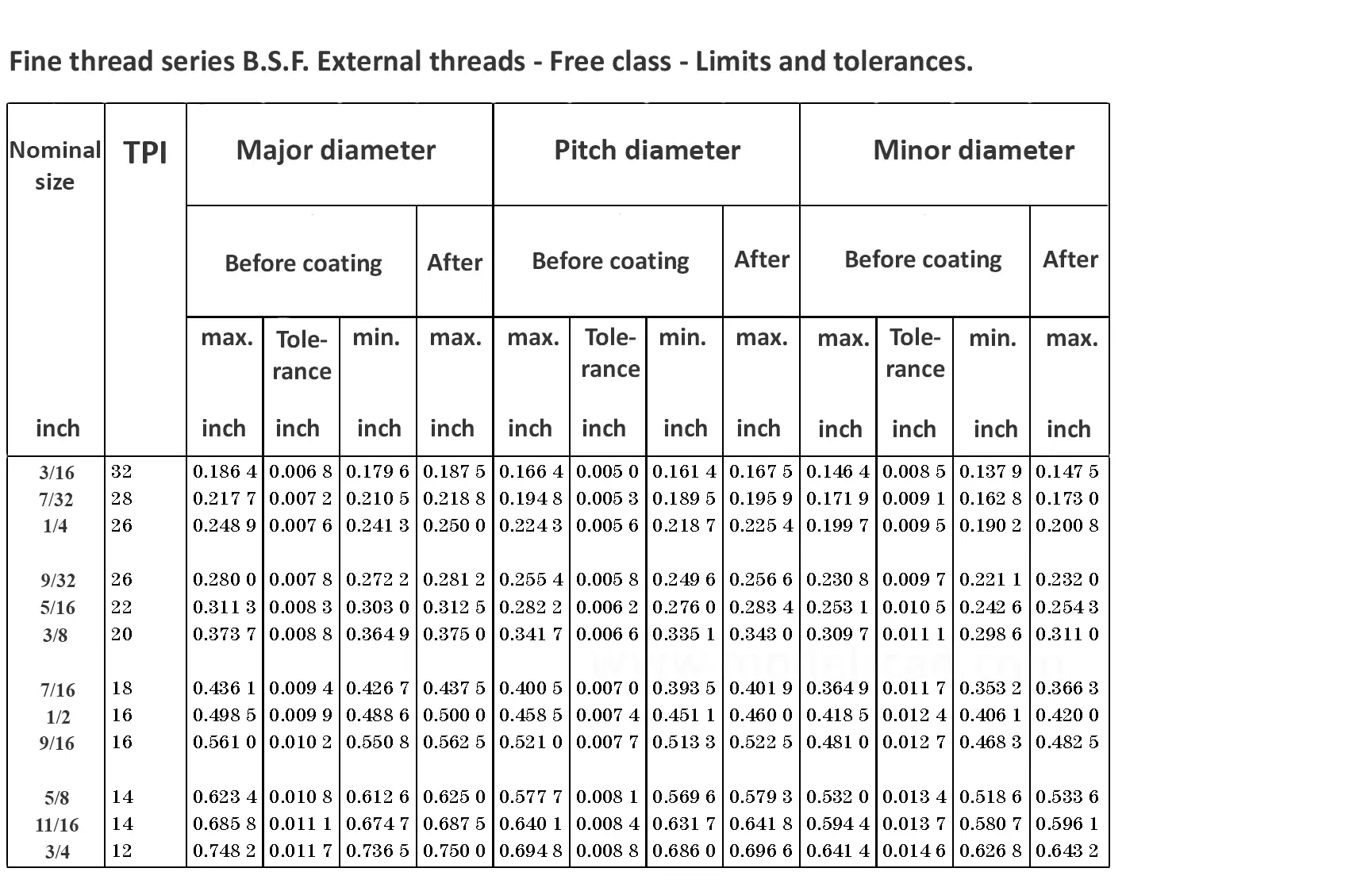
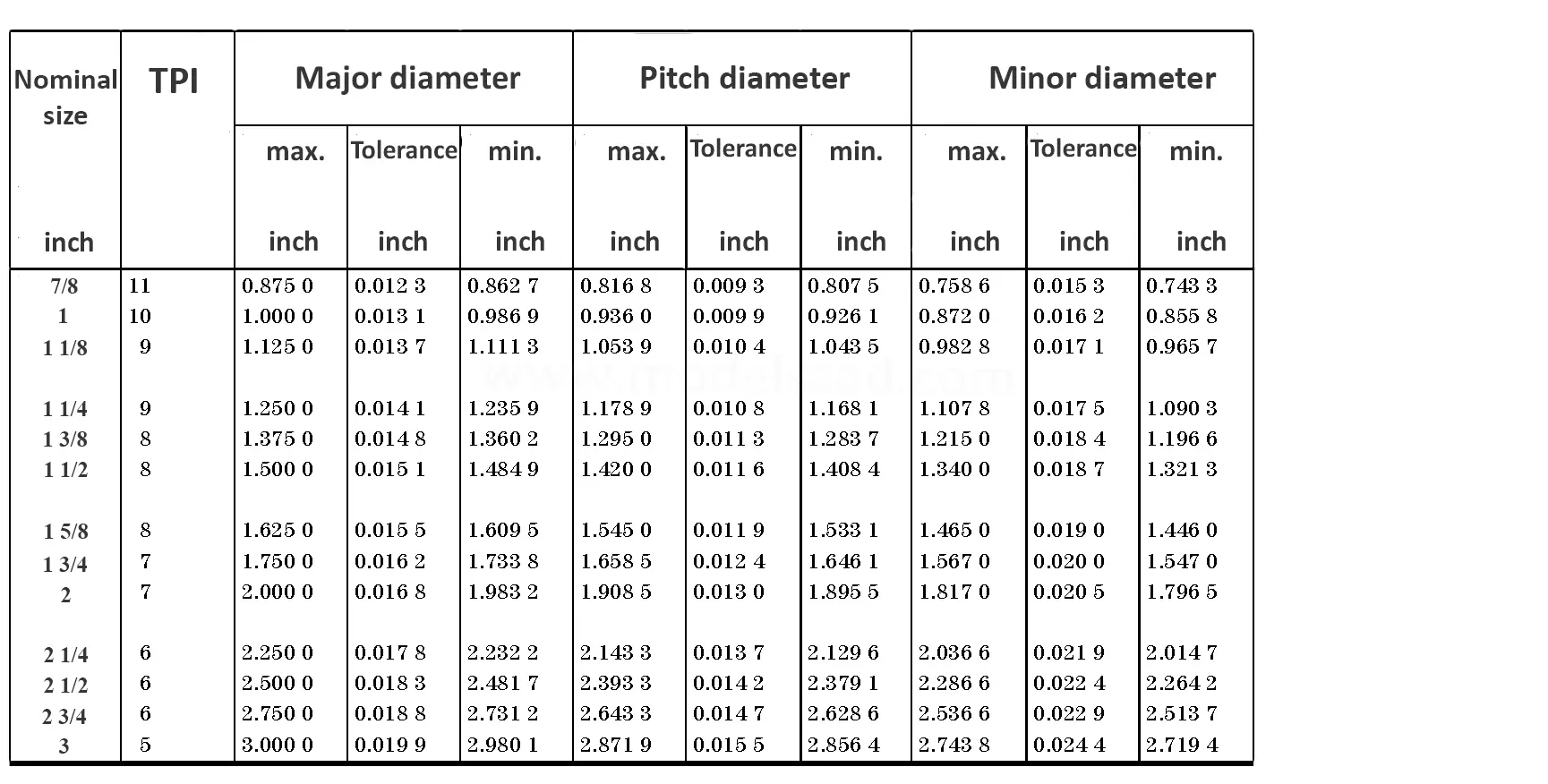
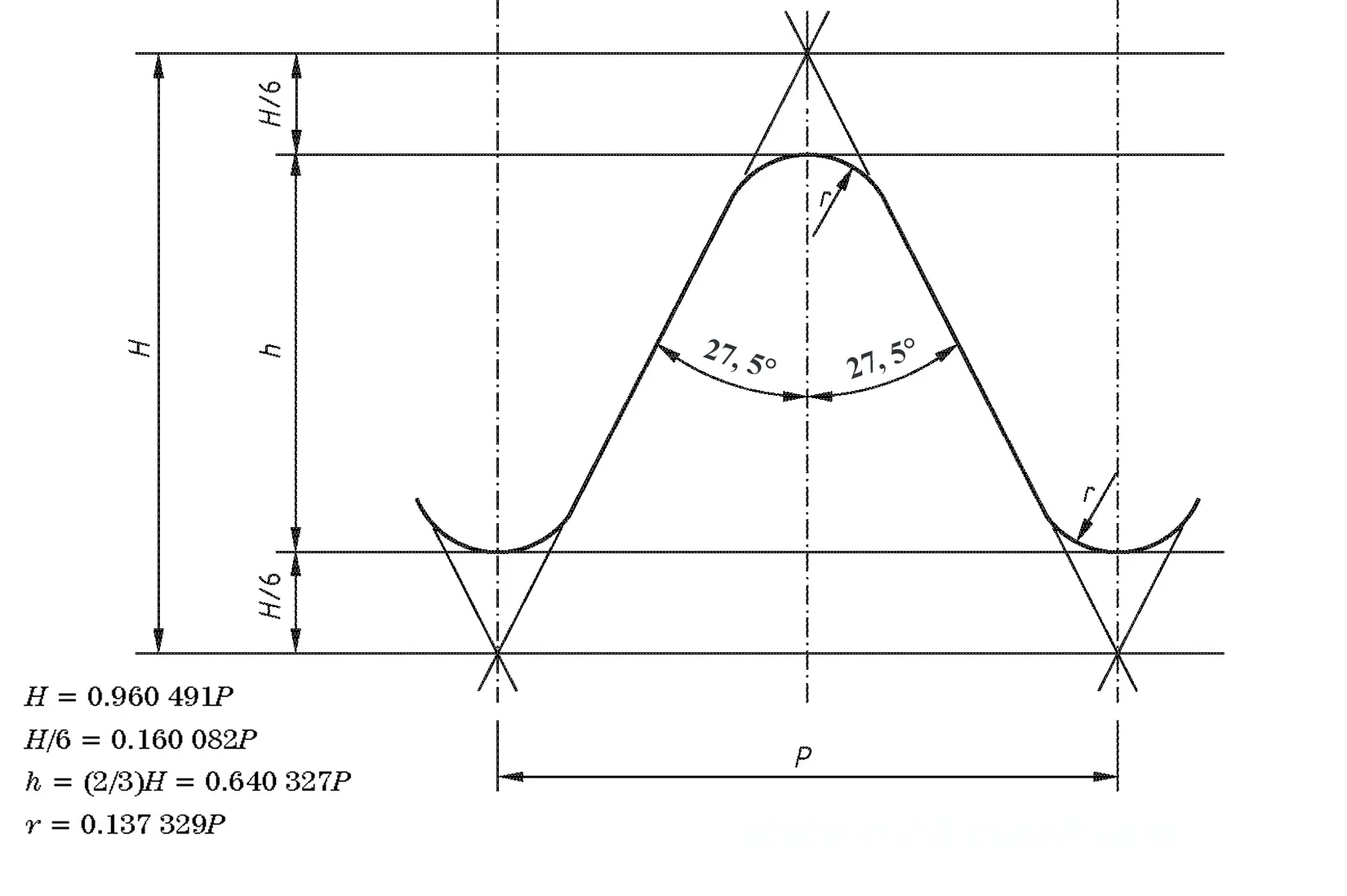
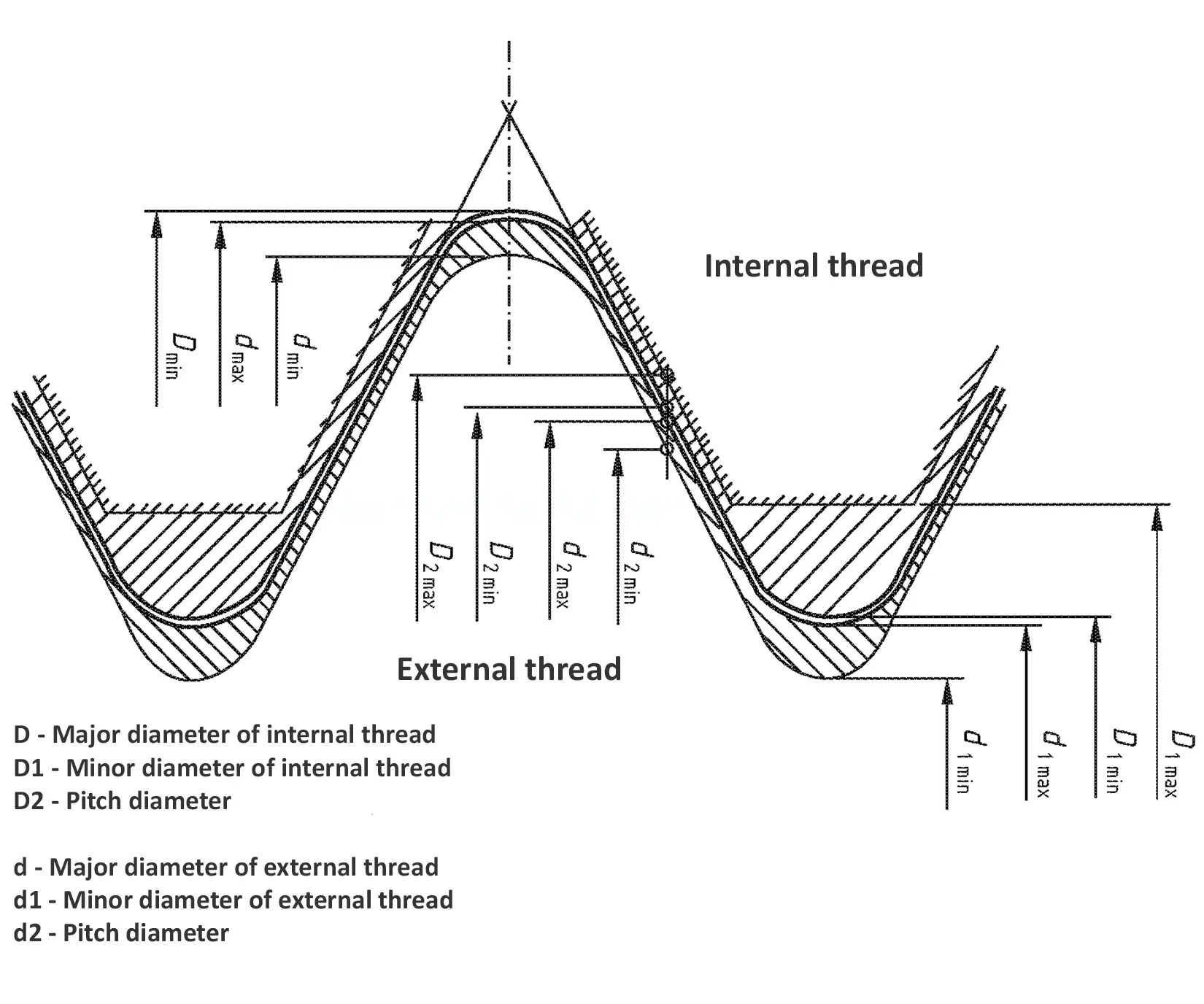
This British standard includes tables of basic sizes, limits and tolerances for British Standard Fine (B.S.F.) screw threads. In addition it provides a selected thread series of recommended diameter and pitch combinations for use in applications where the standard fine (B.S.F.) series have insufficiently fine pitches. The flank angle is 55°.
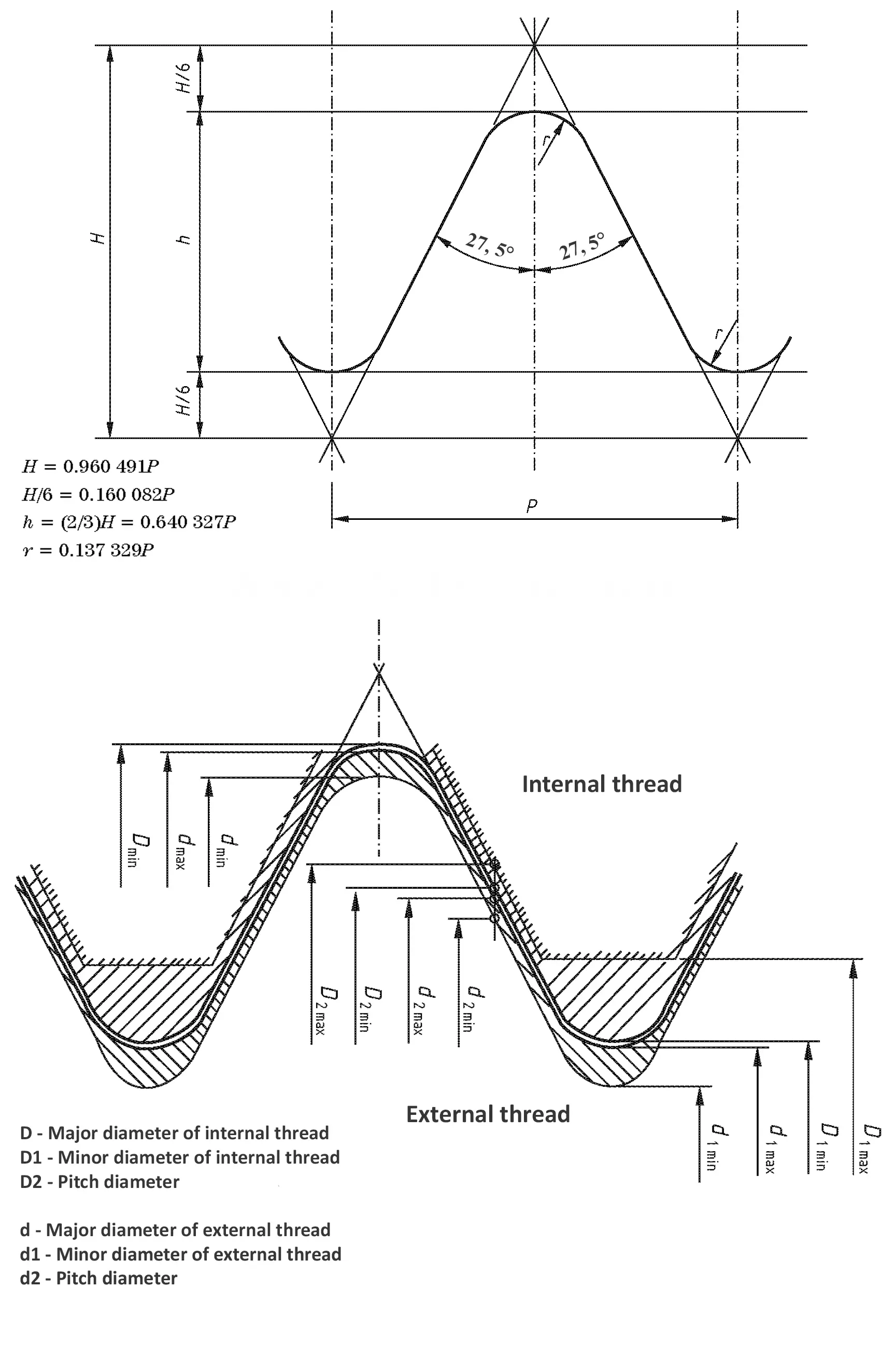
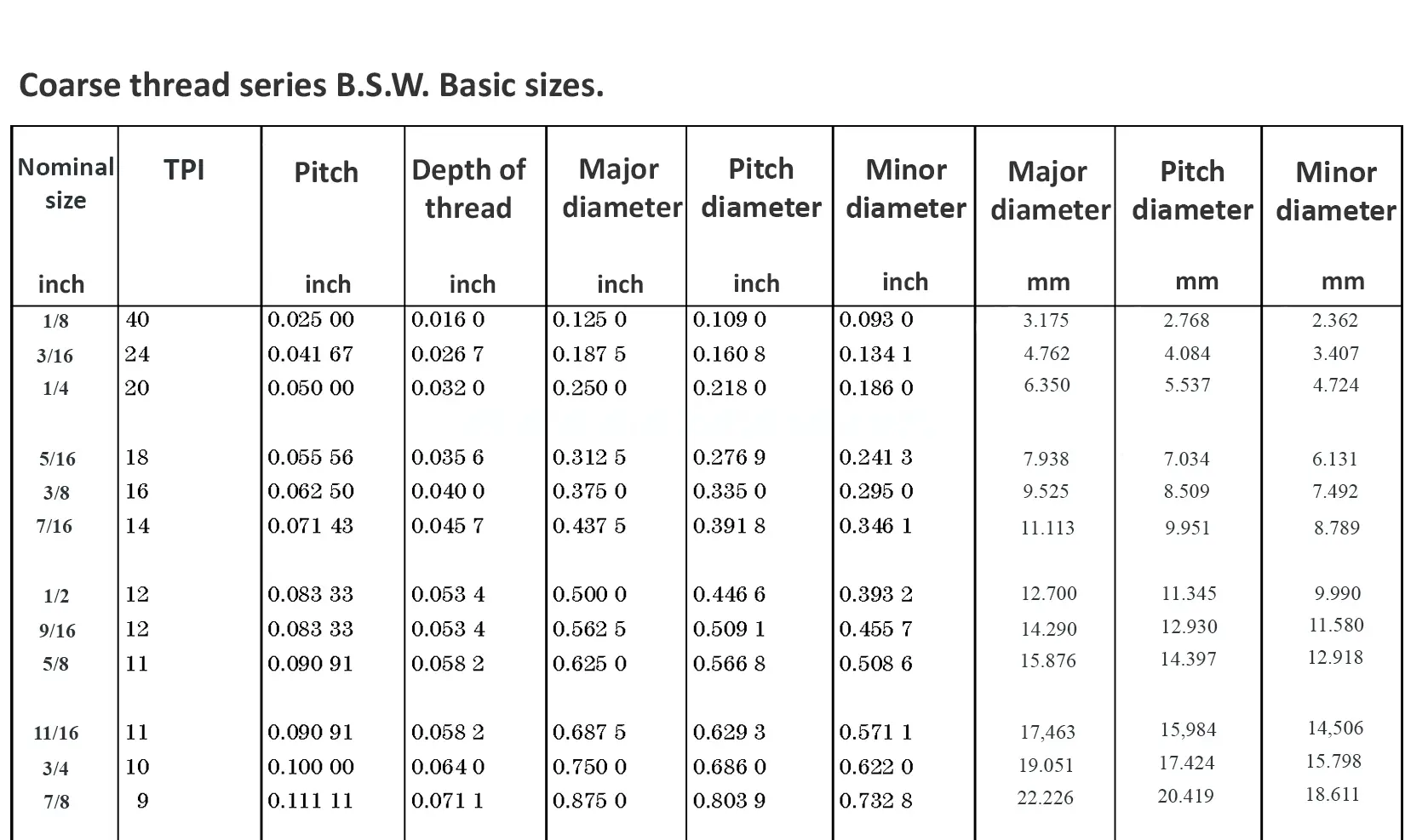
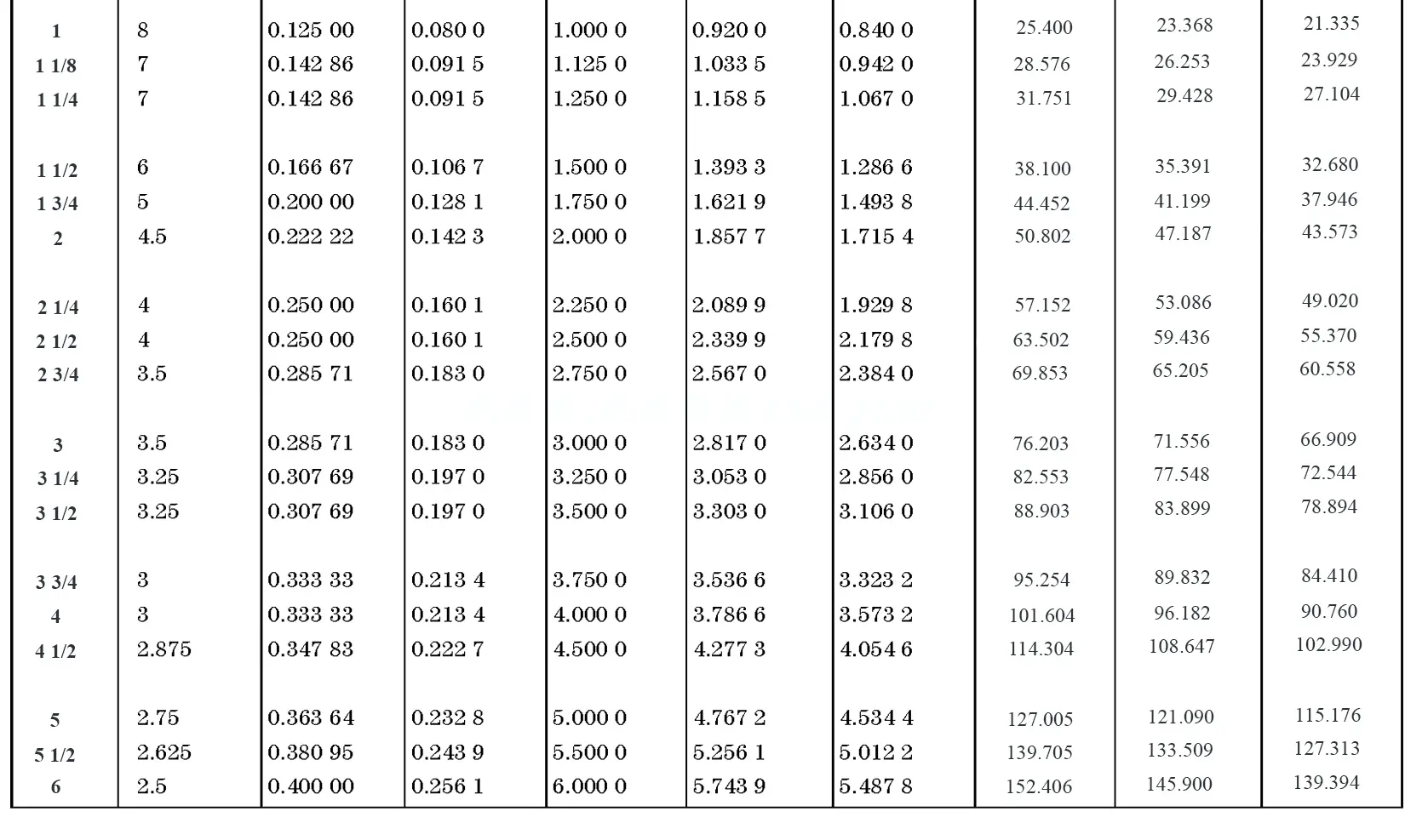
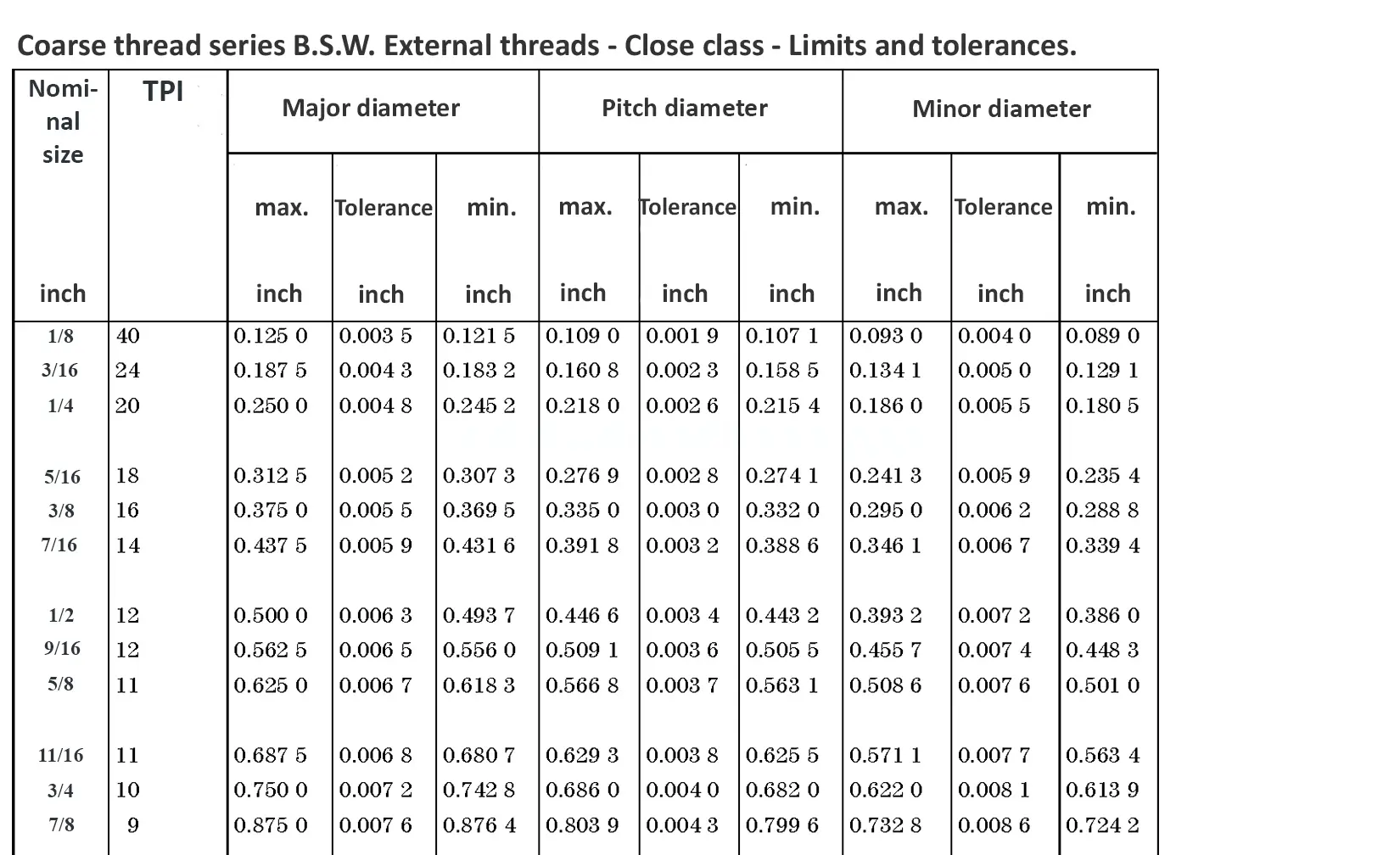
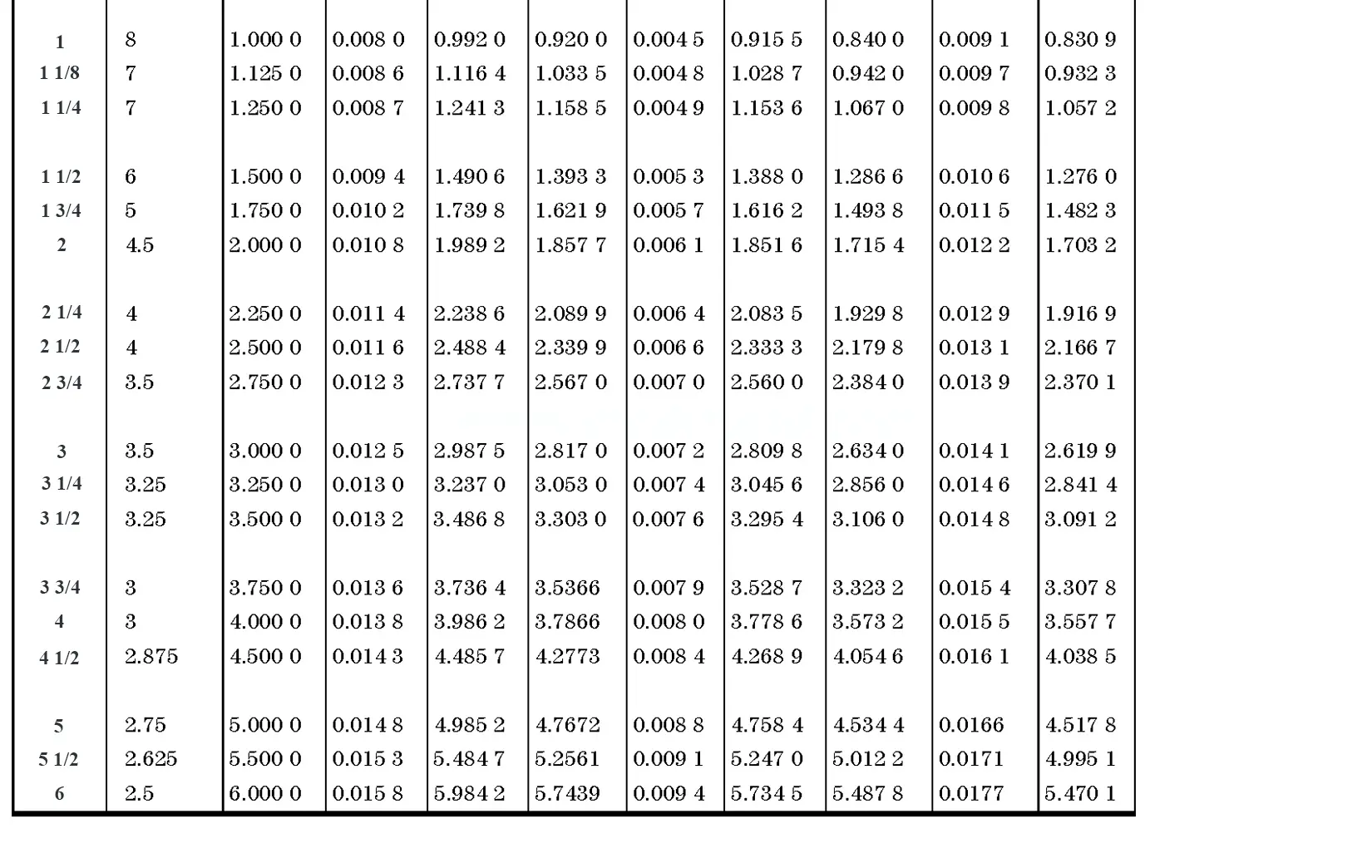
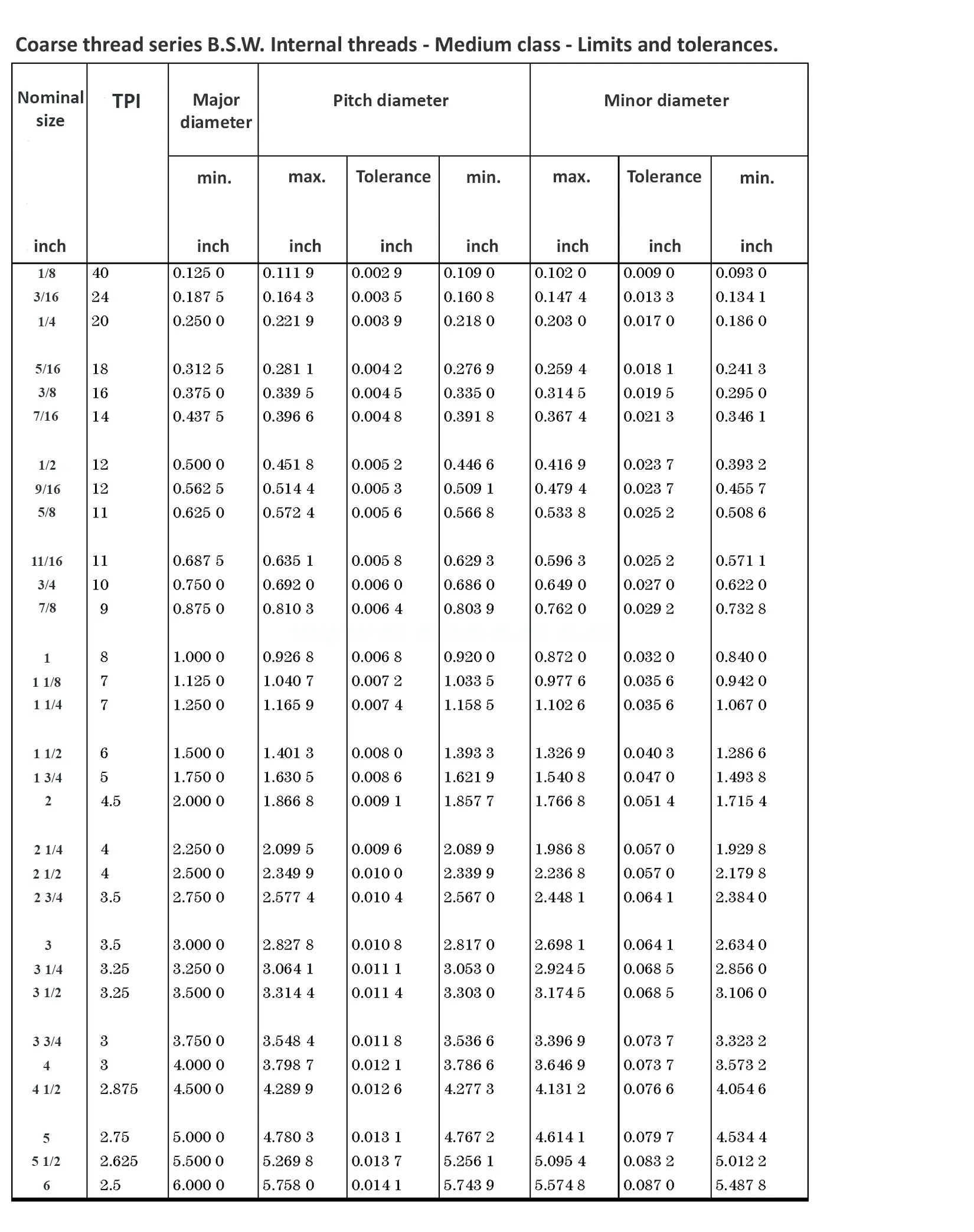
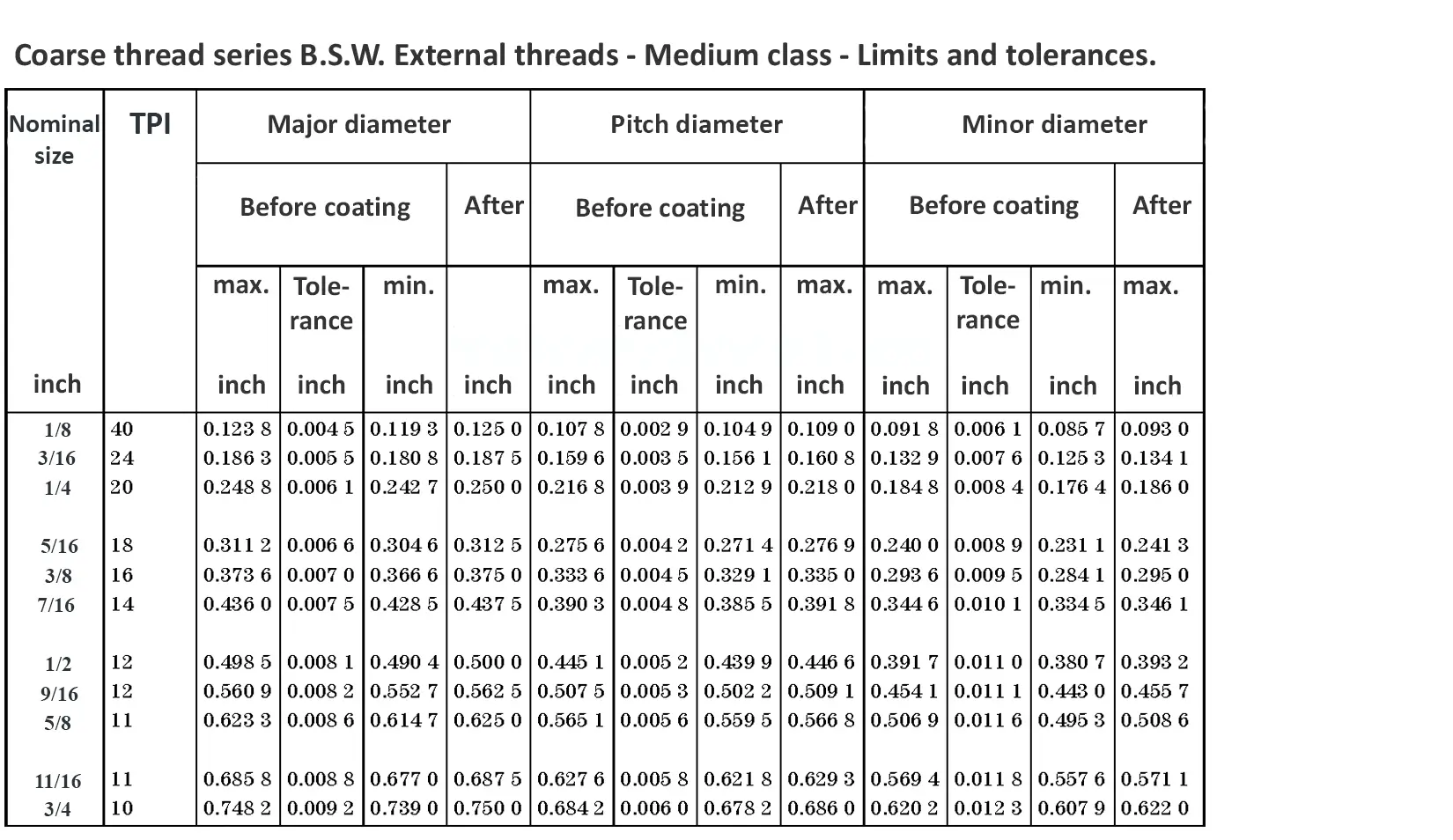
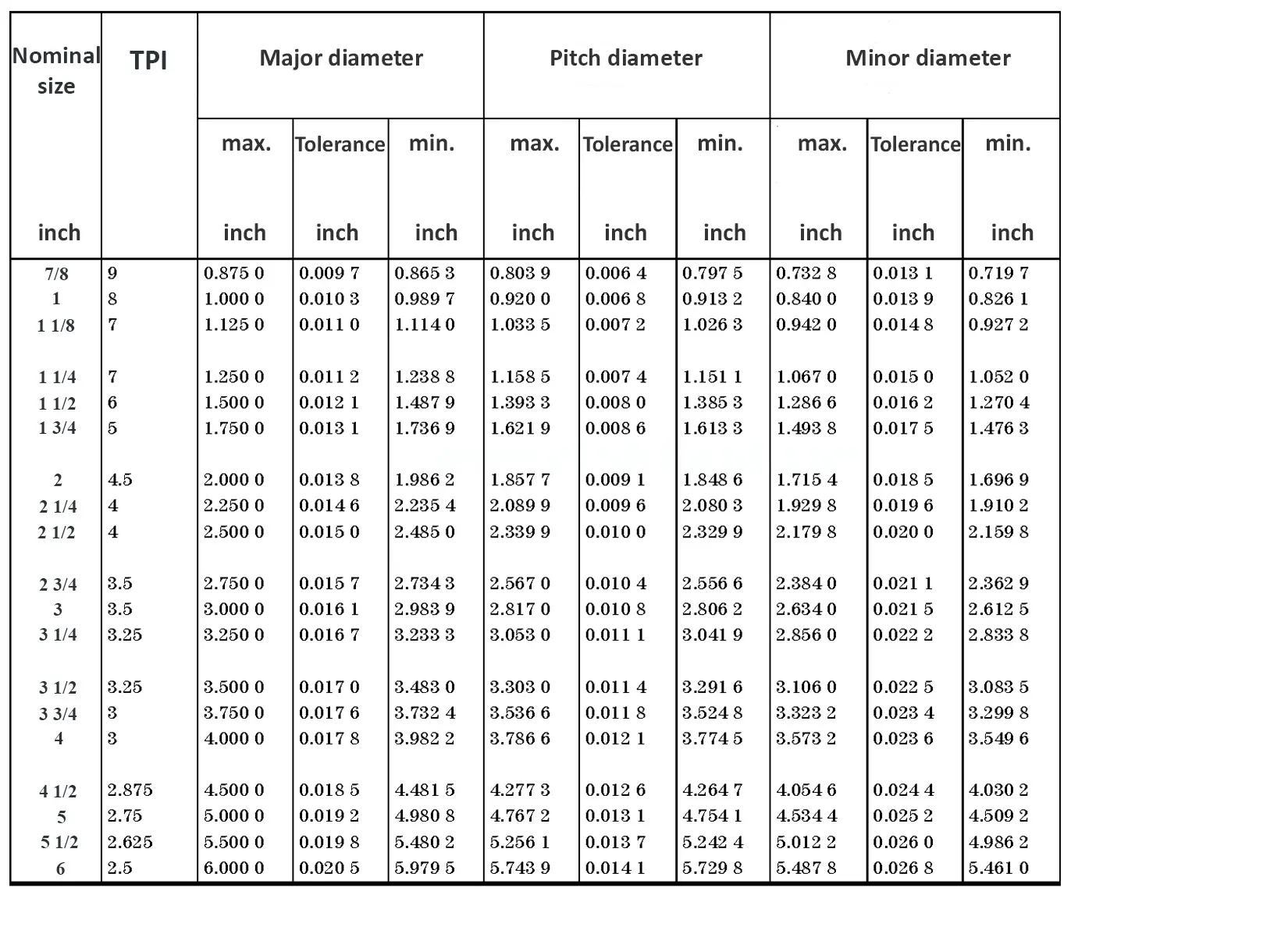
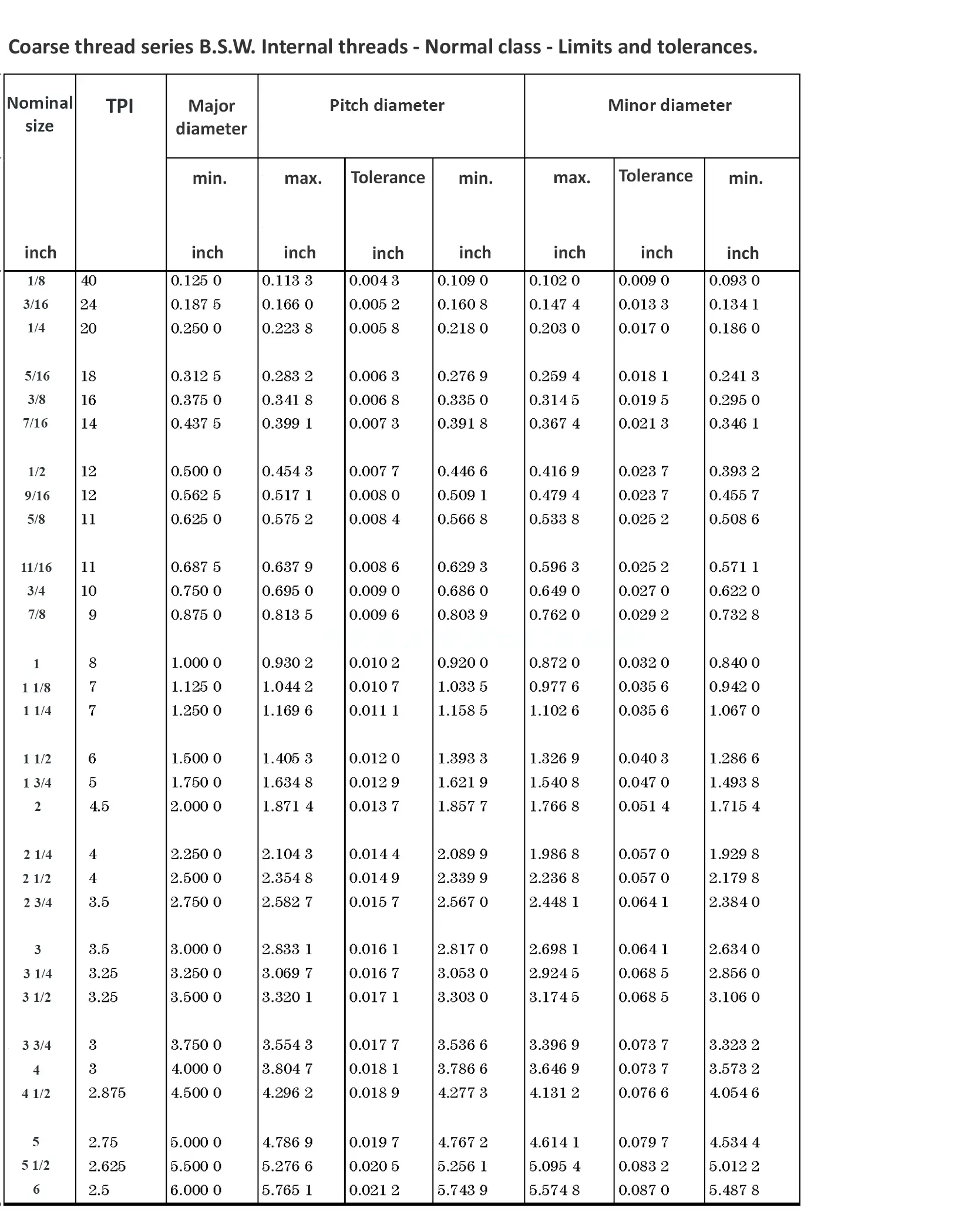
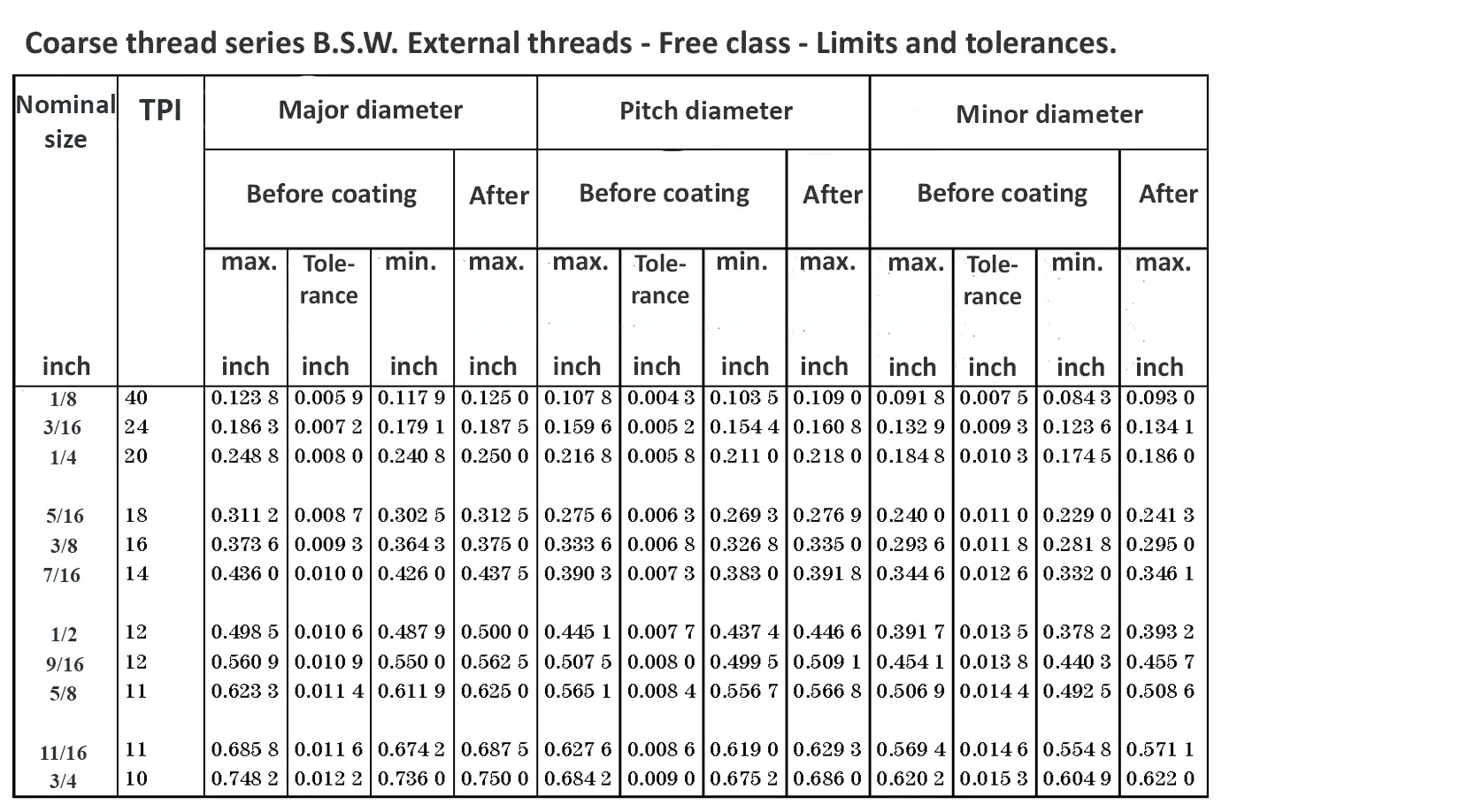
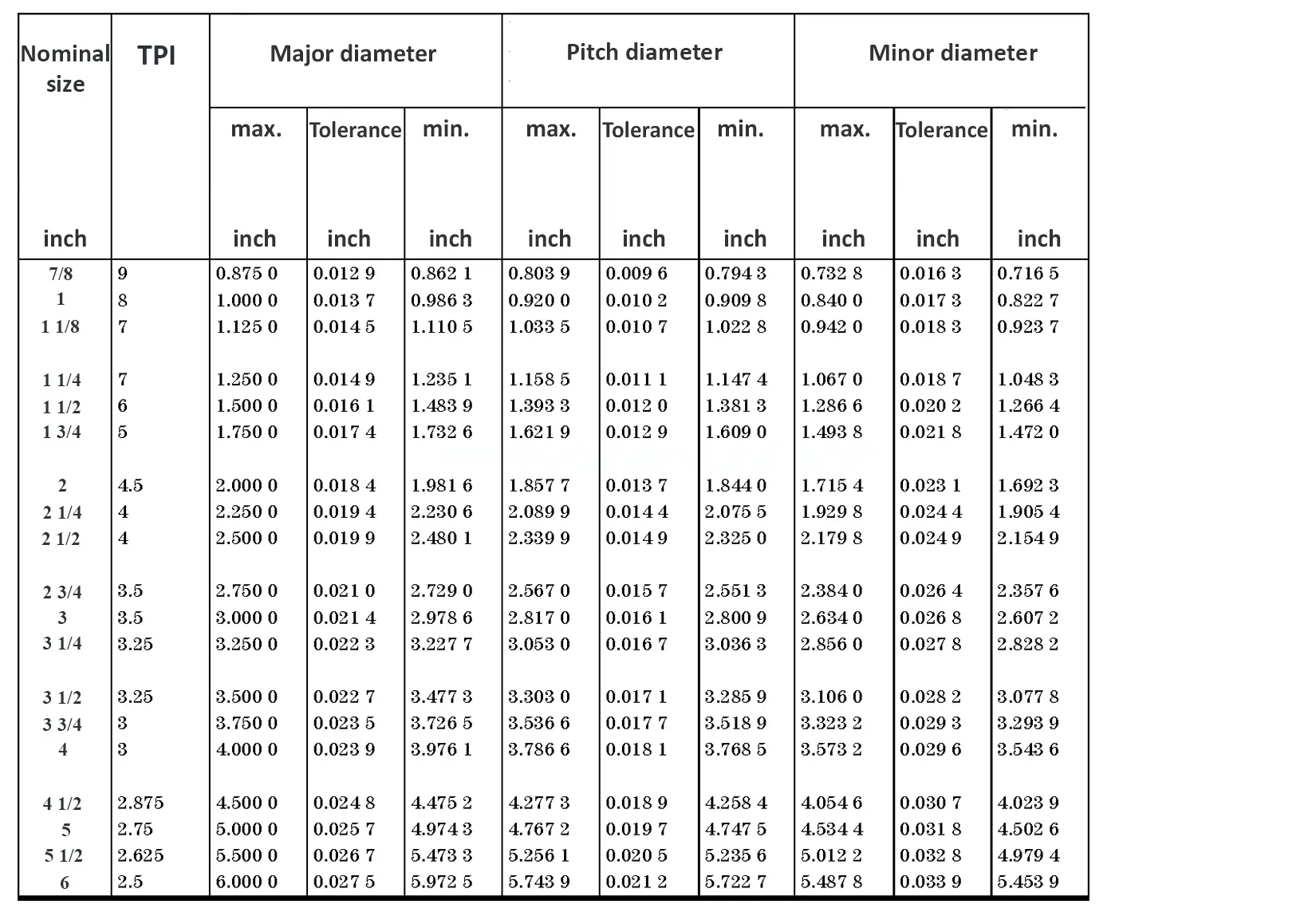
This British standard includes tables of basic sizes, limits and tolerances for British Standard Whitworth (B.S.W.) screw threads. The flank angle is 55°.
DIN standards
It is used in fire extinguishing systems and in the food industry, the profile angle is 30°.
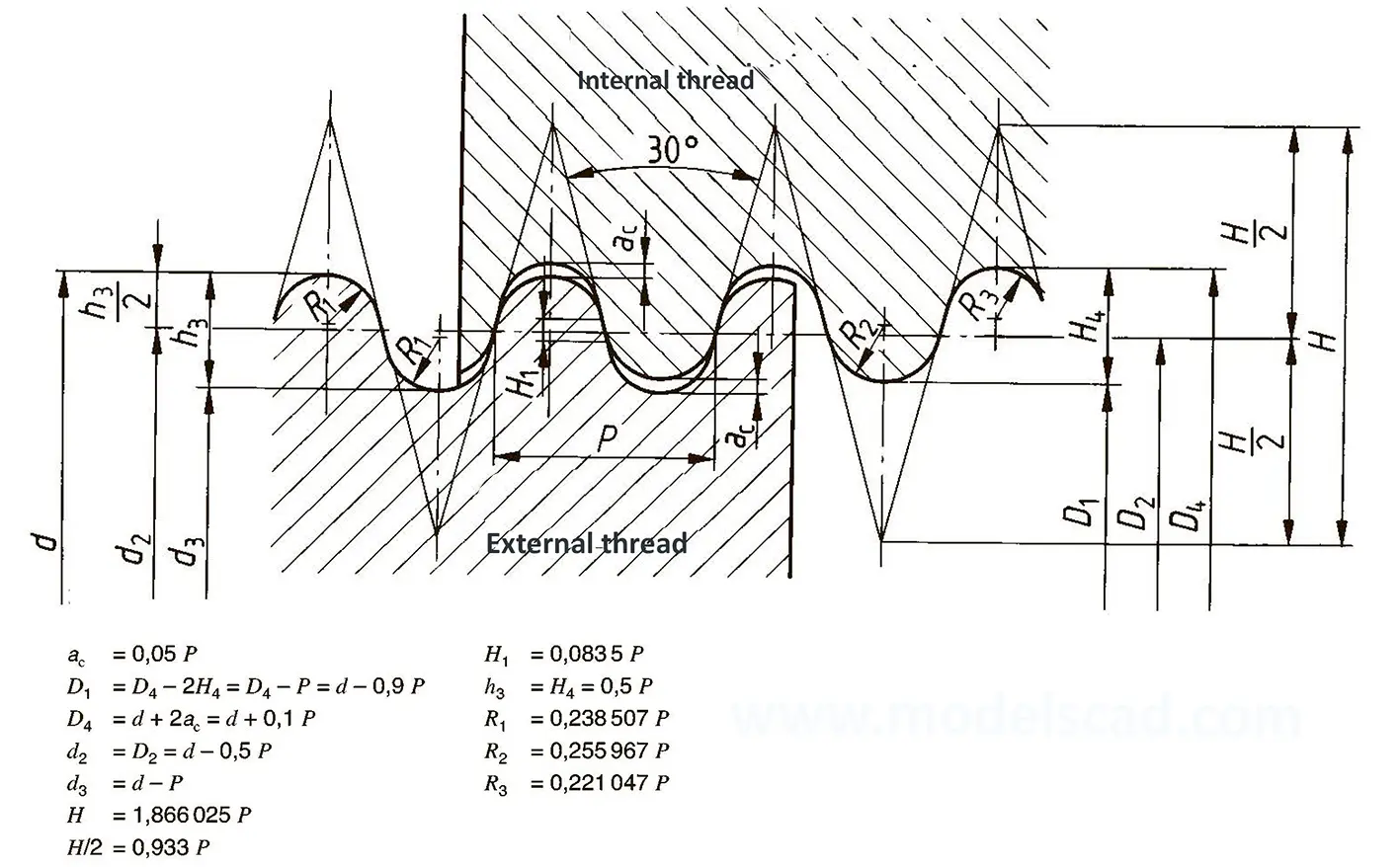
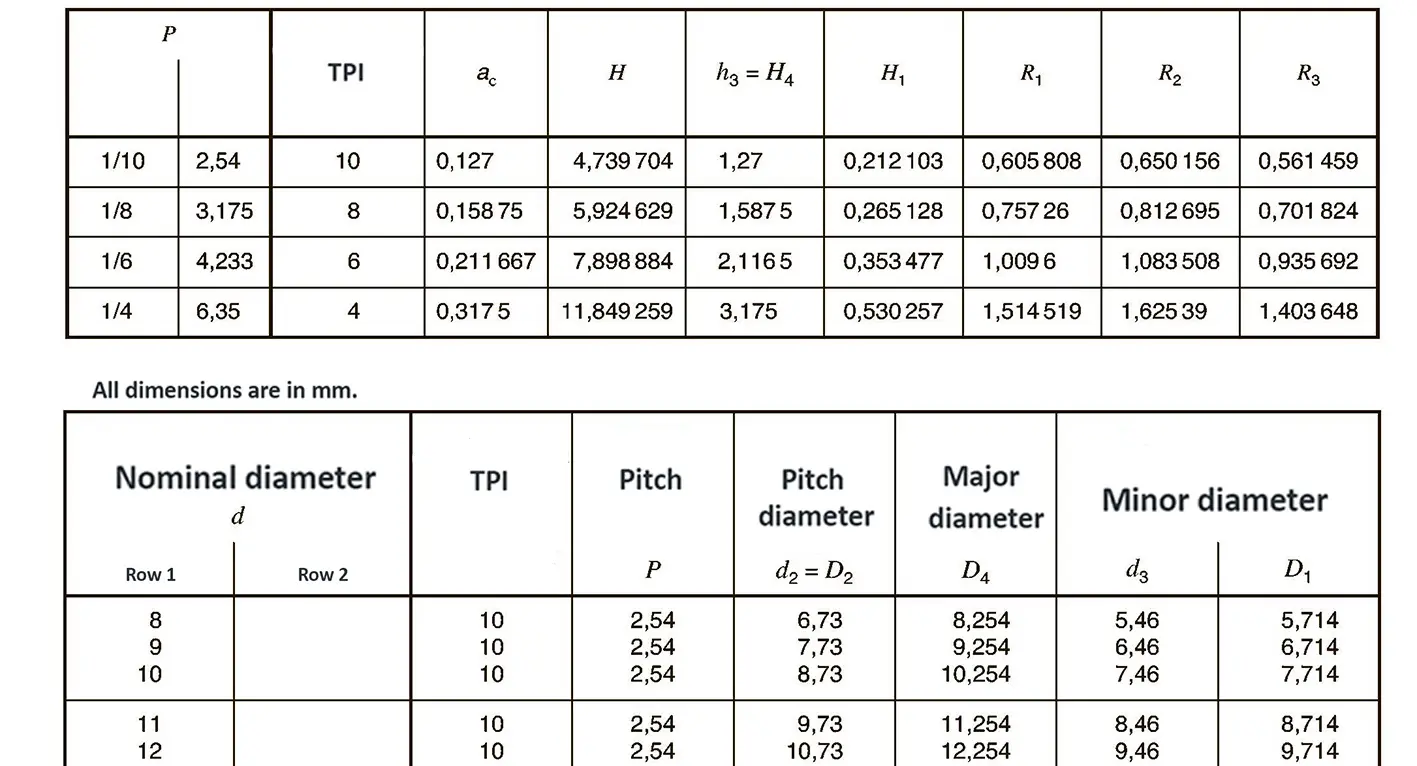
Used in large valves or, for example, coupling spindles of railway carriages, the profile angle is 30°.
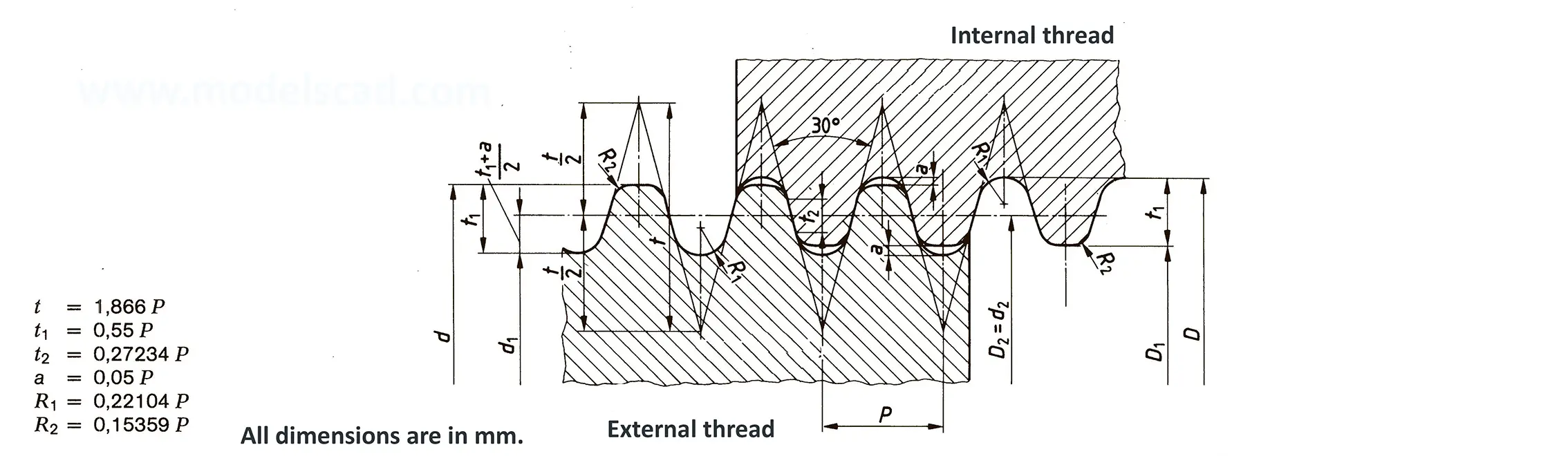
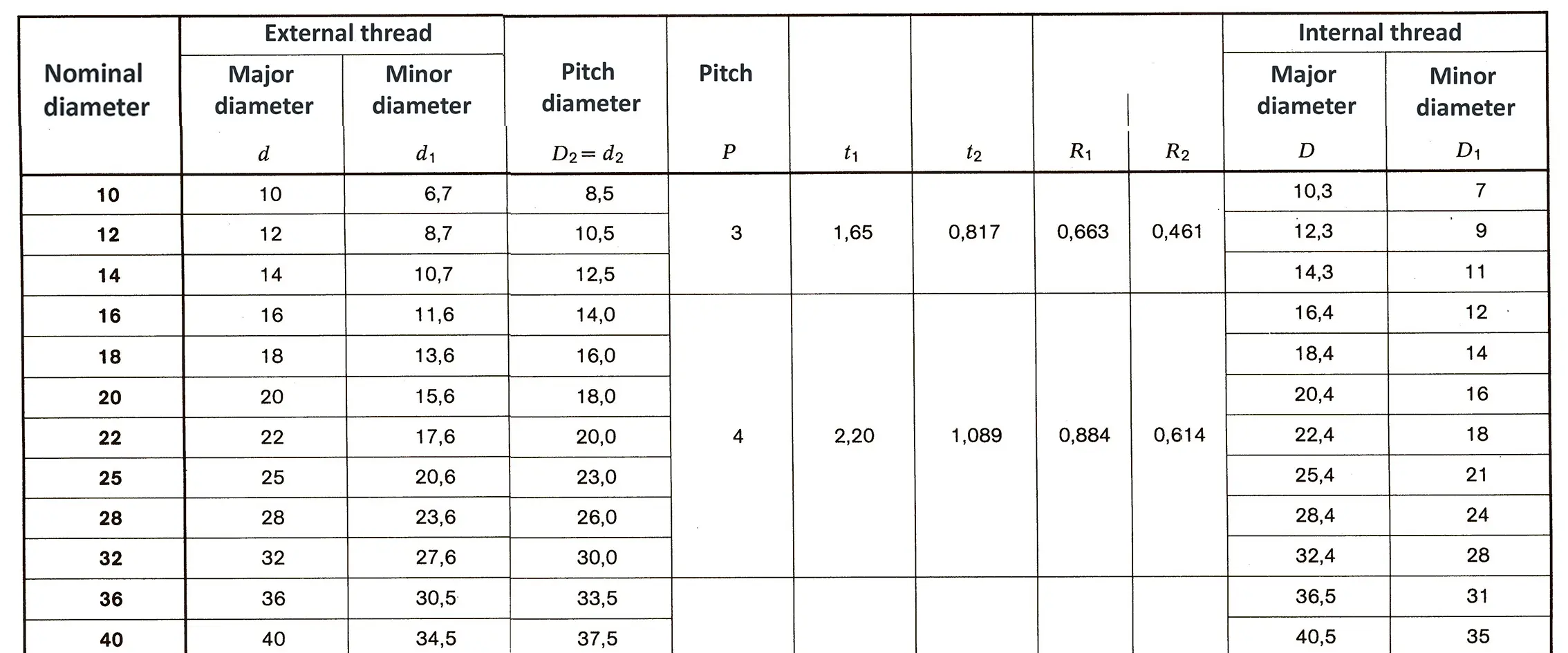
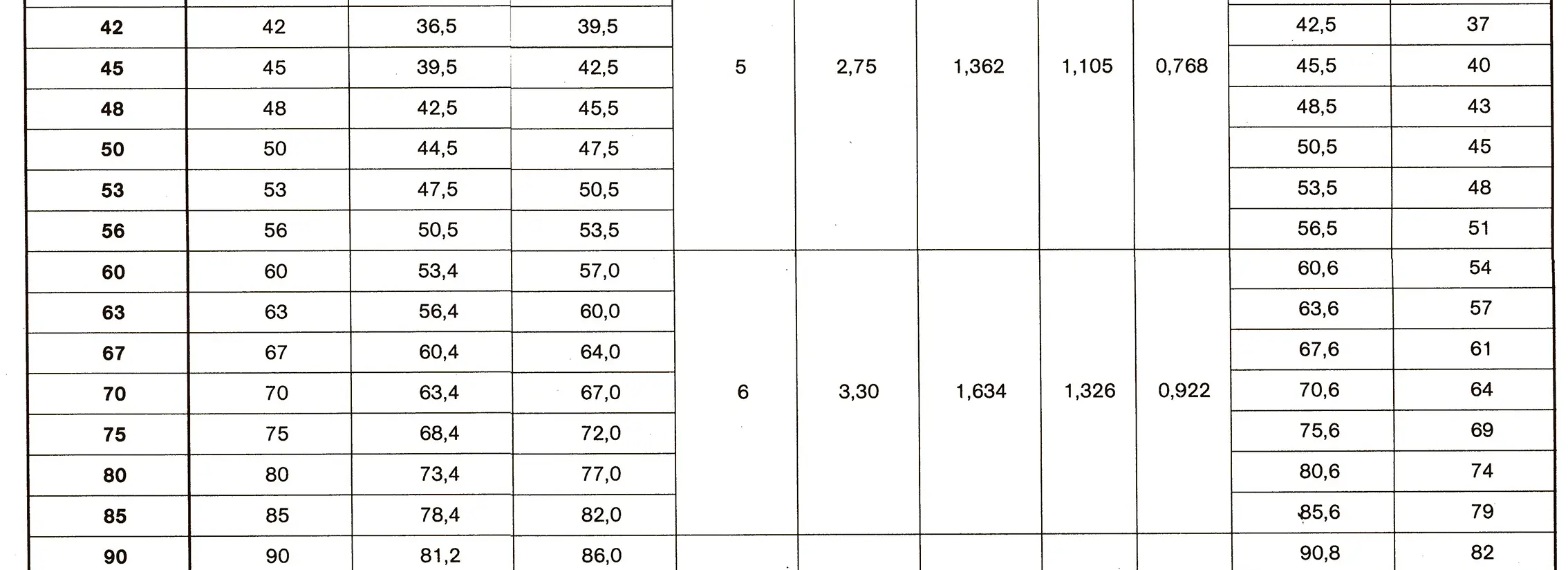
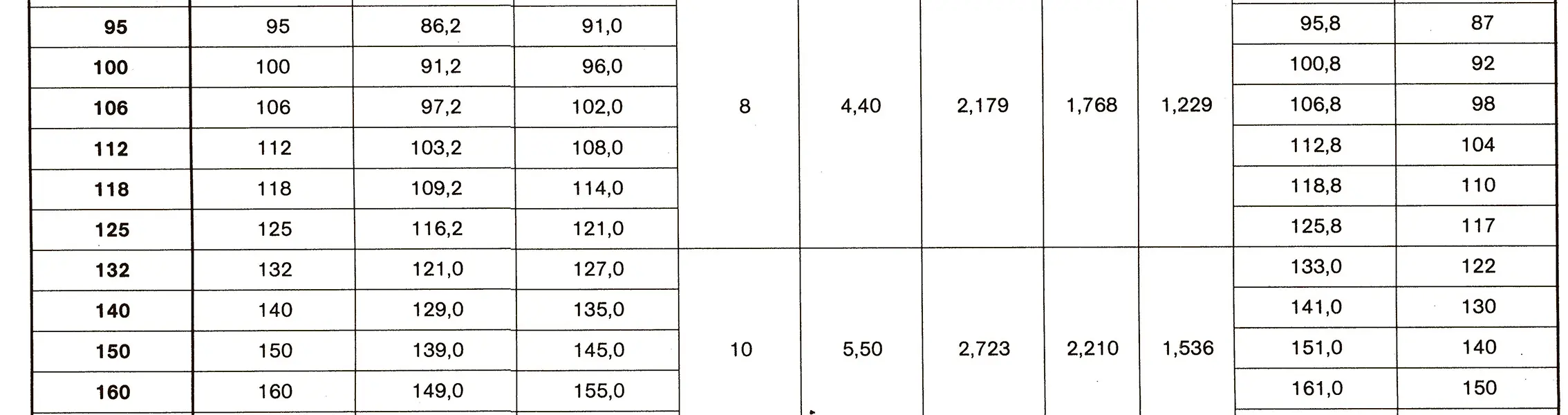
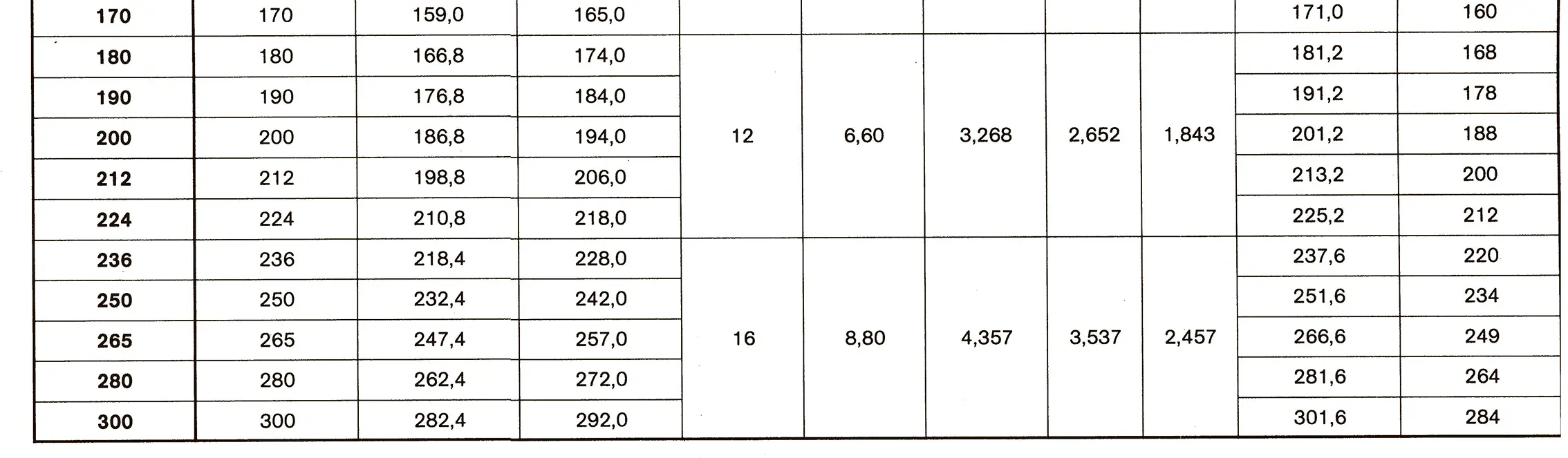
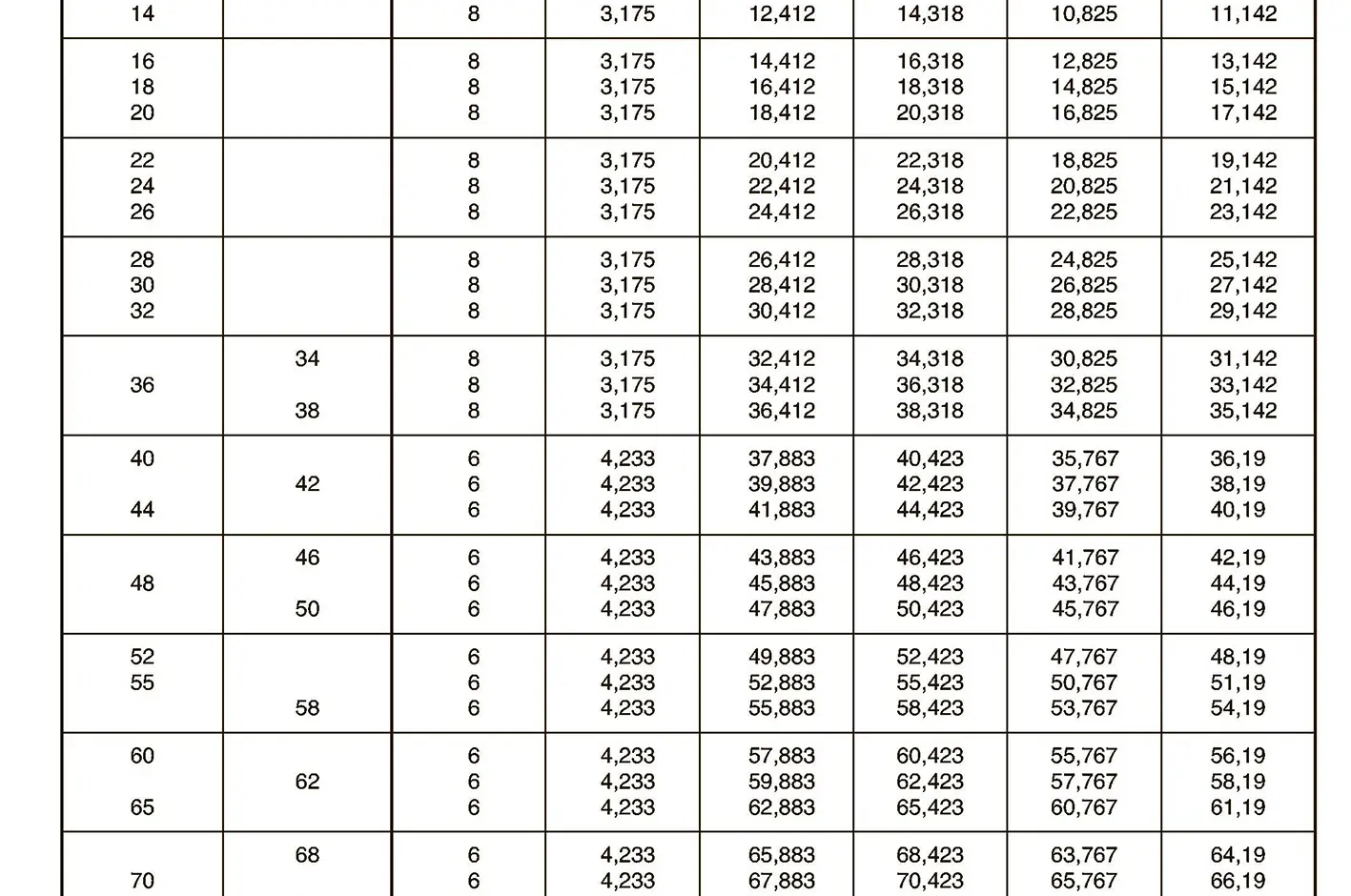
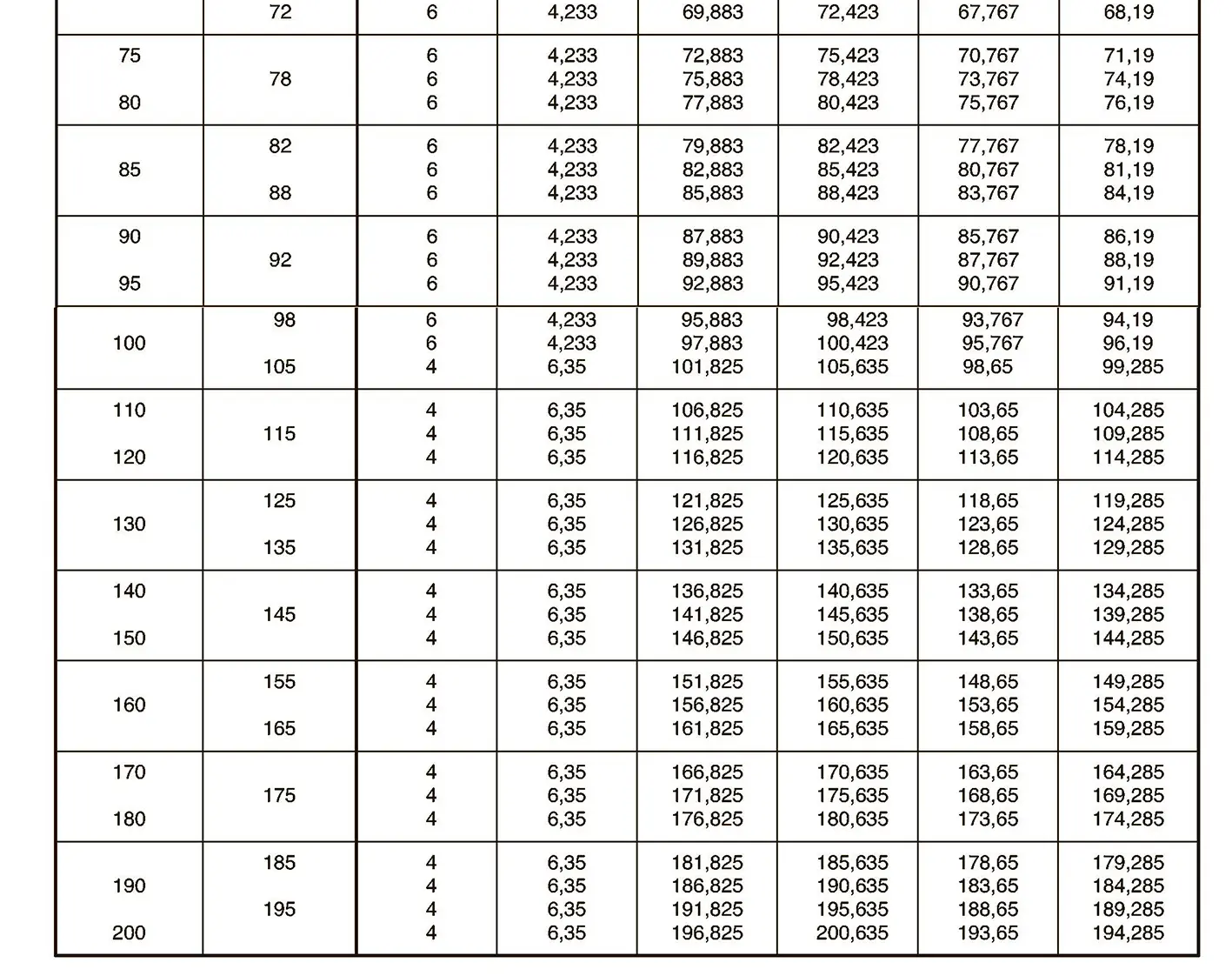
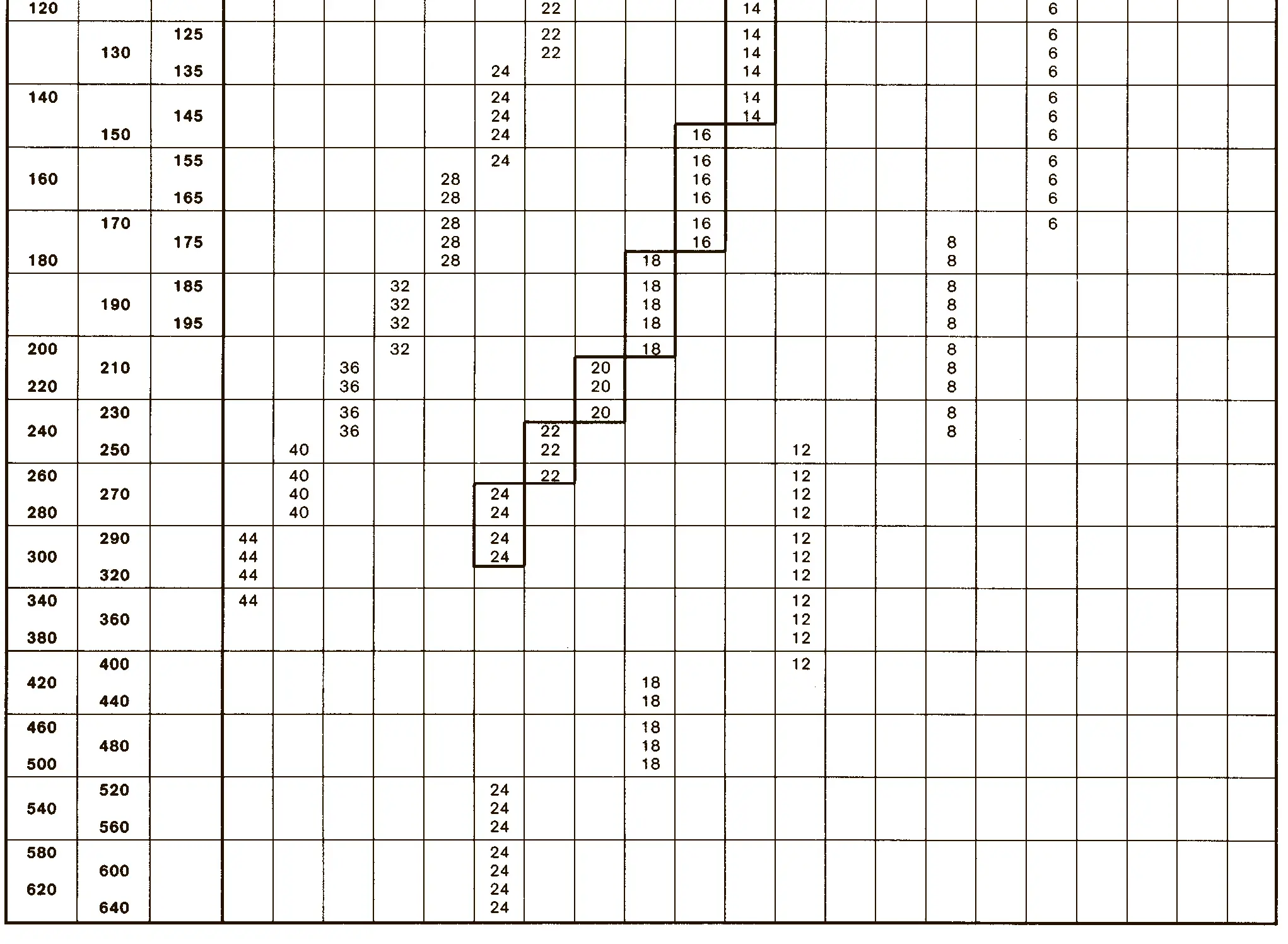
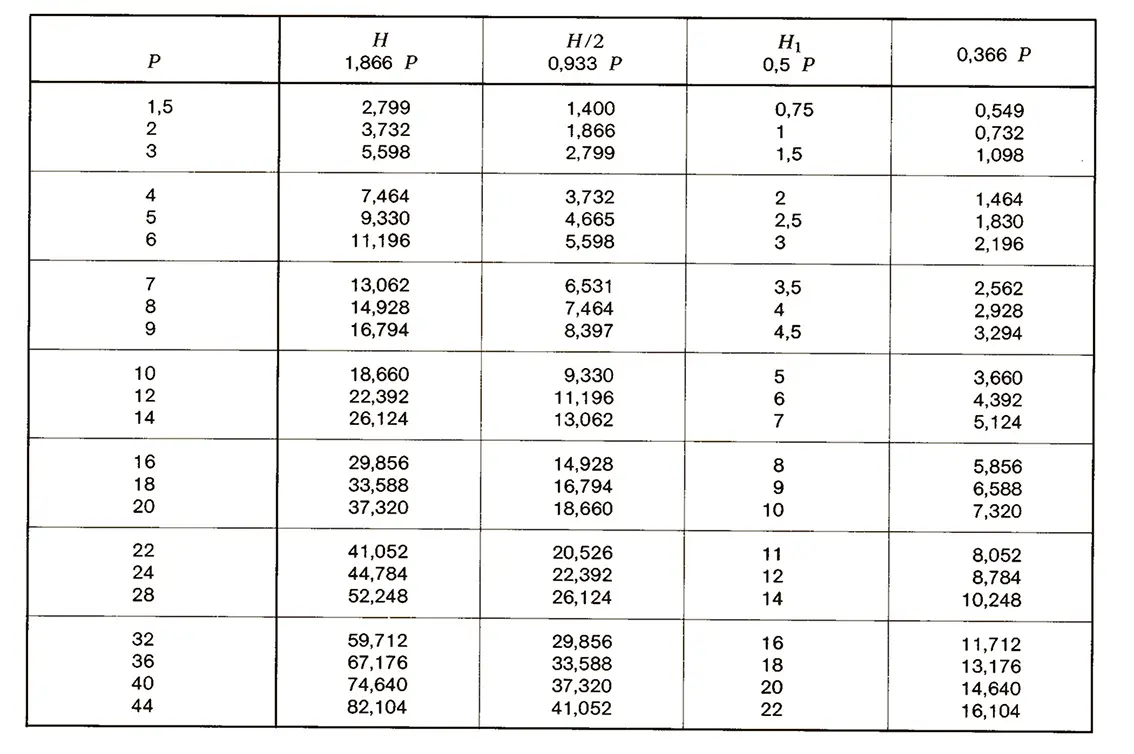
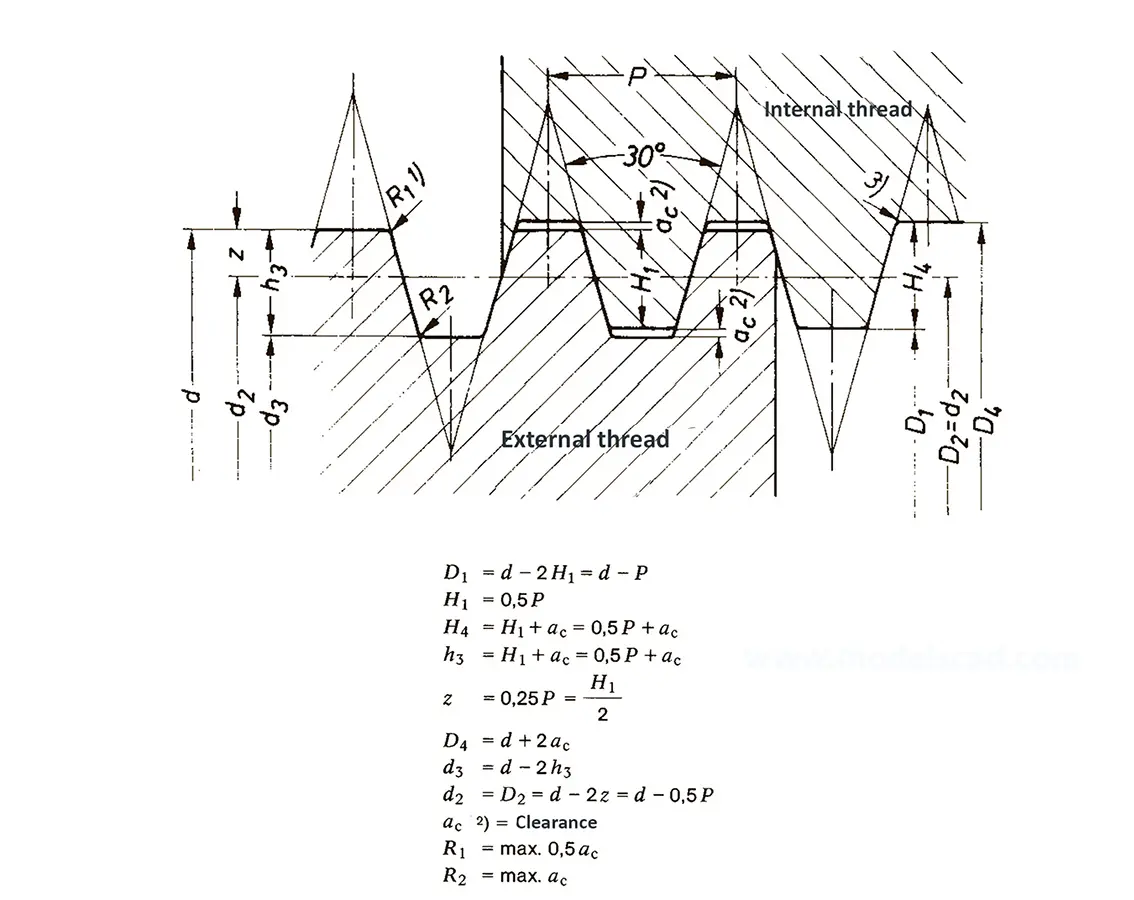
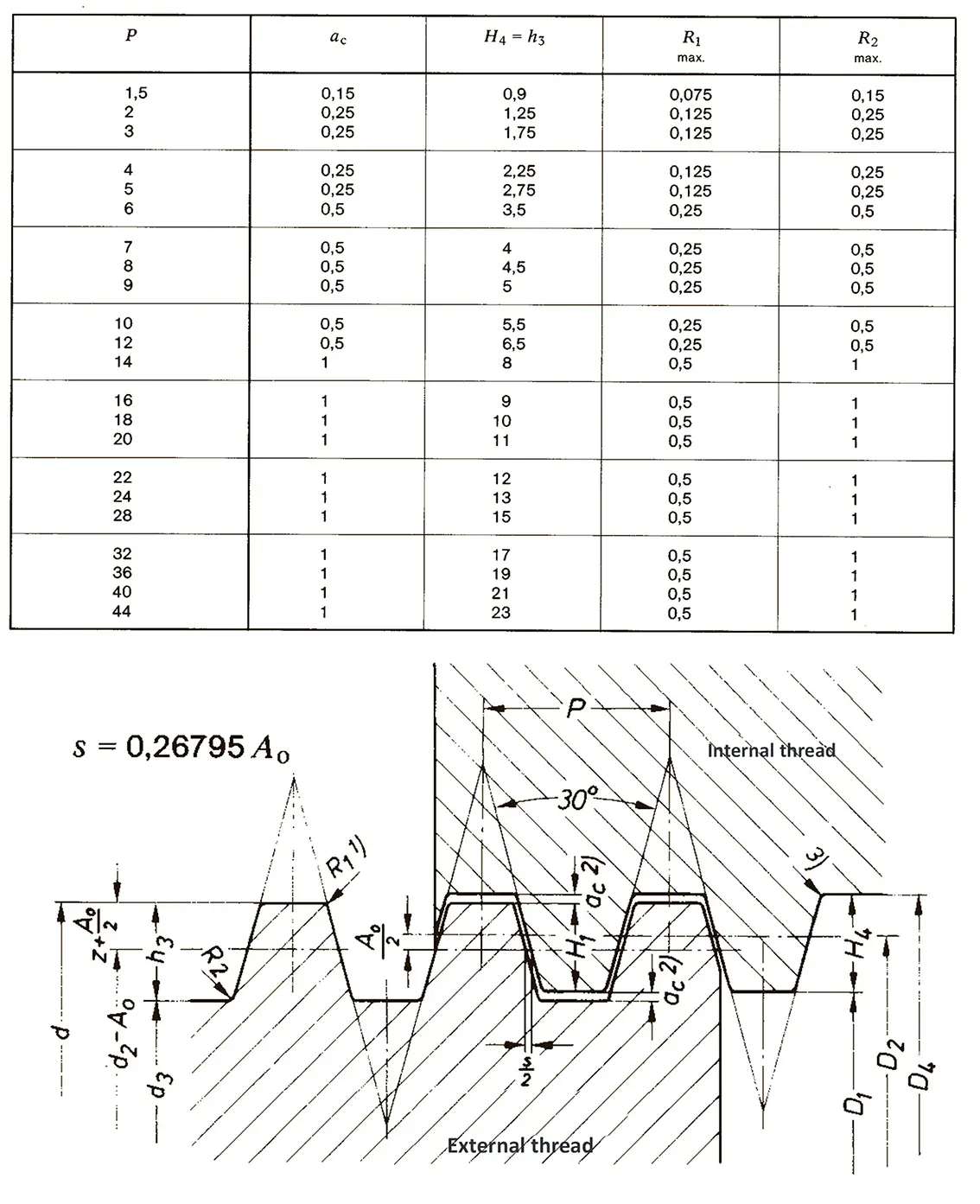
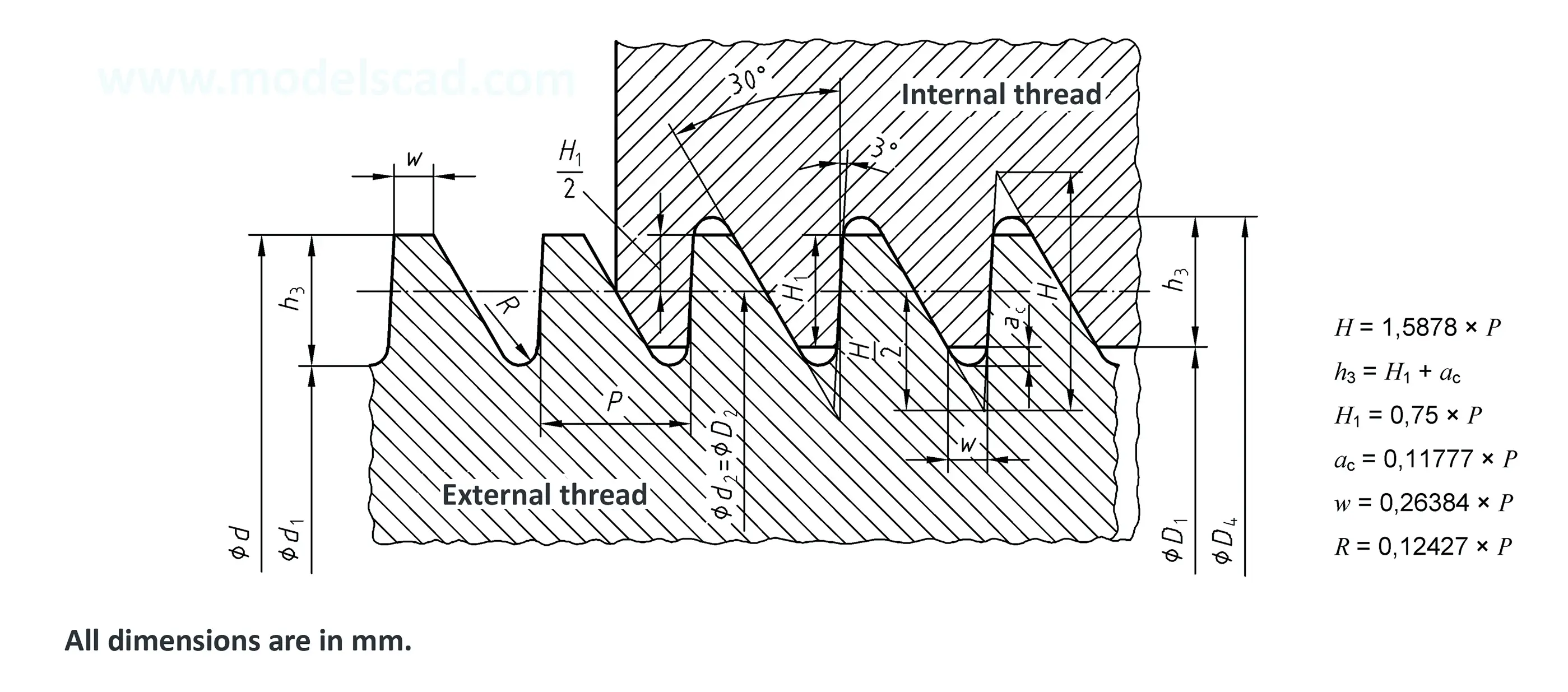
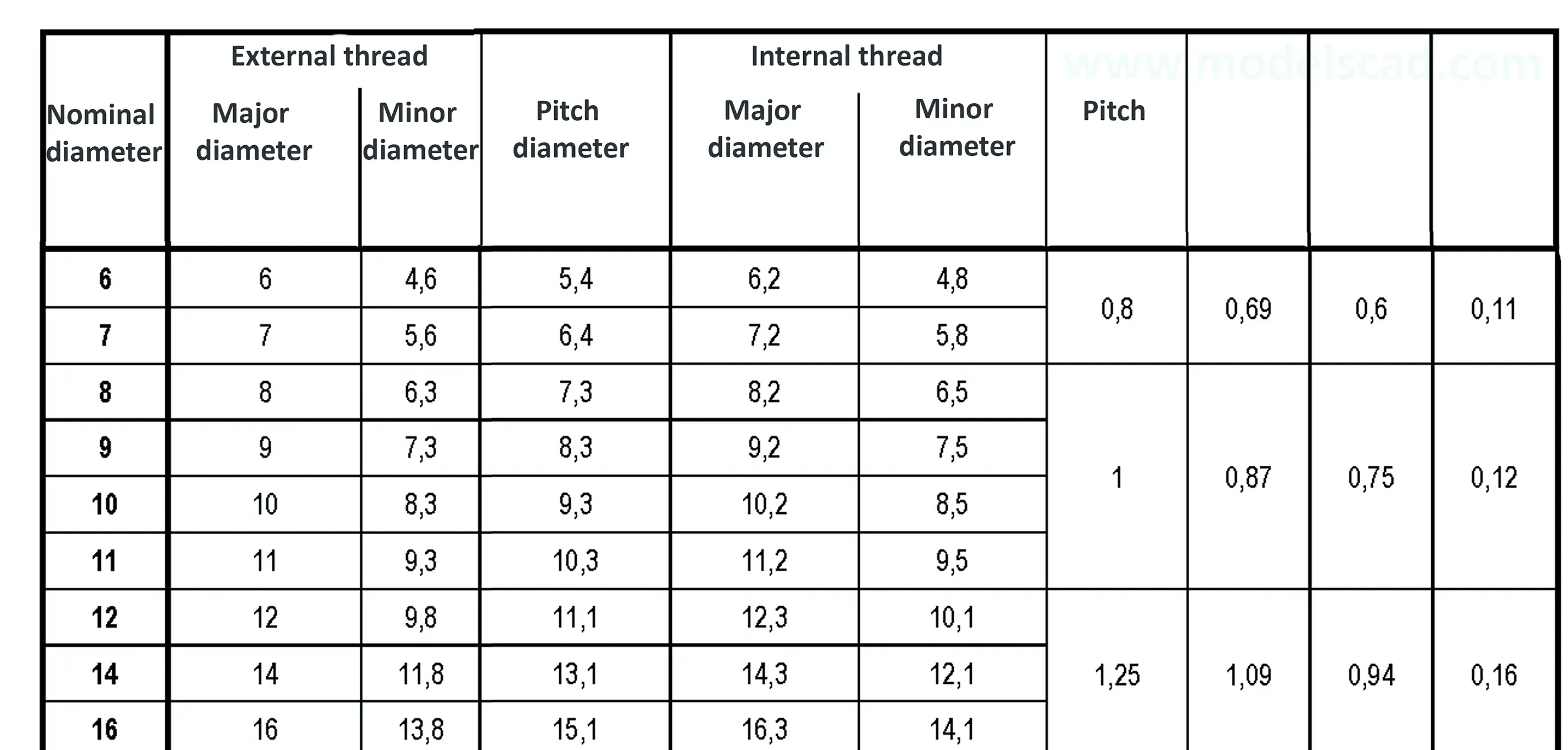
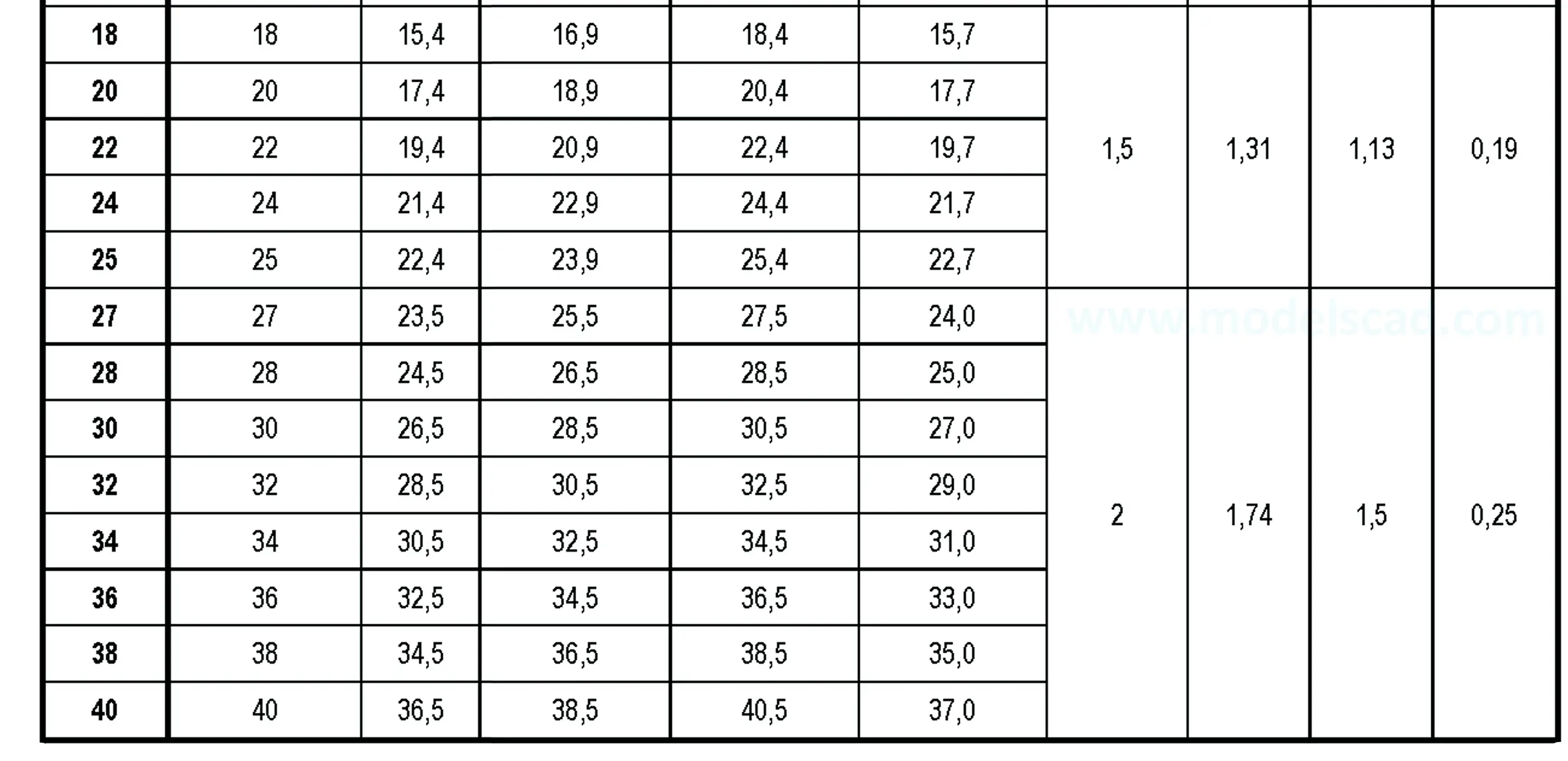
The buttress coarse thread DIN 513 is often used in spindle presses, lifting systems and for collet chucks in lathes und milling machines. The flank angle is 33°.
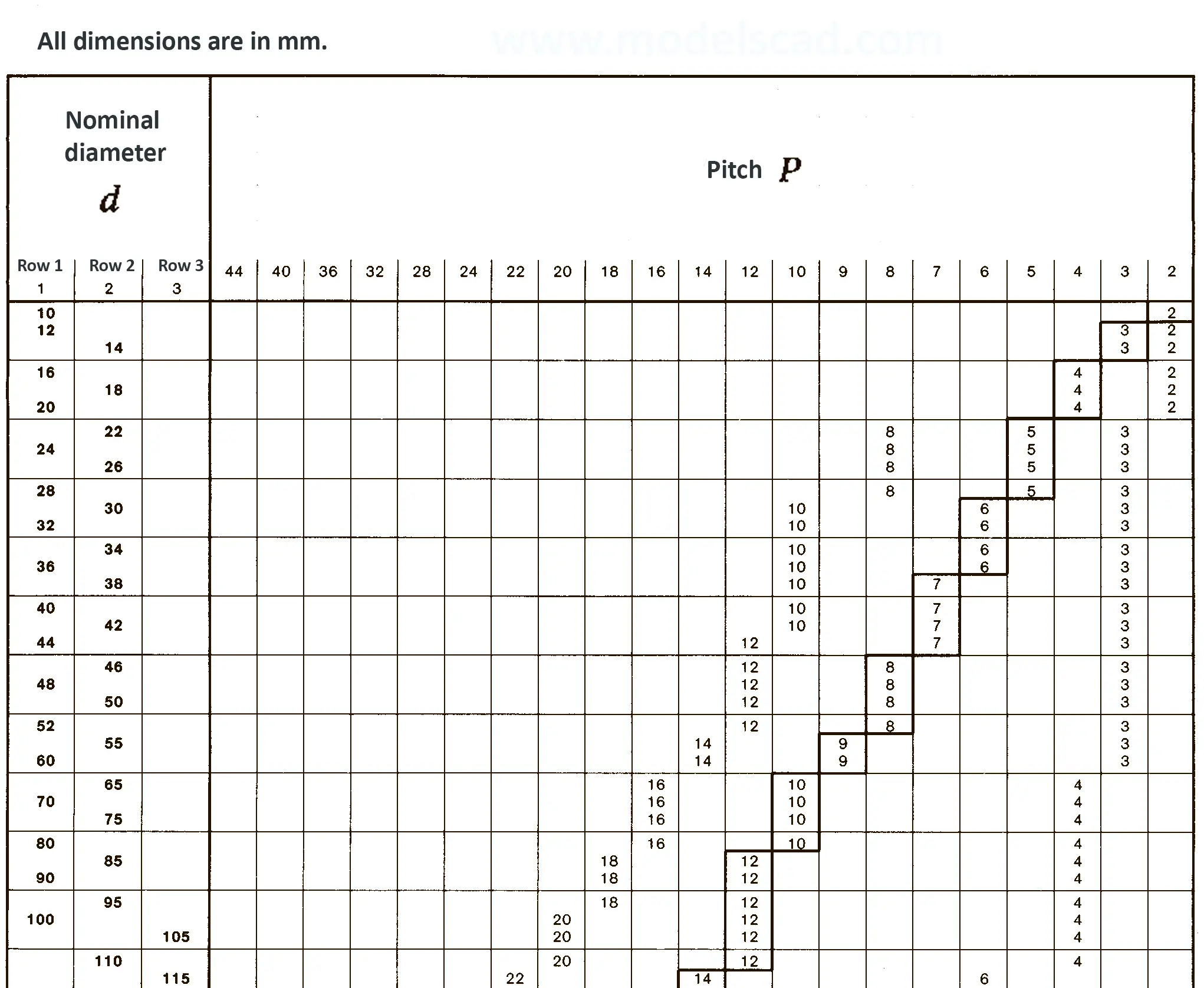
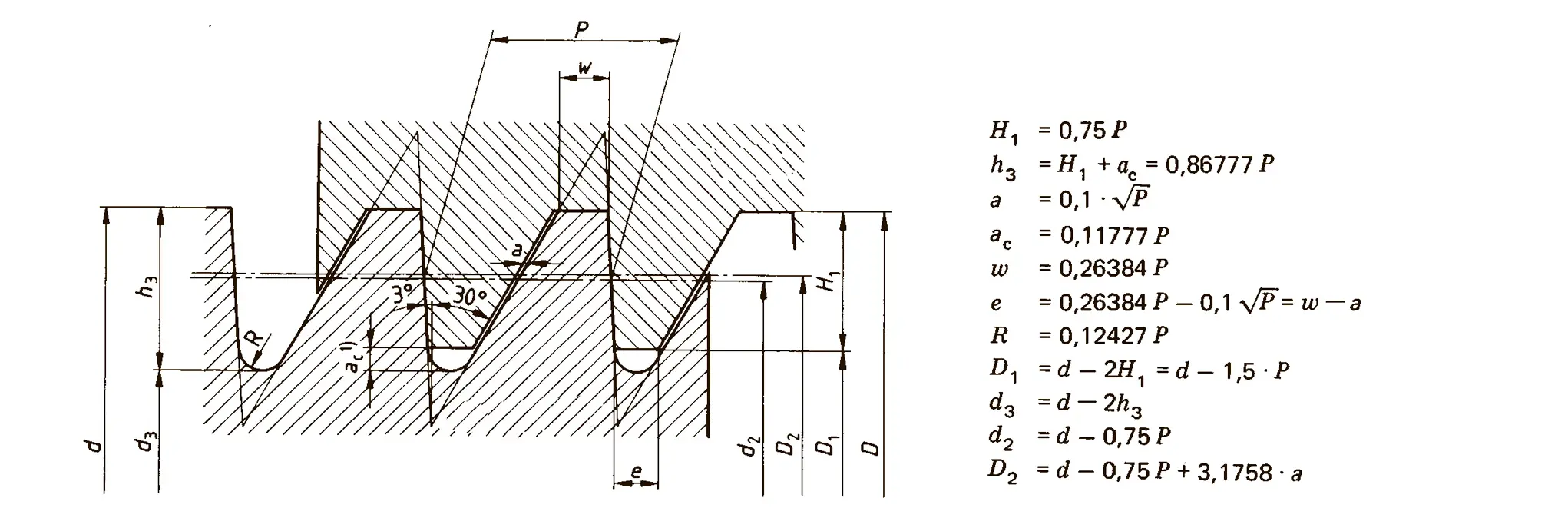
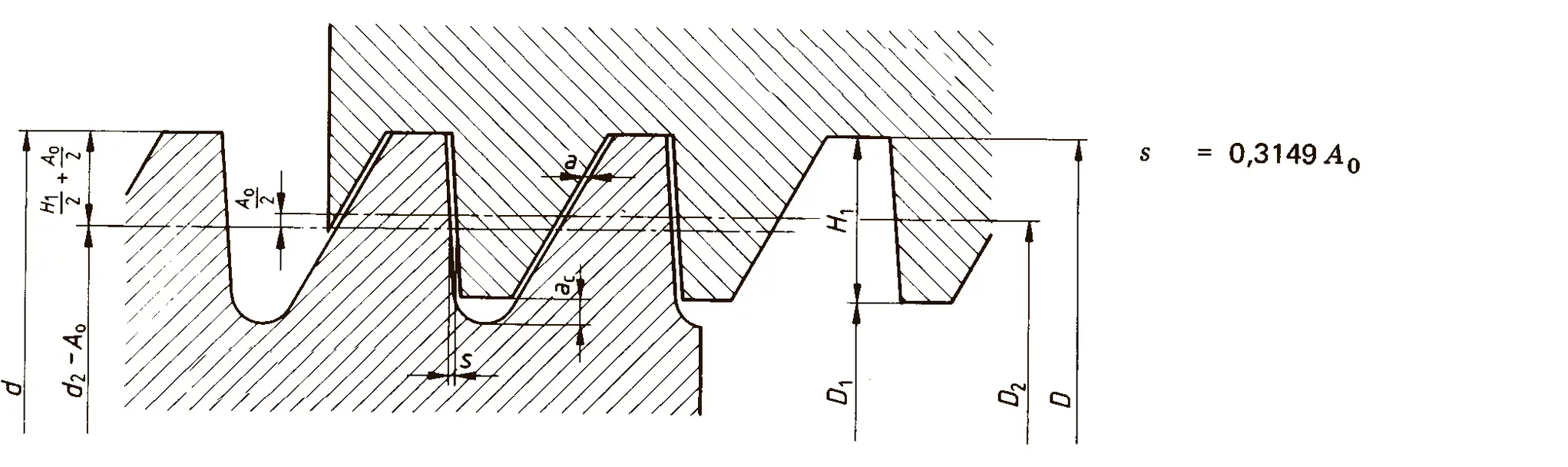
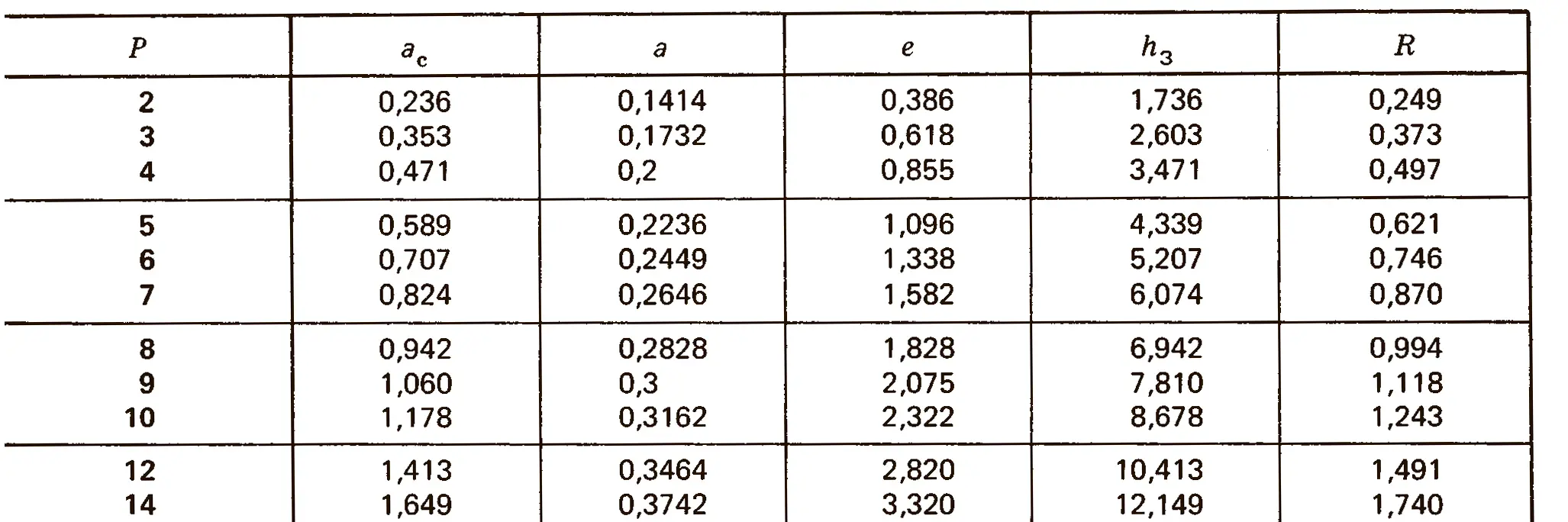
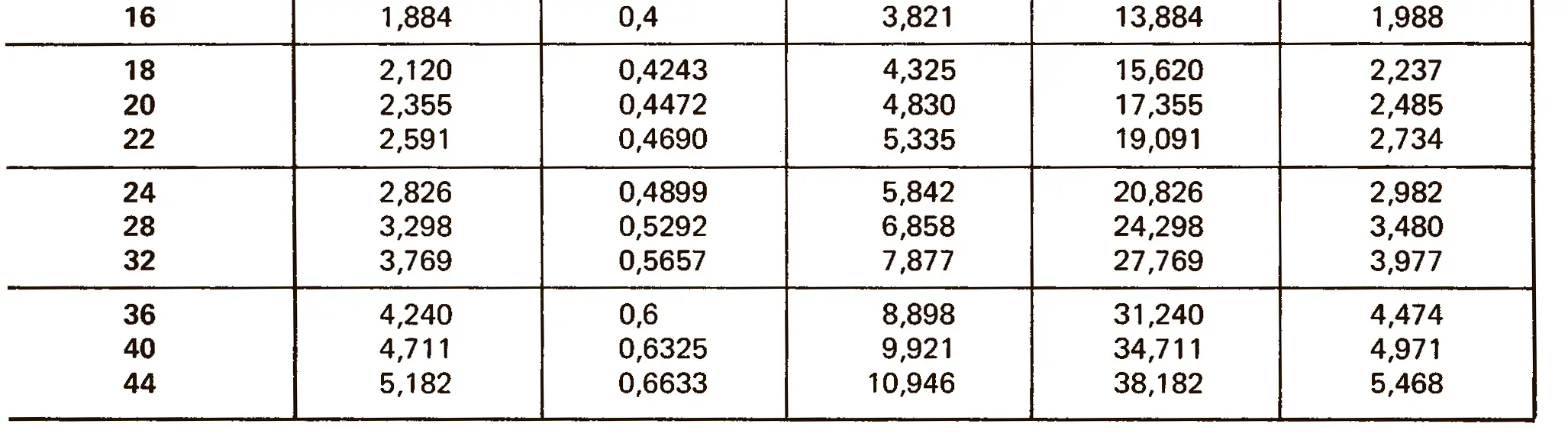
Buttress thread DIN 2781 with 45° angle. It is used on hydraulic presses and mechanisms operating under high load.
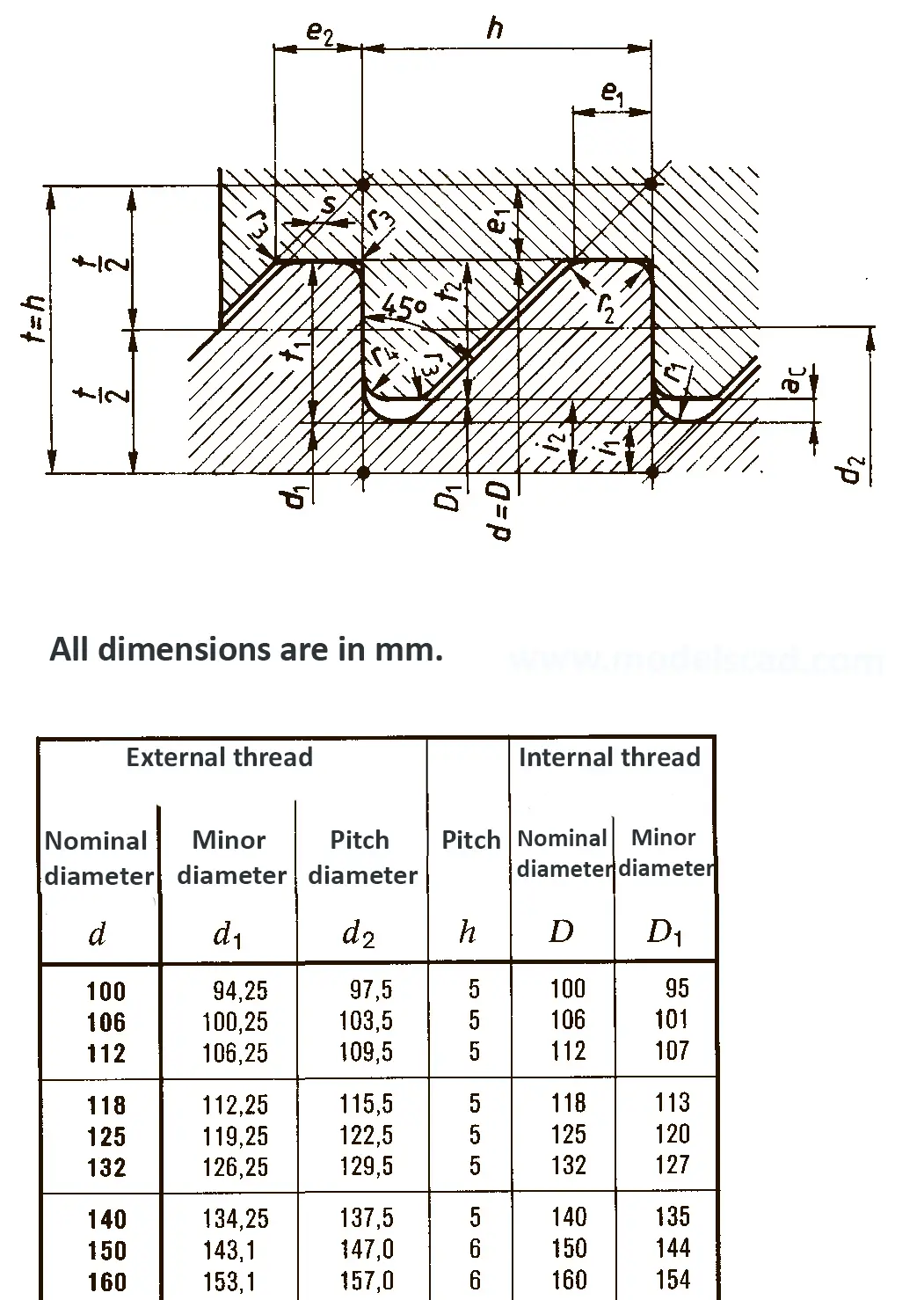
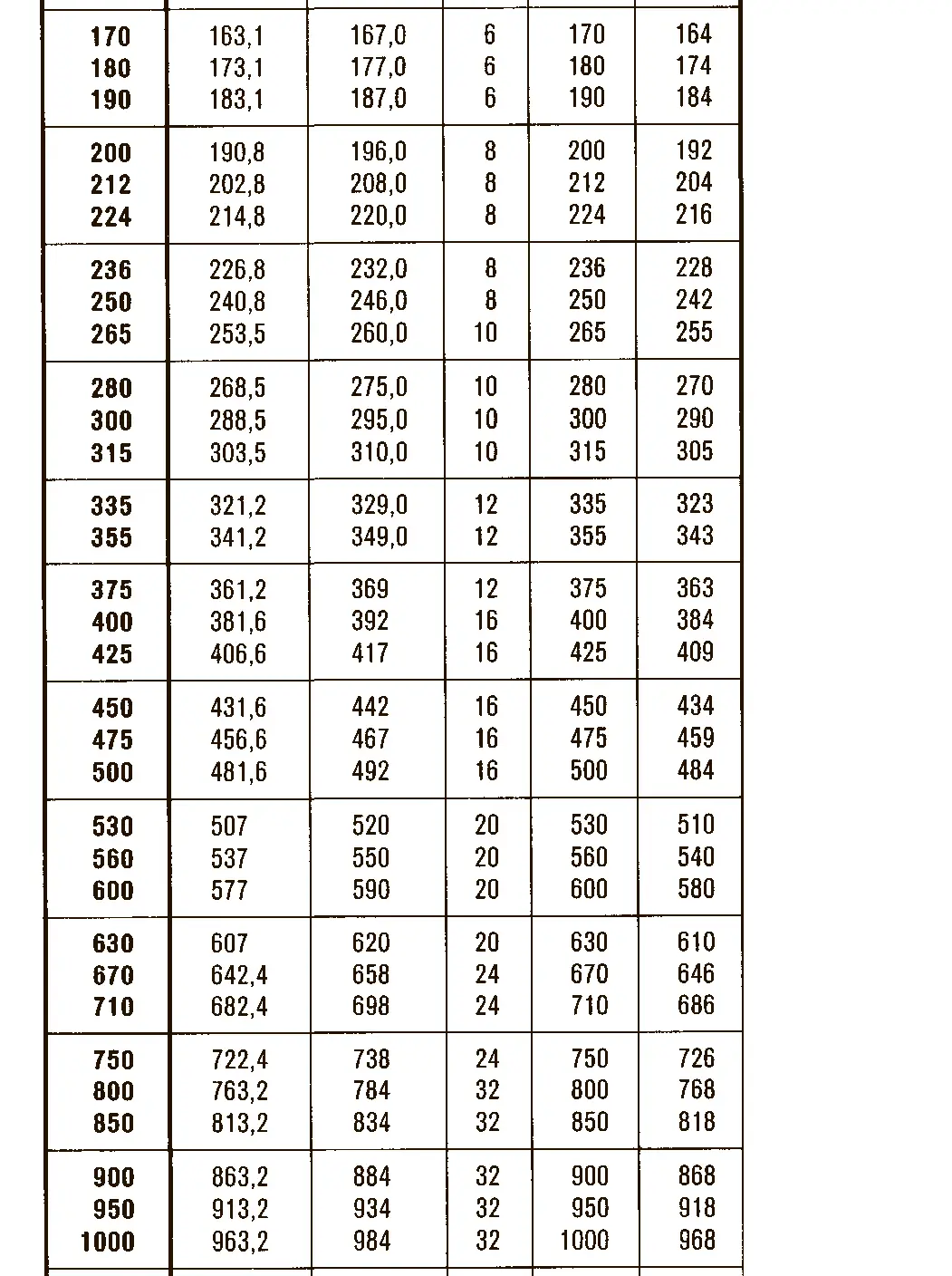
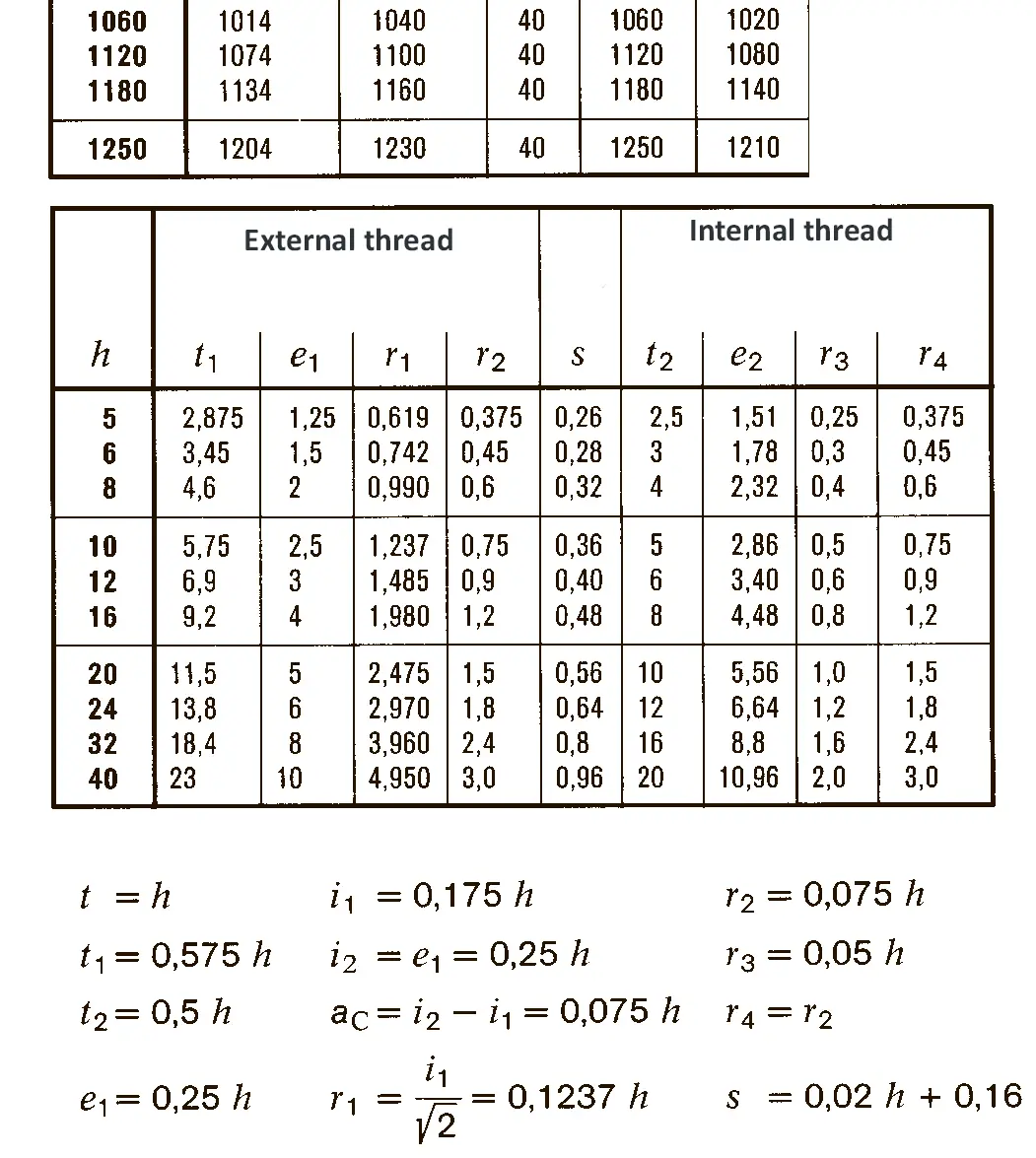
The trapezoidal thread DIN 103 is shaped like an isosceles trapezium. Trapezoidal thread are used in lead screw of lathe or spindle presses because they are able to transmit higher axial forces. The flank angle is 30°.
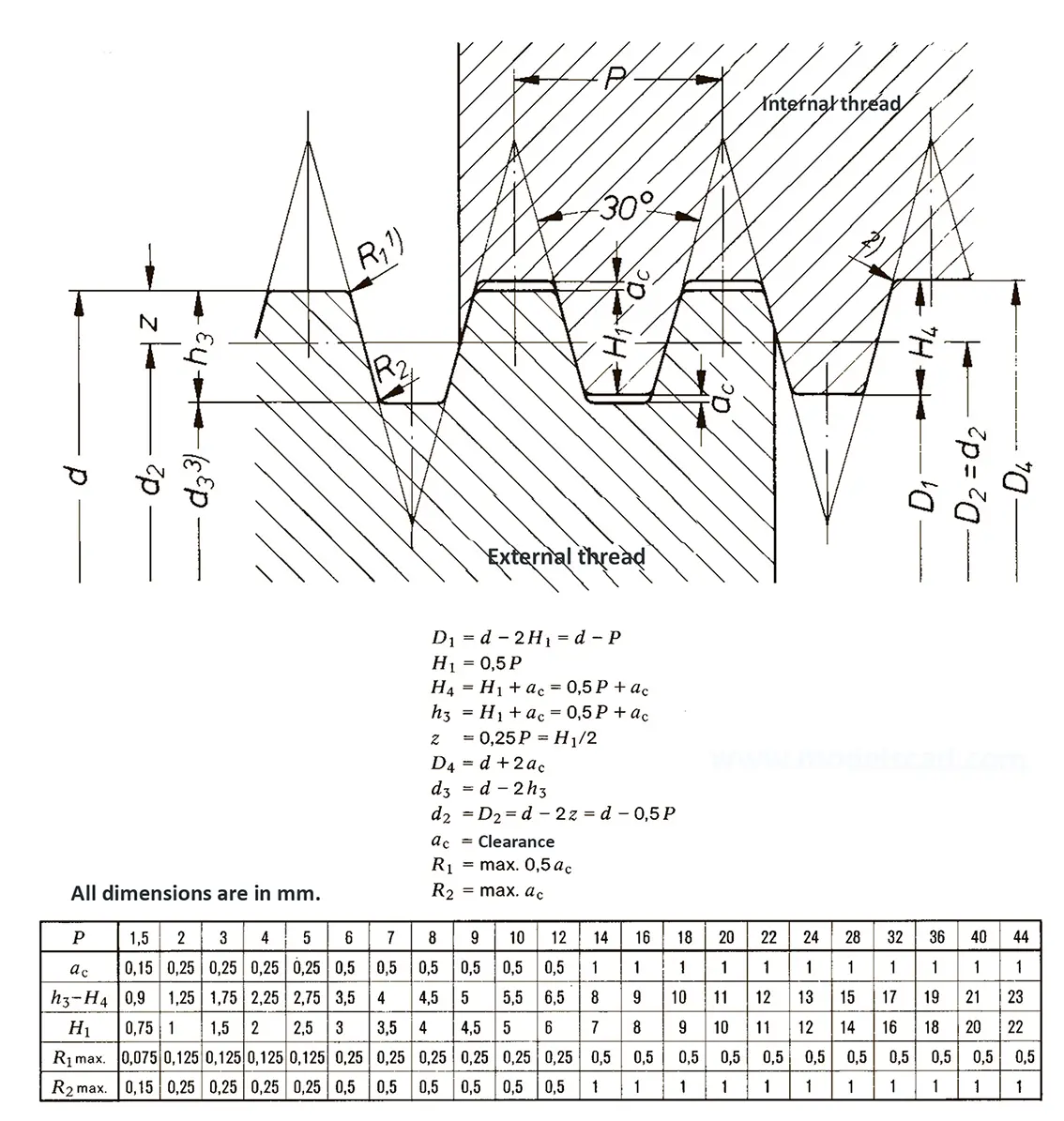
Valves for vehicle tyres DIN 7756. The flank angle is 60°.
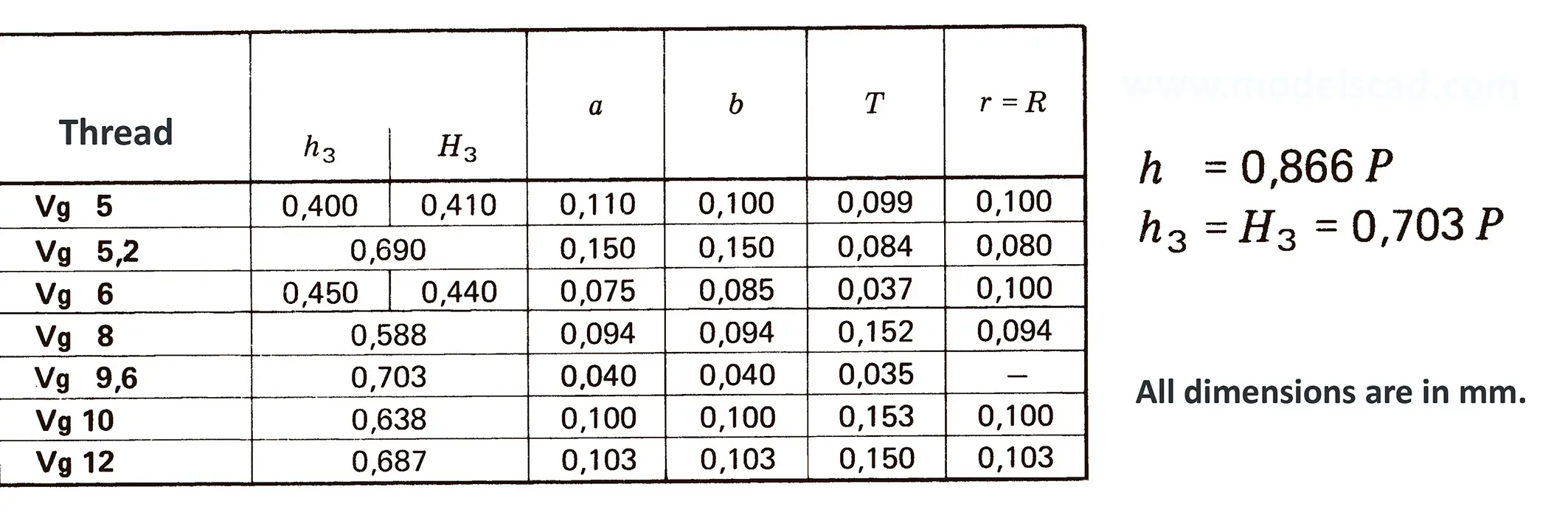
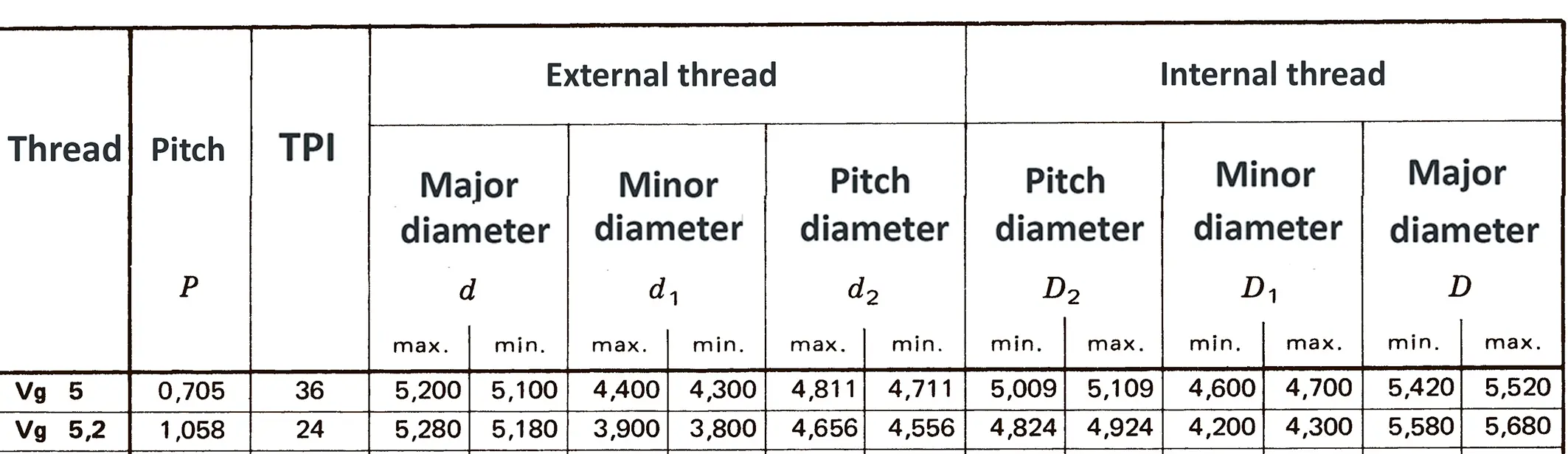
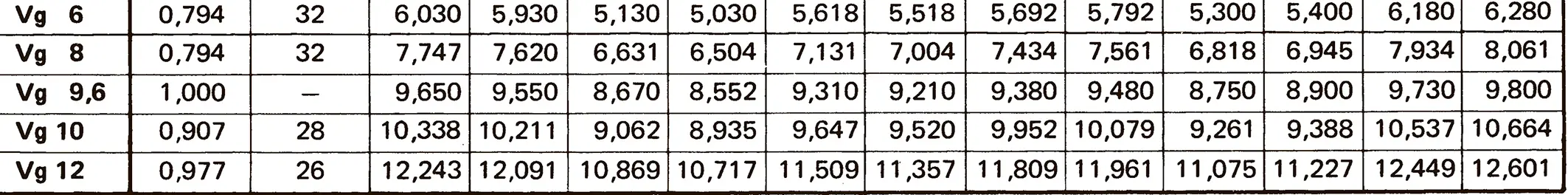
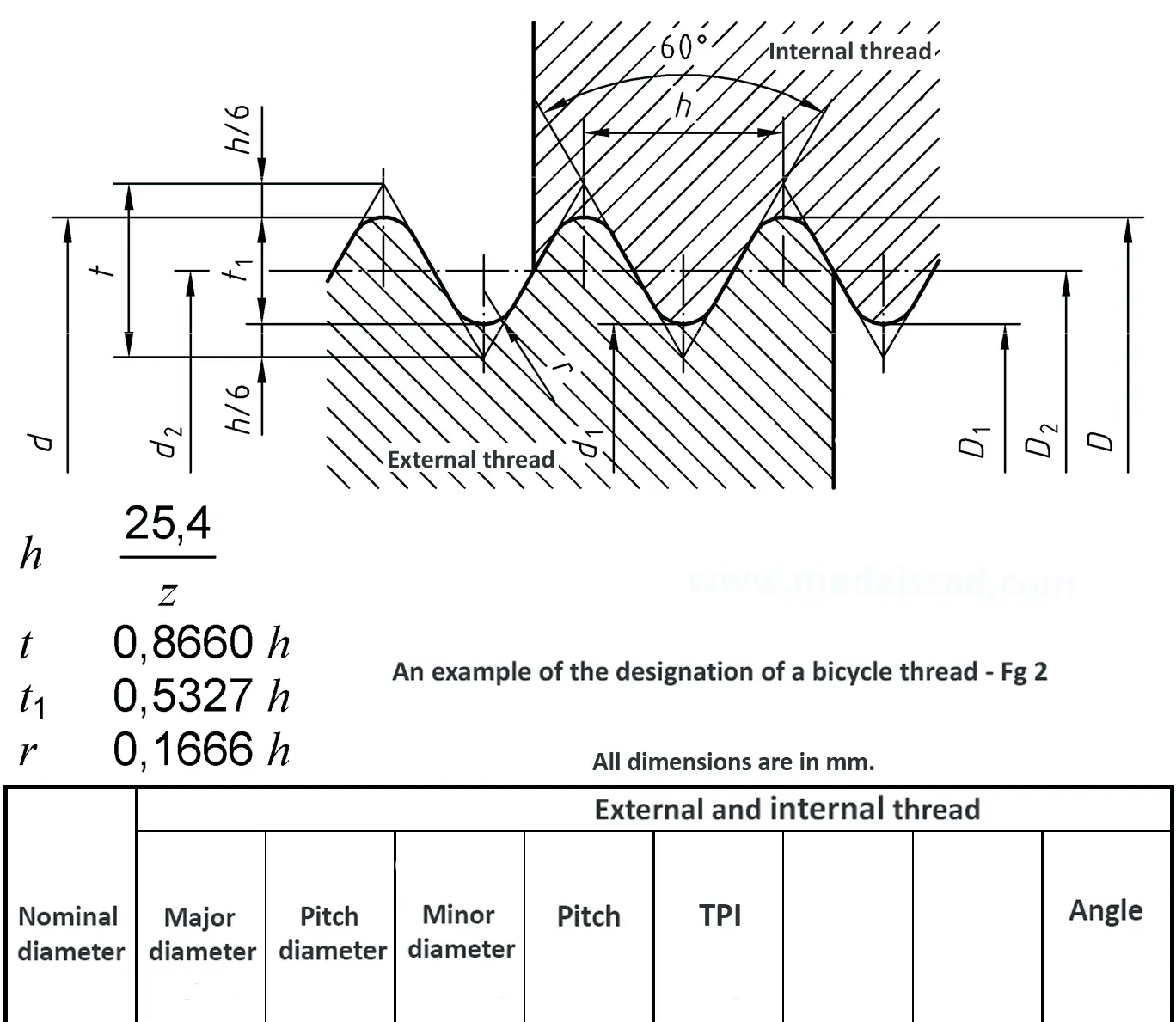
Different threads emerged from developments in bicycle production, some of them from the US and Great Britain, which is the reason why inch dimensions are actual until today. The flank angle is 60°.
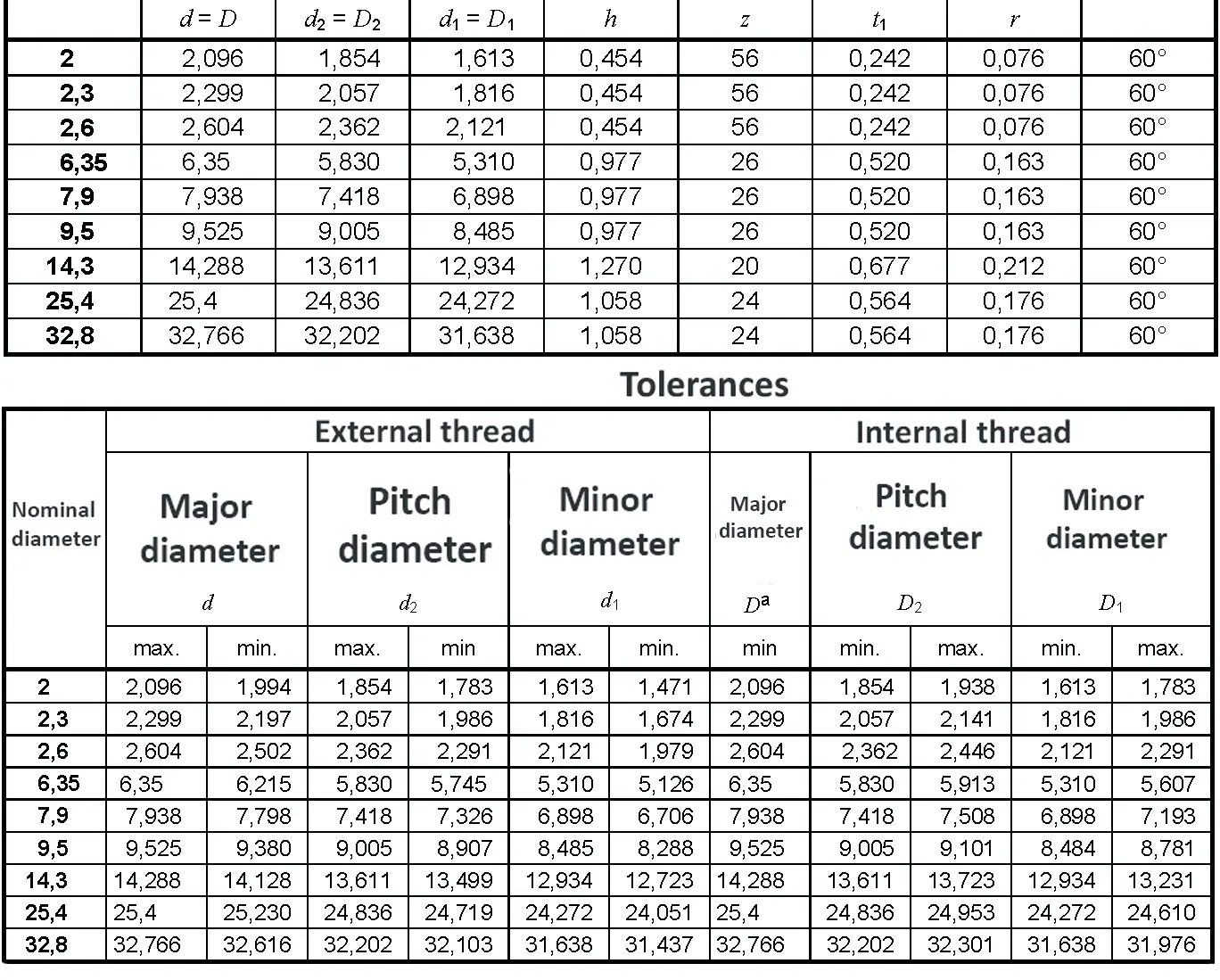
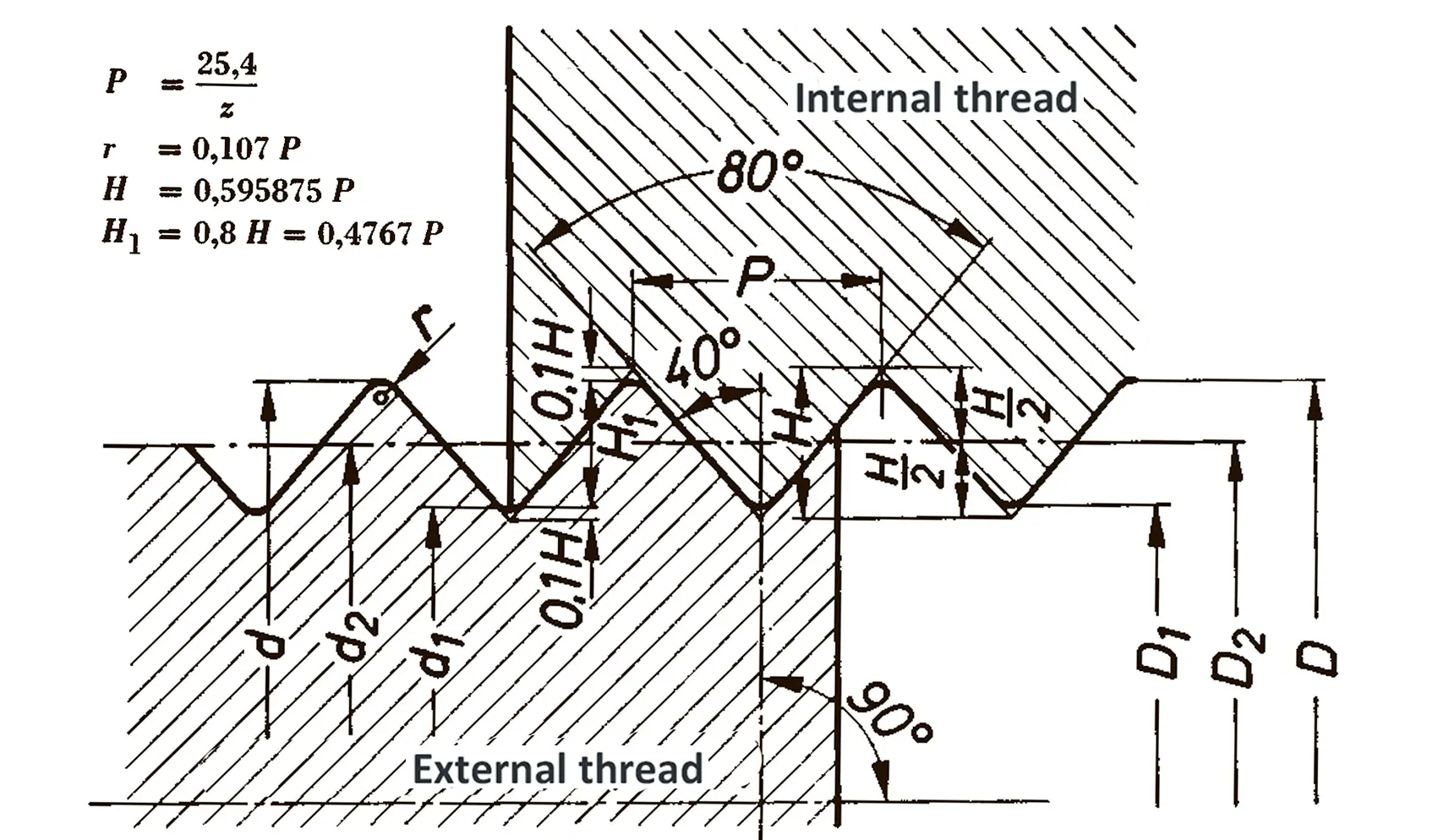
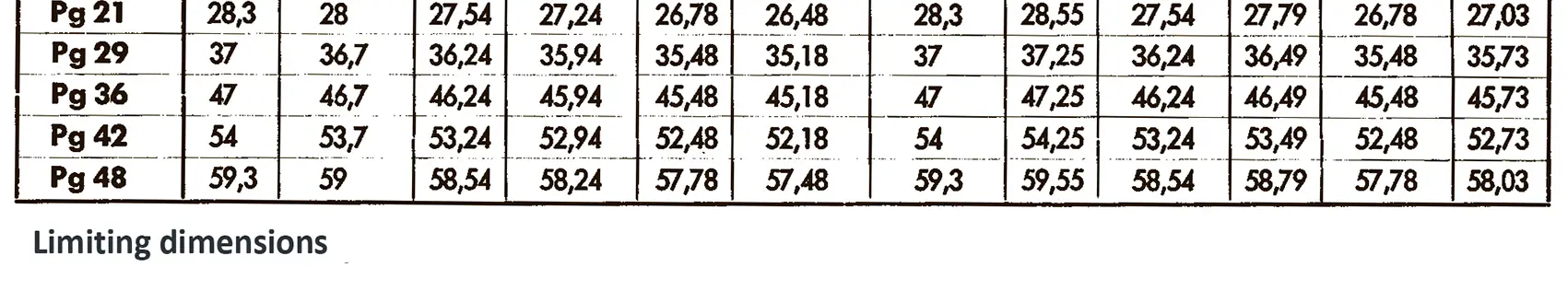
Steel conduit thread DIN 40430. The flank angle is 80°. On 31.12.1999 the safety standard VDE 0619 which included the standards DIN 46319 for metric sizes and DIN 46320 for PG-sizes were withdrawn. On 01.01.2000 the new standard DIN EN 50262 came into force. The new standard uses the new metric sizes. In the transitional period - until 01.03.2001 - the PG-standard could still be used. For replacement PG-items may still be used. The ten sizes PG 7 / 9 / 11 / 13,5 / 16 / 21 / 29 / 36 / 42 and PG 48 were replaced by eight new metric sizes, i.e. M 12 / 16 / 20 / 25 / 32 / 40 / 50 and M 63. No direct conversion is possible.
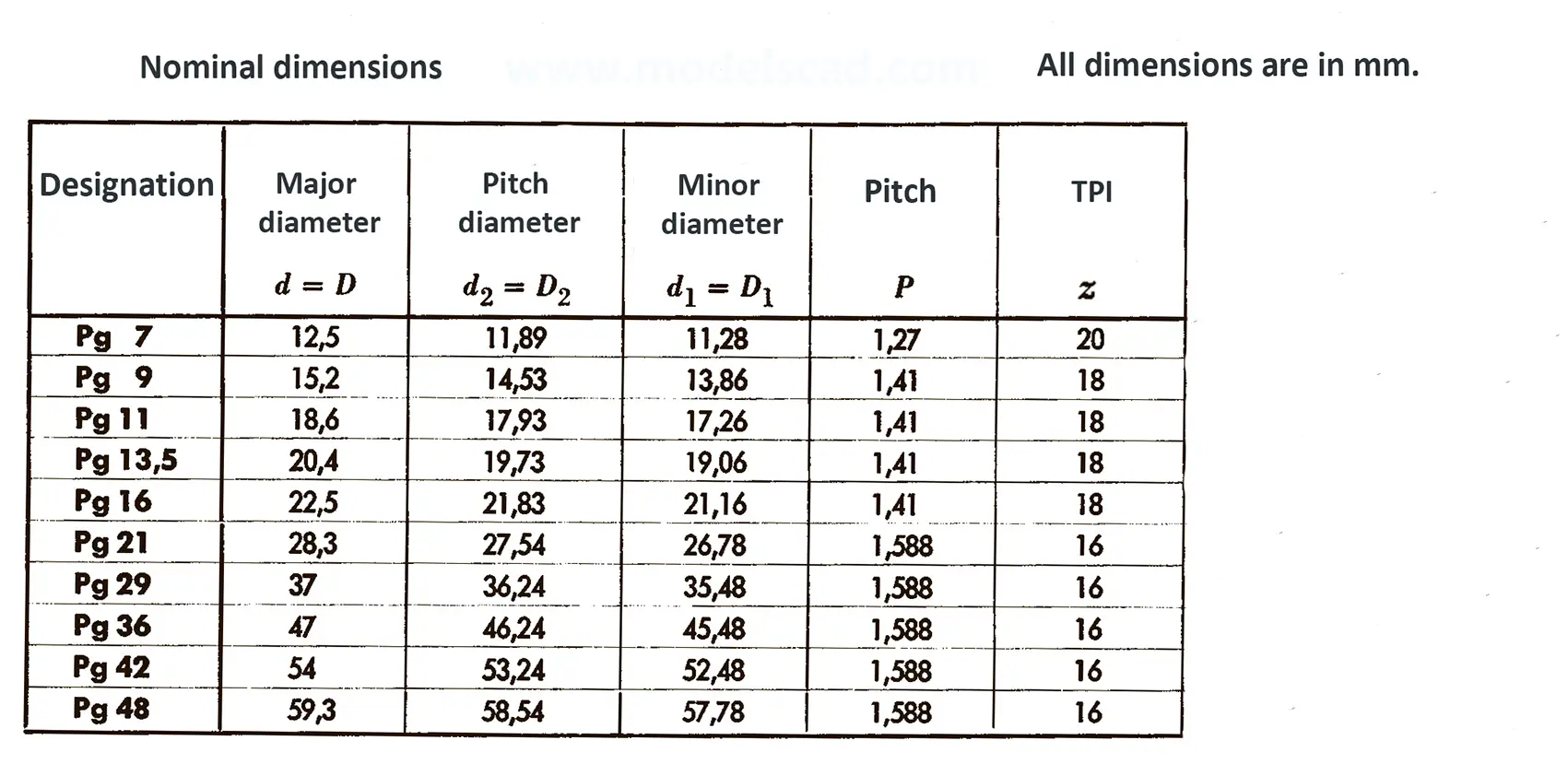
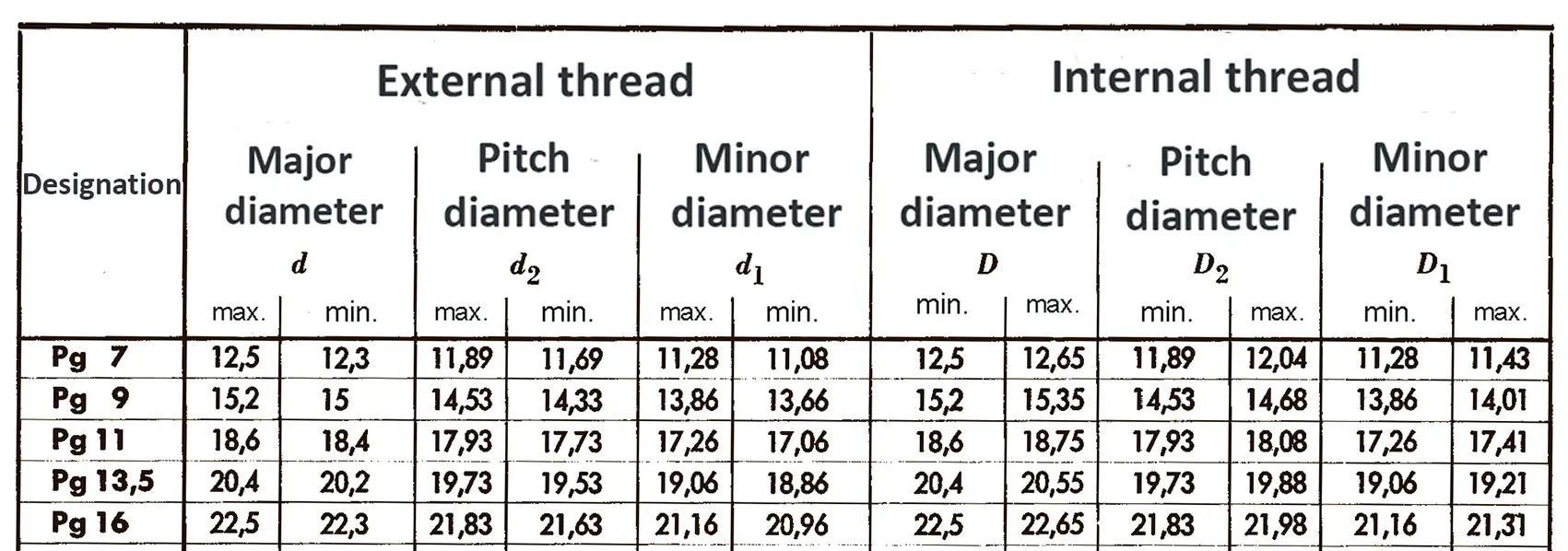
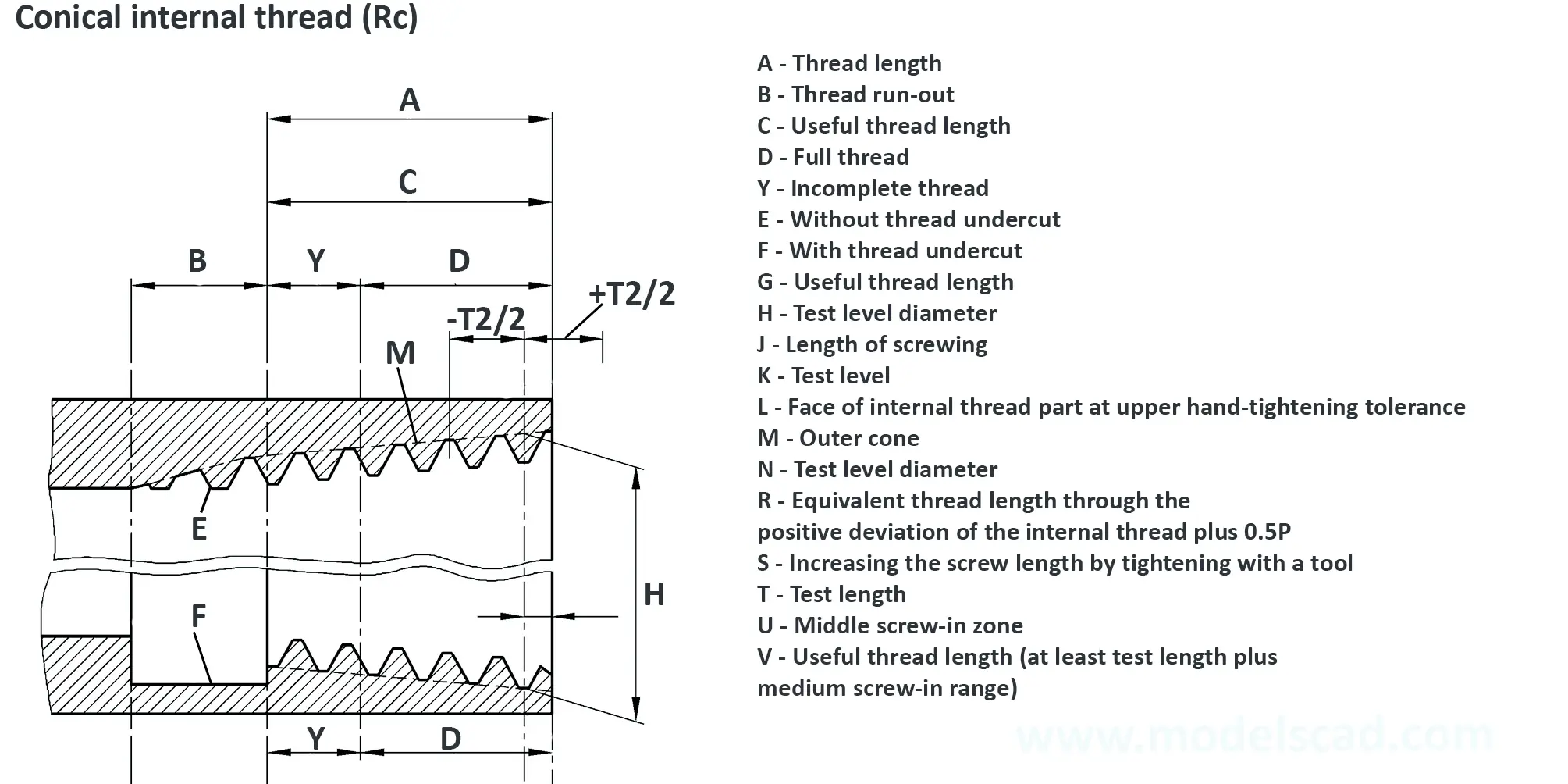
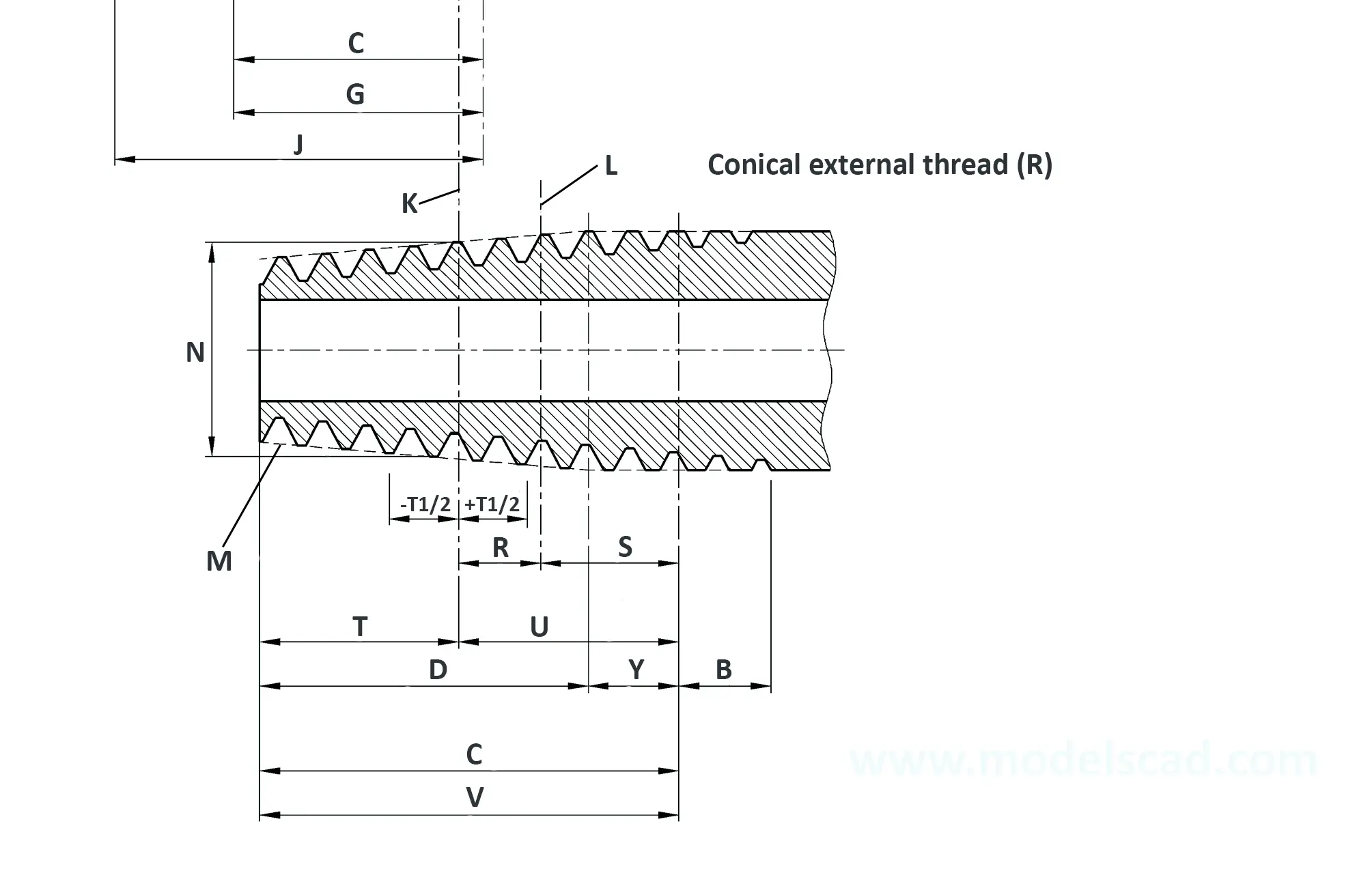
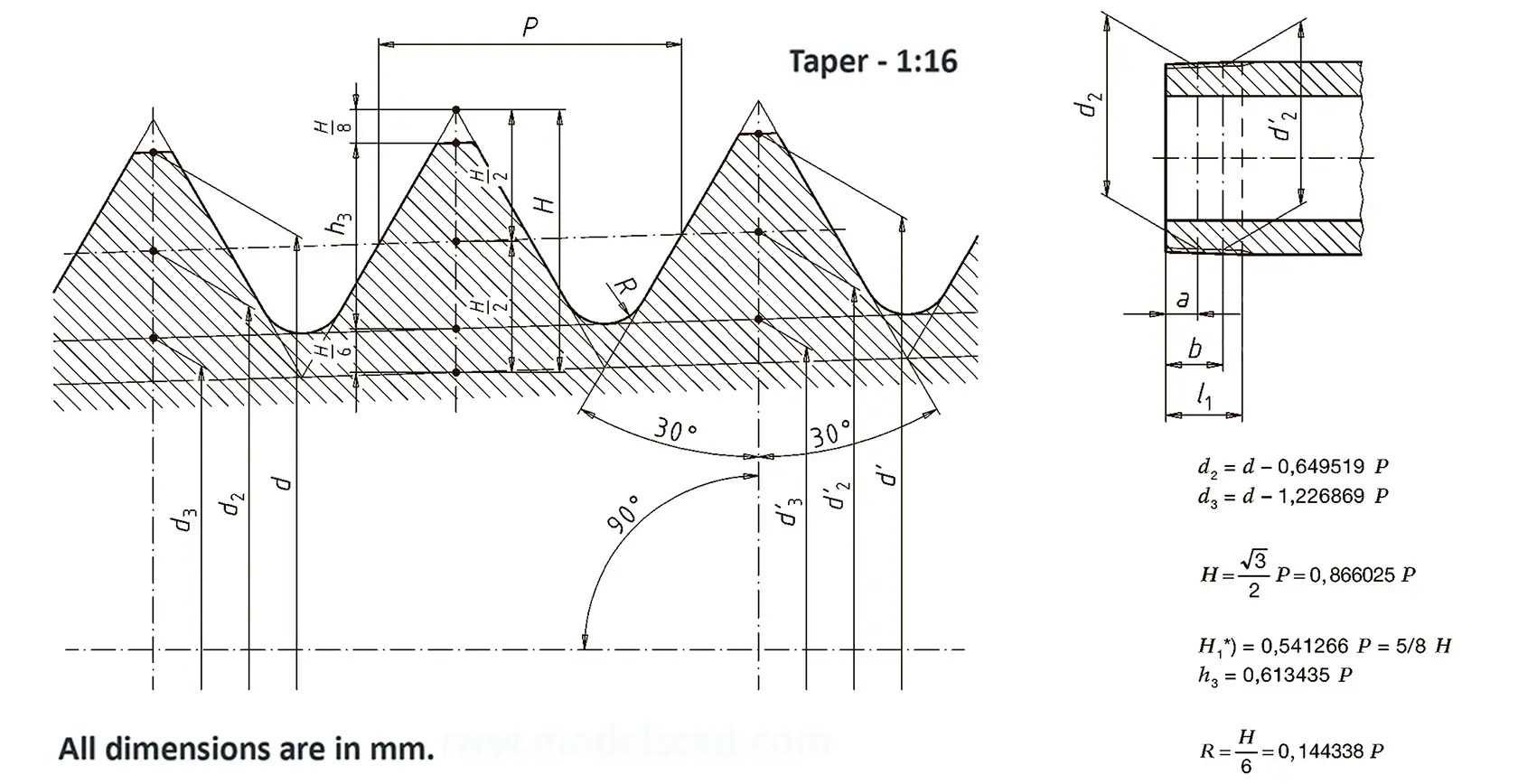
According to DIN 158, only the external thread is conical (taper 1:16), the internal thread is cylindrical according to DIN 13. According to the old standard DIN 158, internal and external thread are tapered. Today, the tapered internal thread is still in use according to the old standard. The thread is used on sealing screws, screw-in connectors and lubrication nipples. The flank angle is 60°.
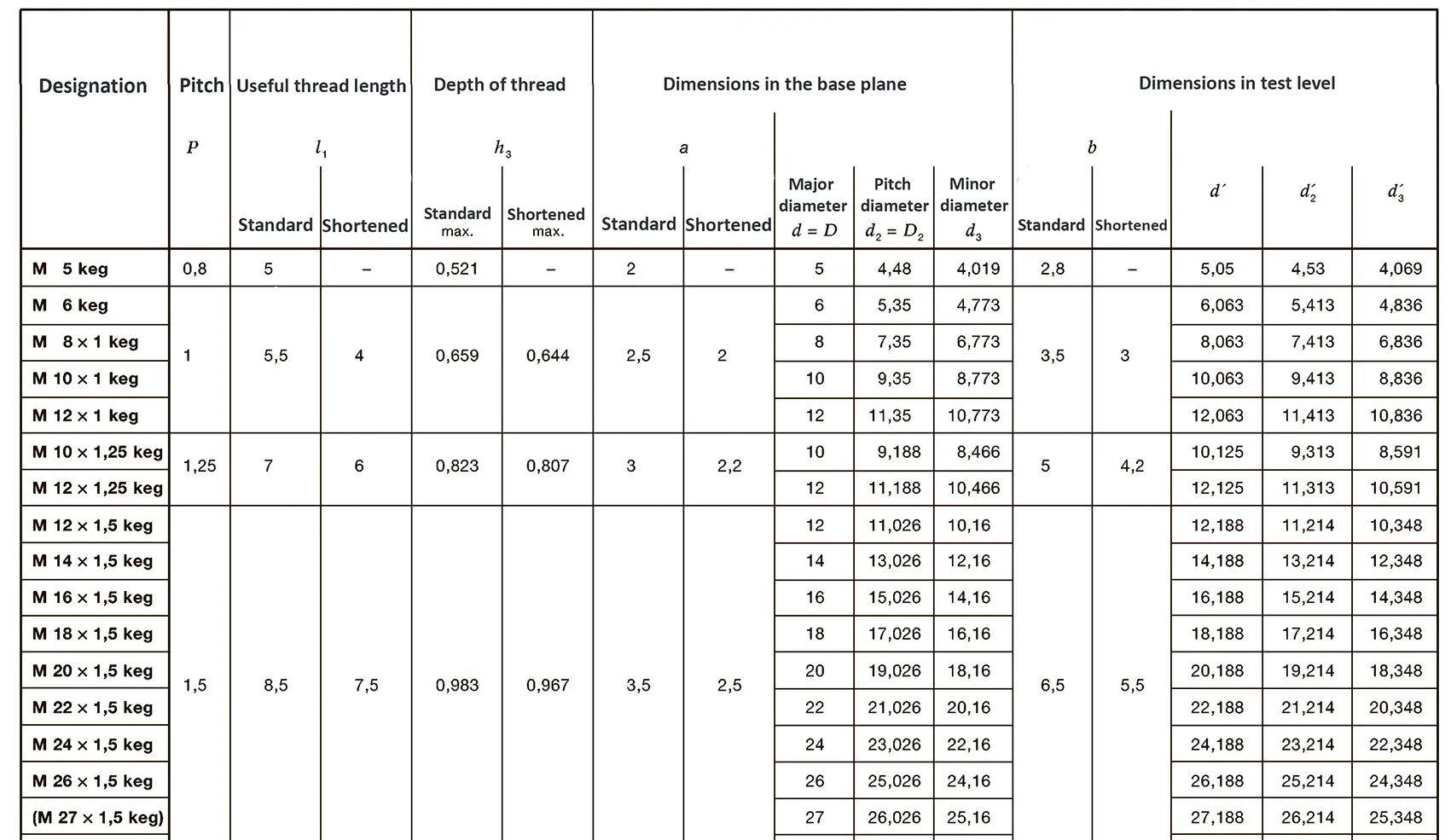
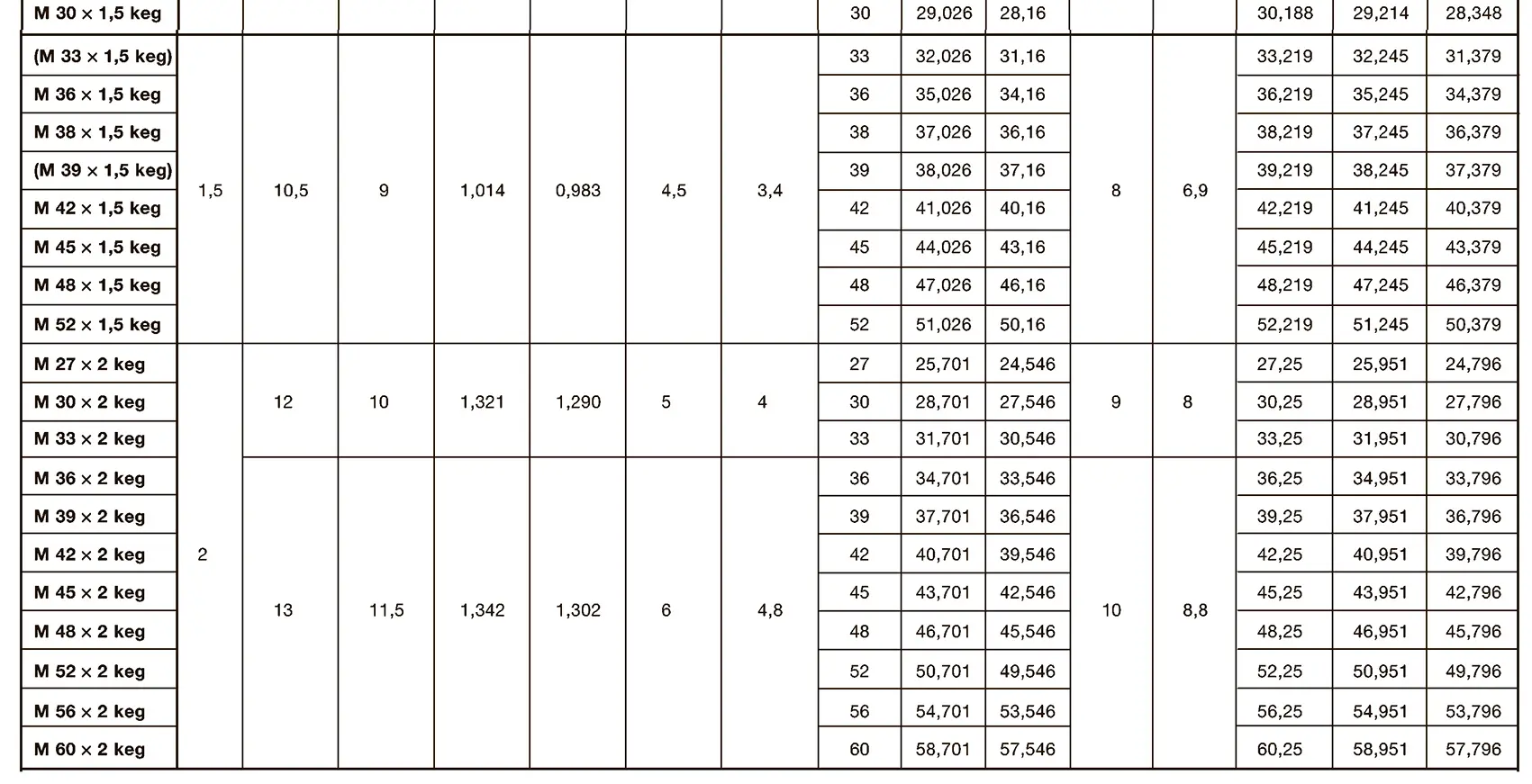
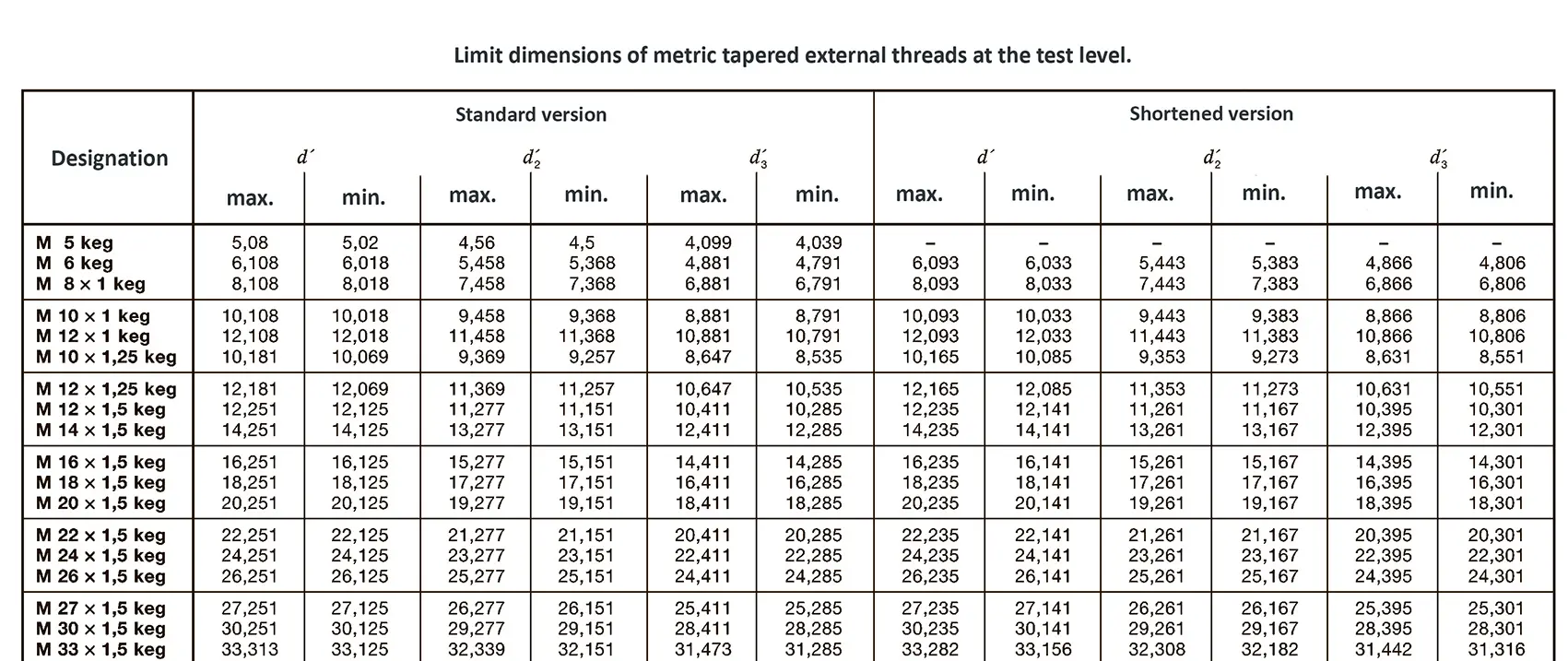
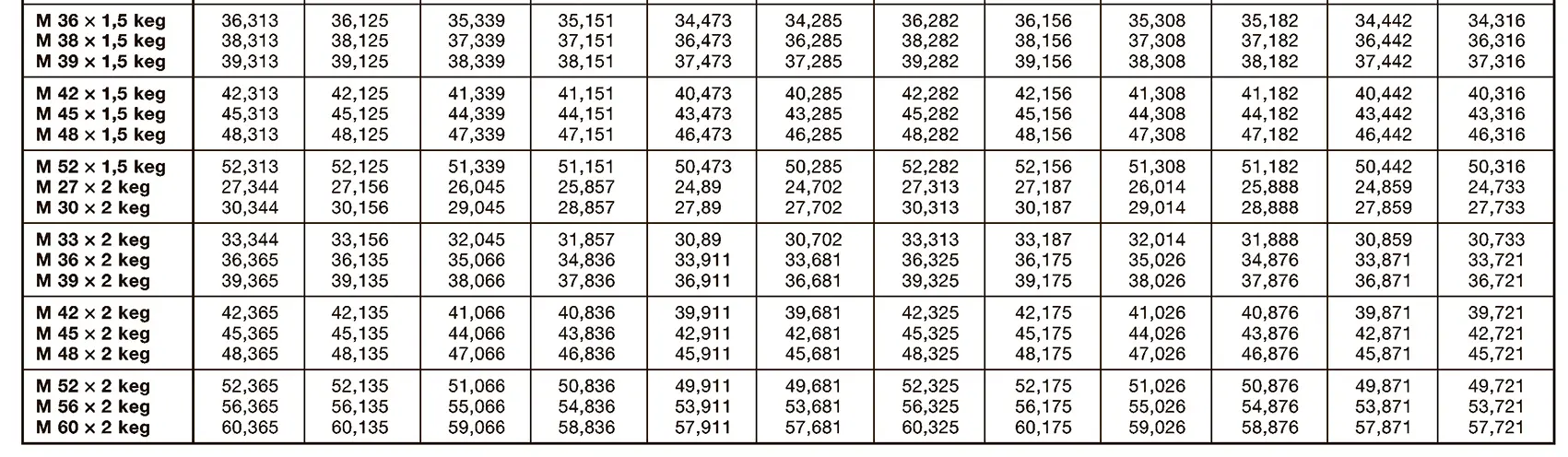
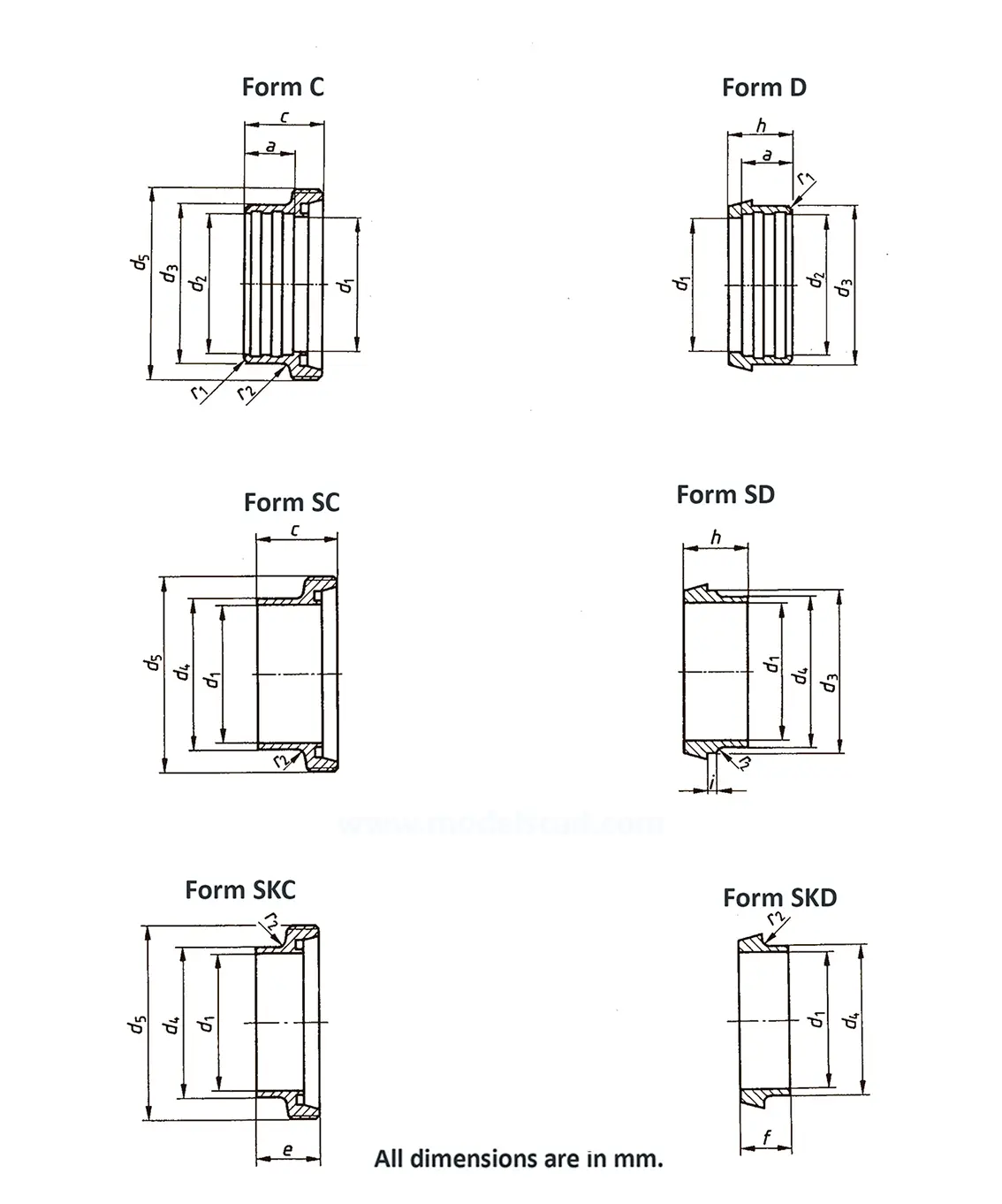
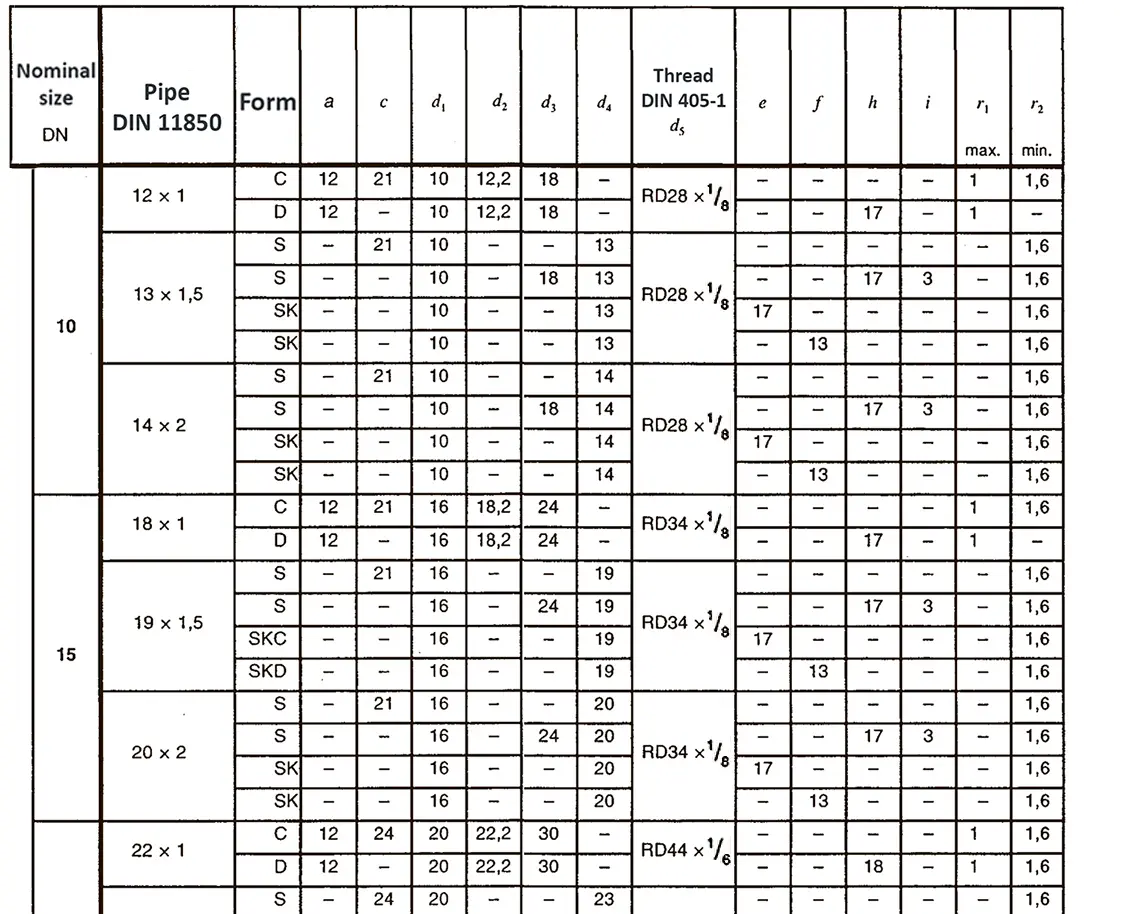
A pipe coupling for foods and chemistry according to DIN 11851, usually called "dairy coupling". It consists of a special clutch thread according to DIN 405, which has rounded thread edges and is thus easy to clean. These pipe couplings are commonly used in the food industry. The flank angle is 30°.
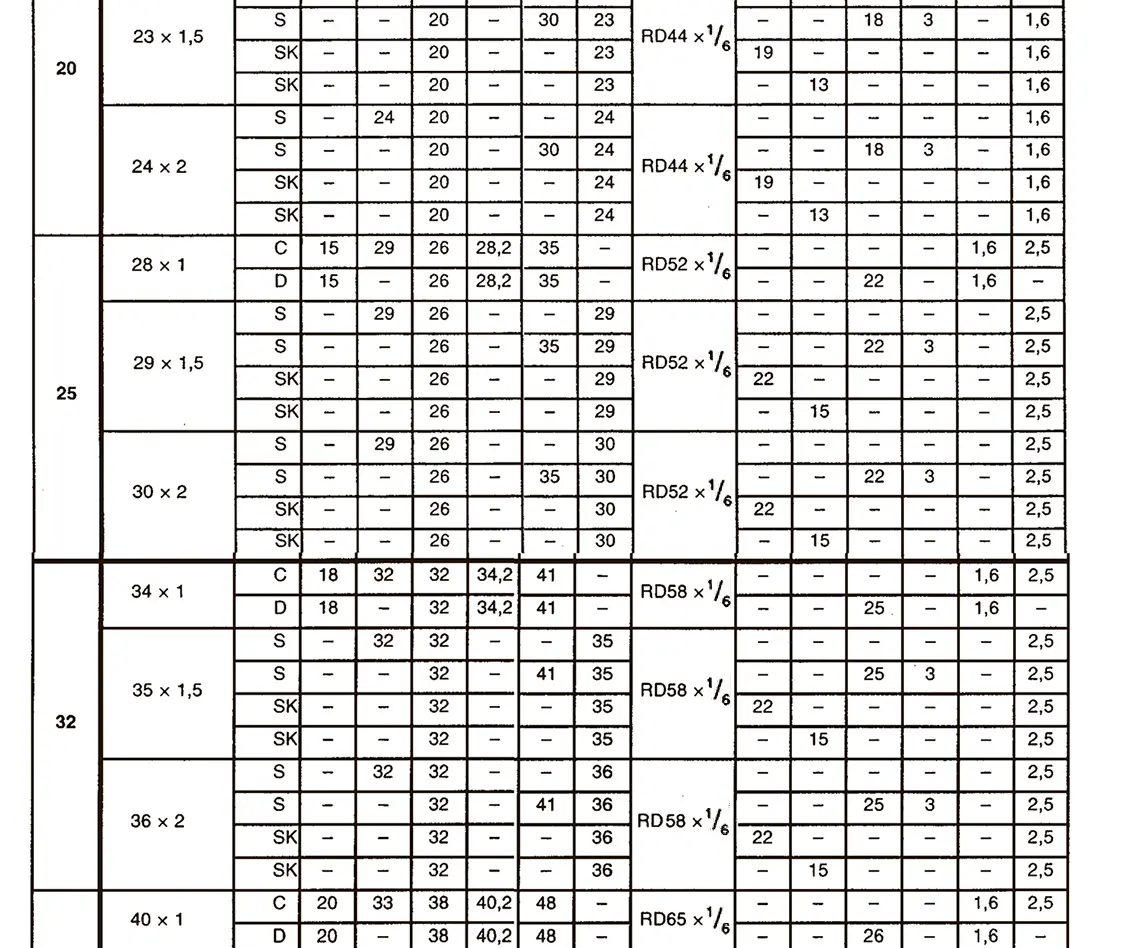
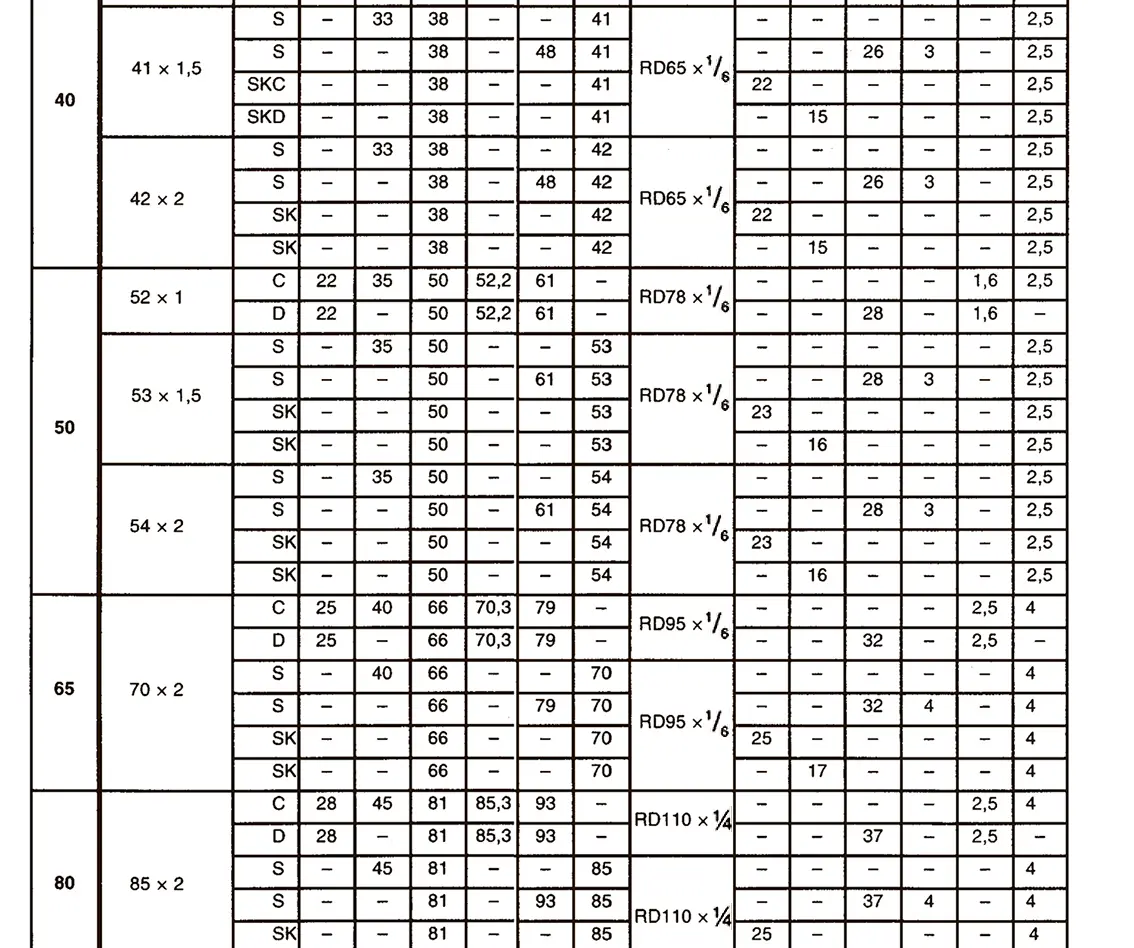
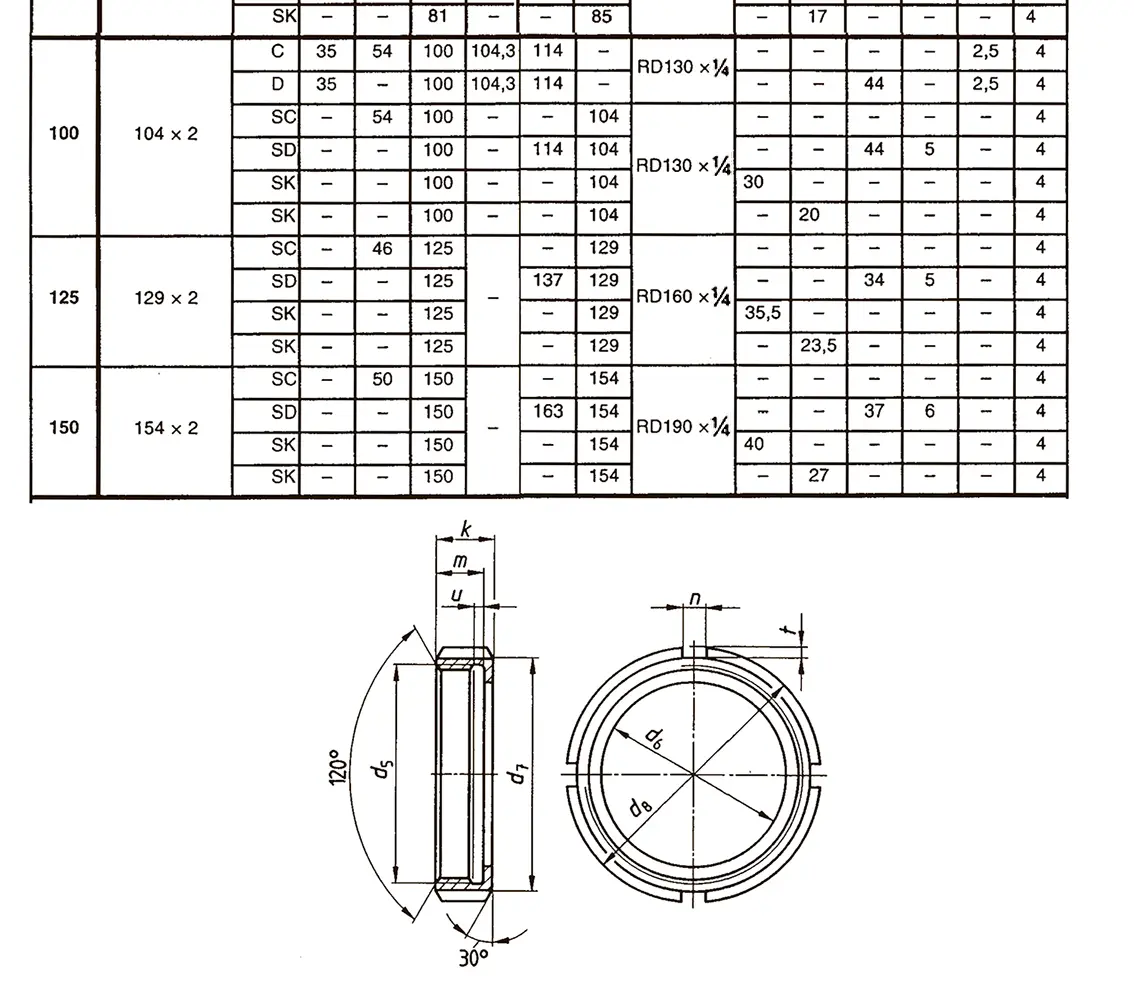
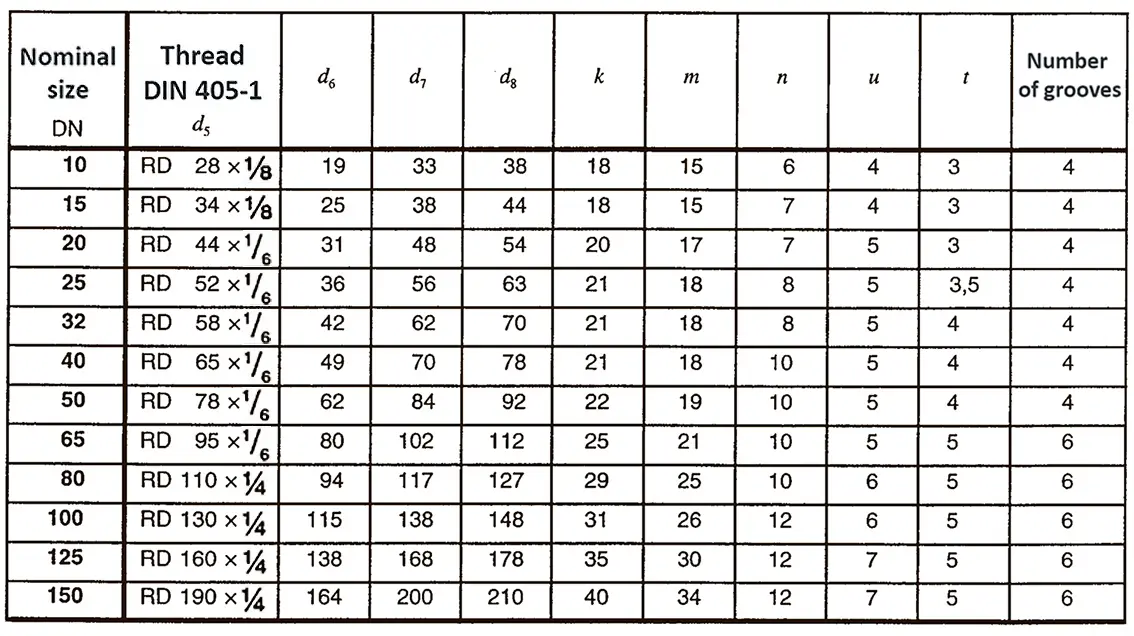
DIN 40400 Edison thread is used for lamp sockets.
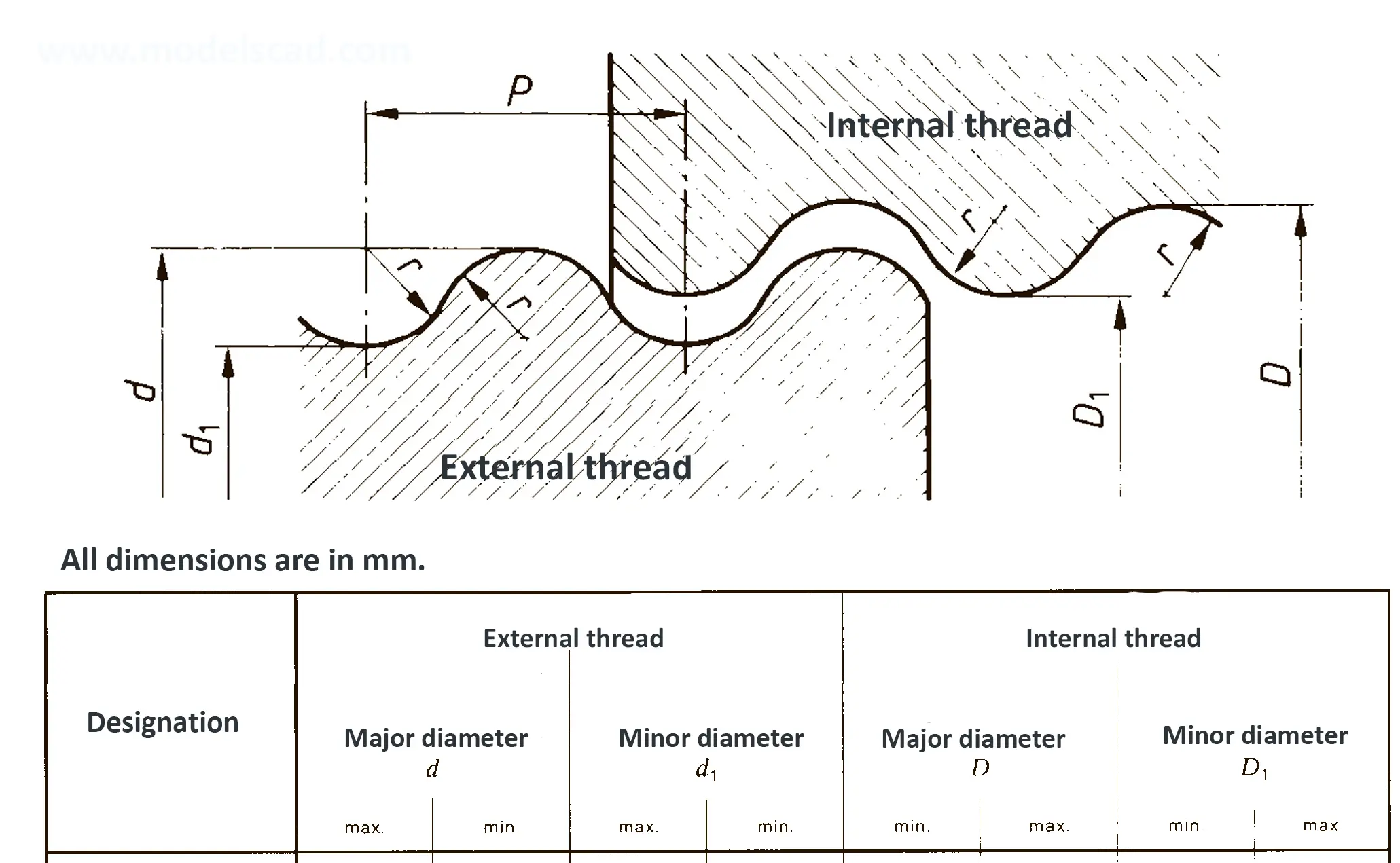
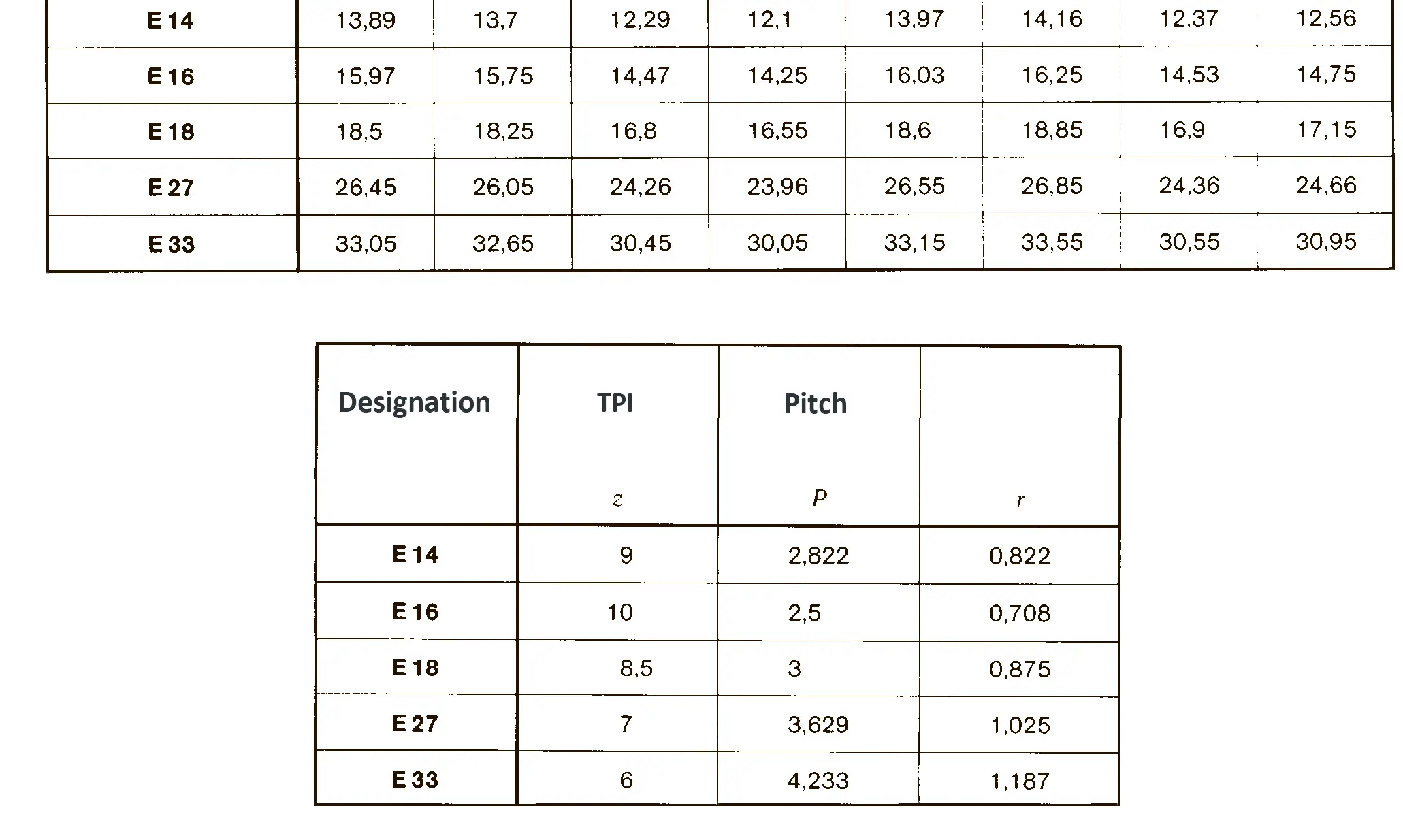
Knuckle thread DIN 168 is designed for glass containers.
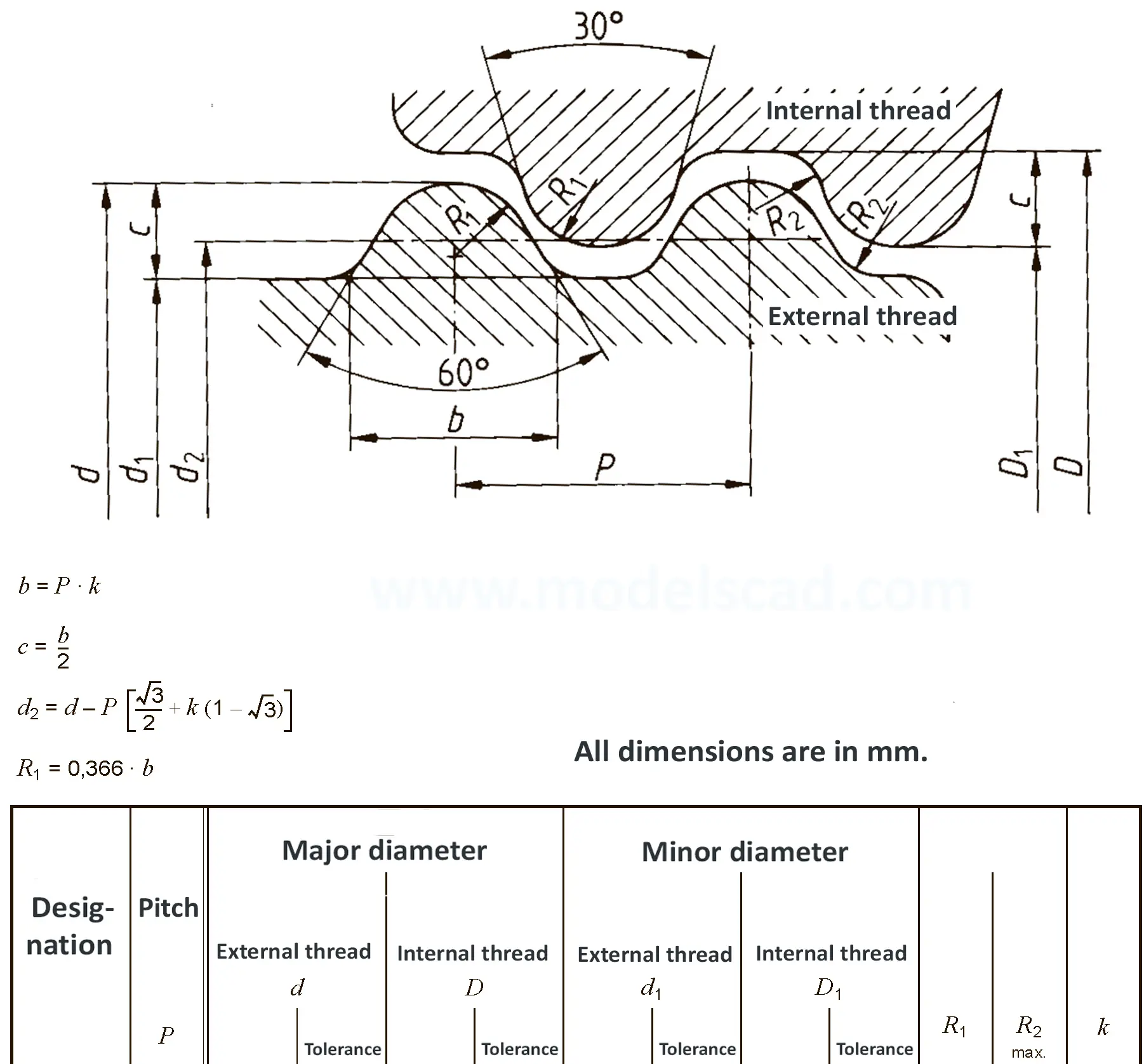
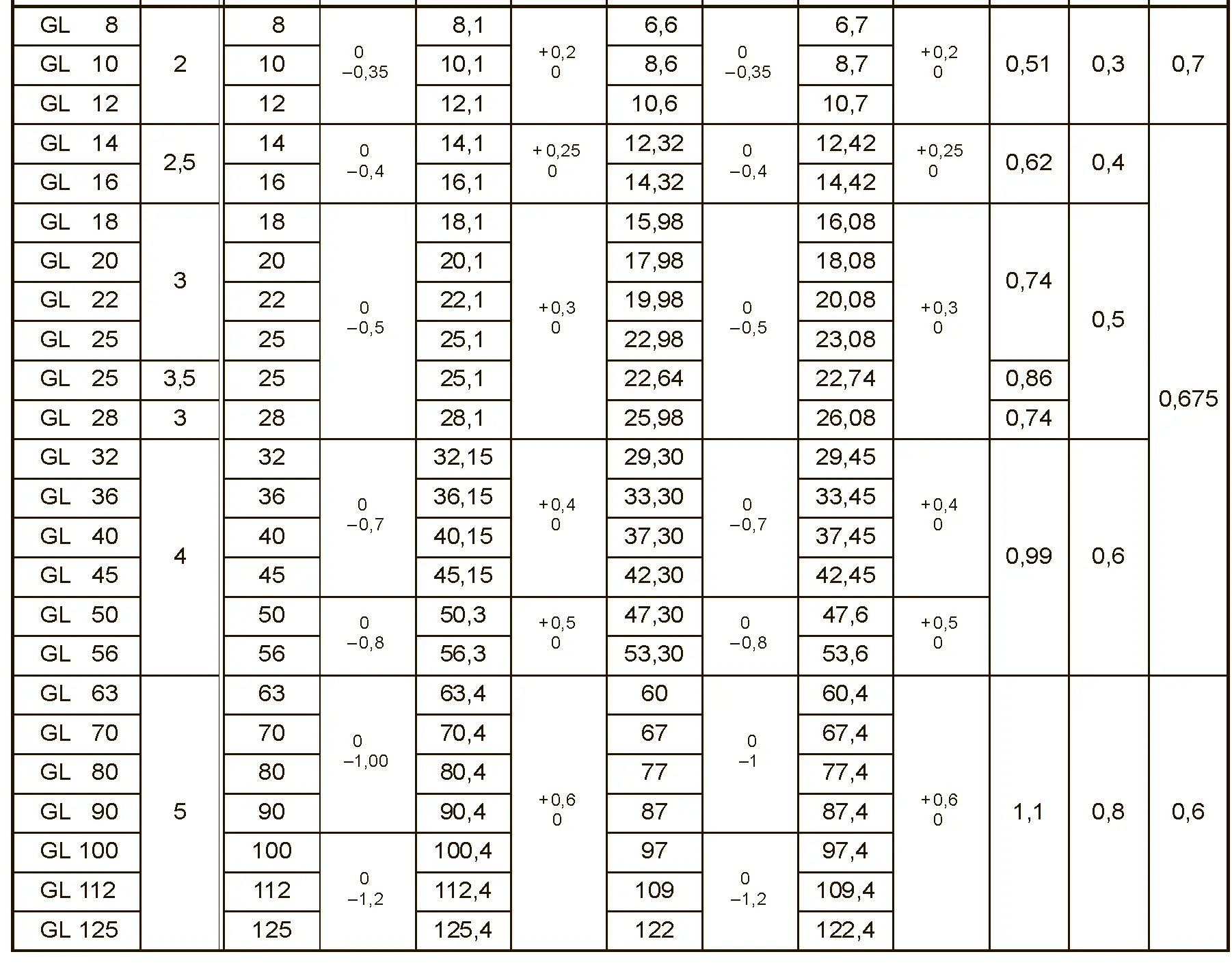
Buttress thread for plastic containers according to DIN 6063-1 and trapezoidal thread for plastic containers according to DIN 6063-2. Thread sizes in brackets is not recommended for use.
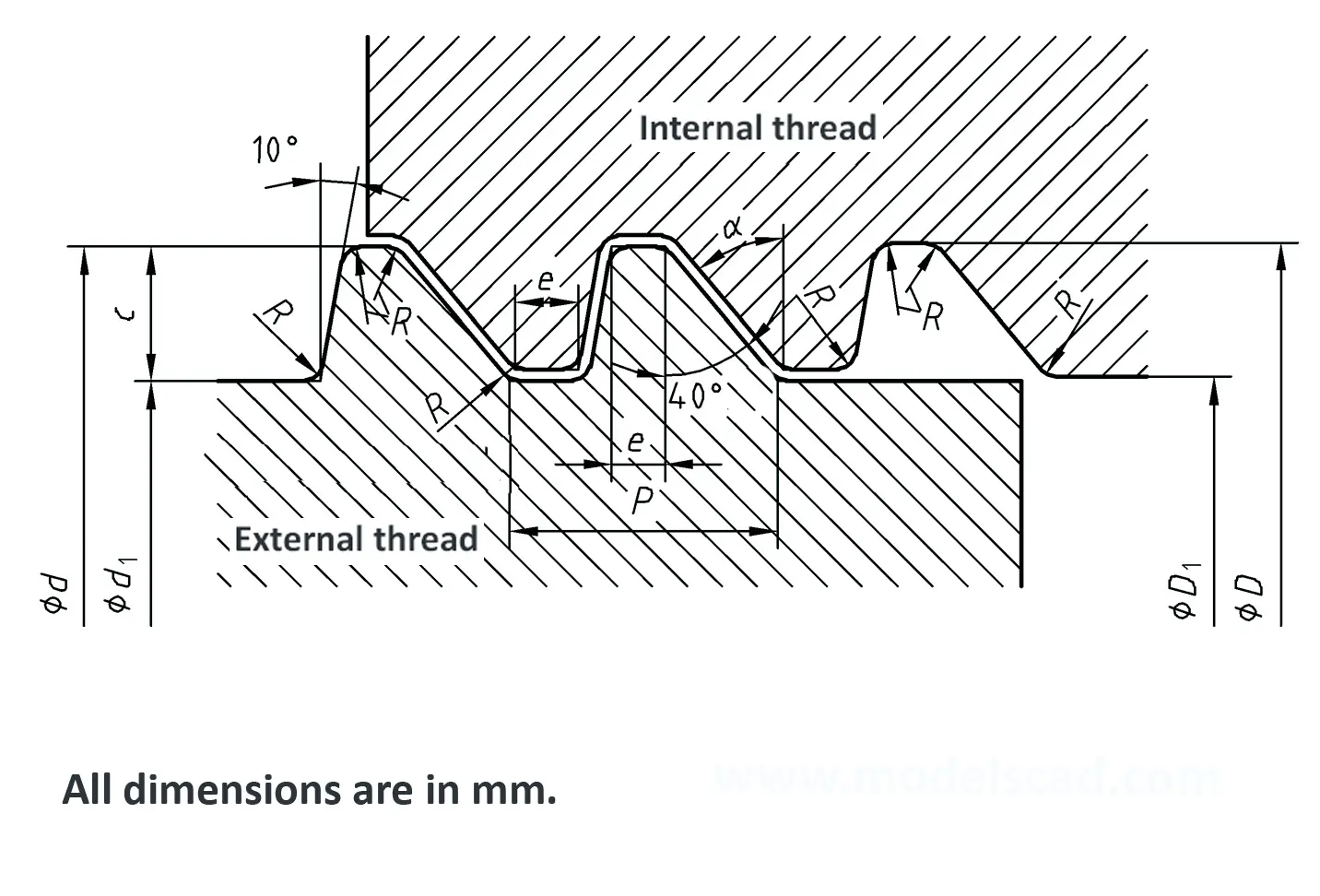
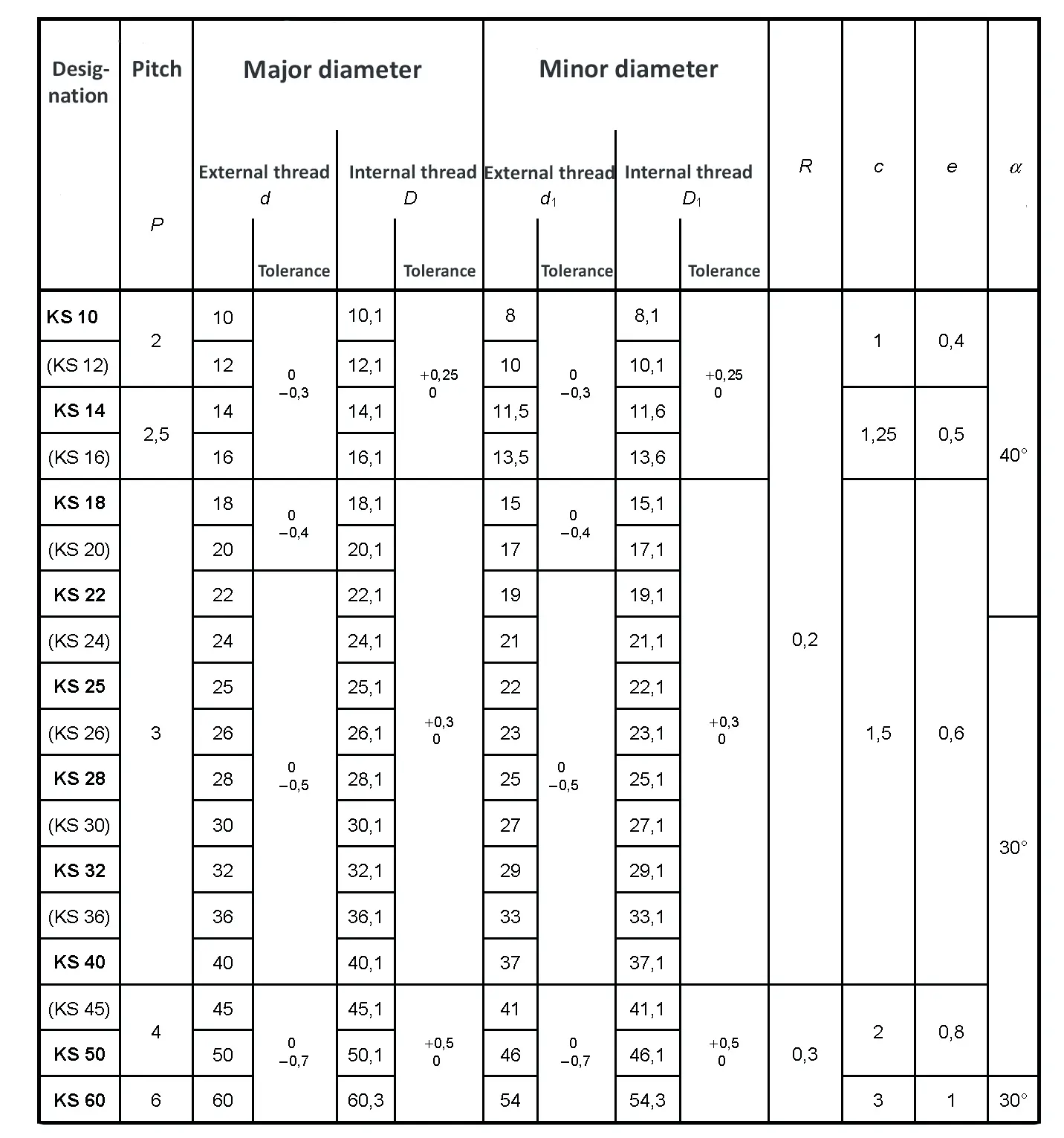
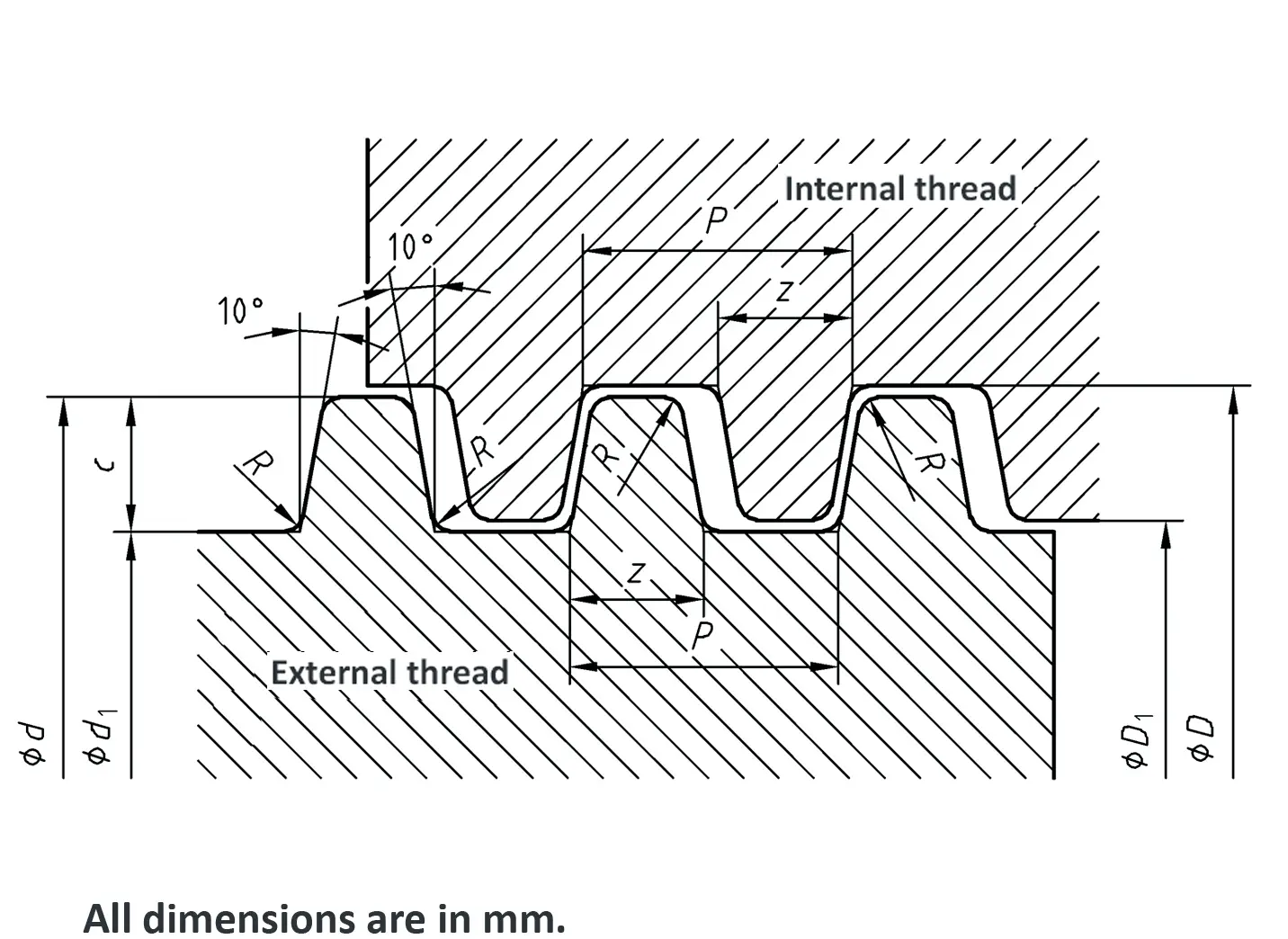
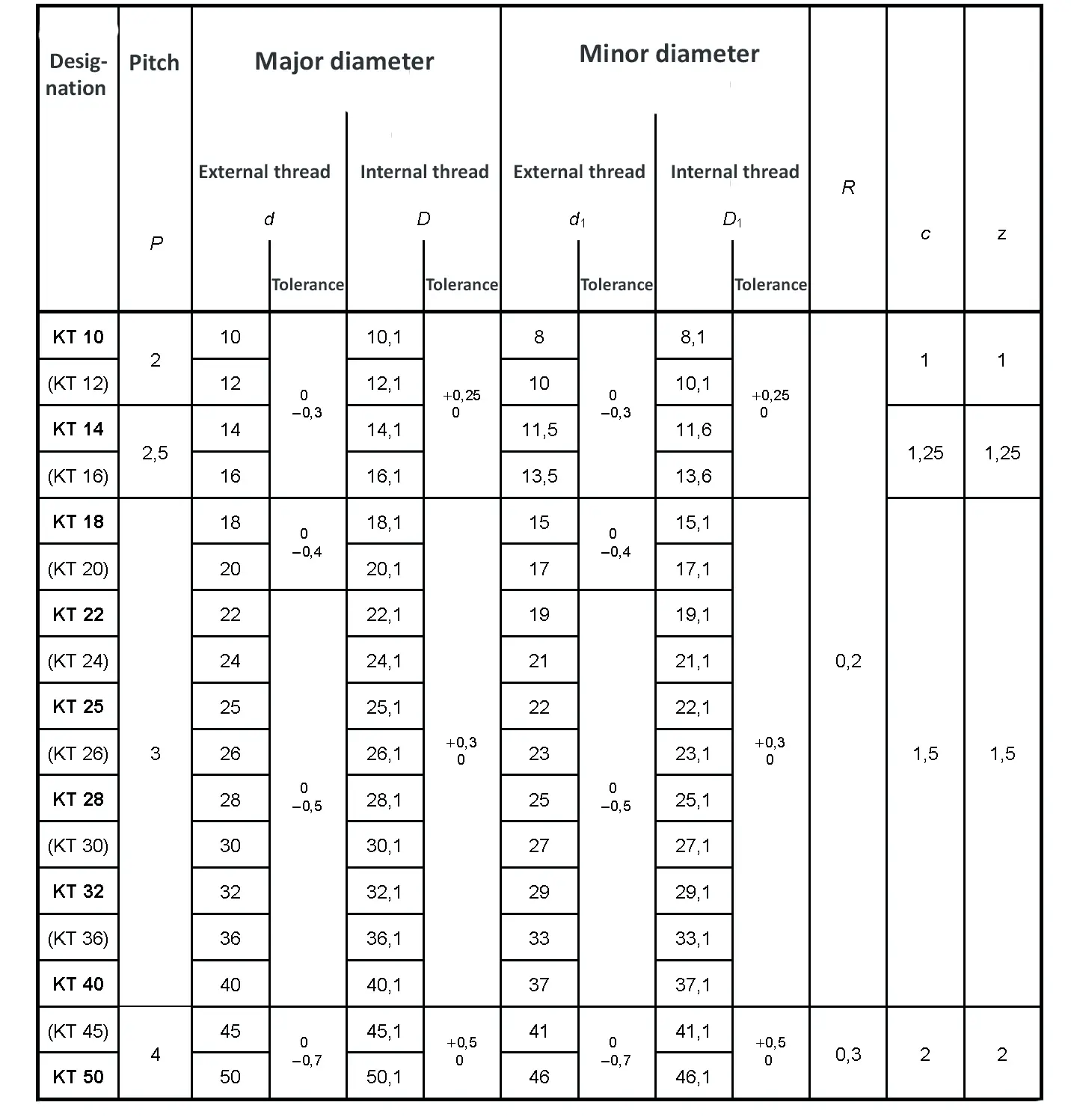
Threads according to this standard are intended for components in which the axial forces generated by tightening the nut are only to be converted into radial forces to a small extent. The flank angle is 33°.
Pipe thread for pipes and fittings. Parallel female thread and tapered male thread. Taper 1:16. The flank angle is 55°.
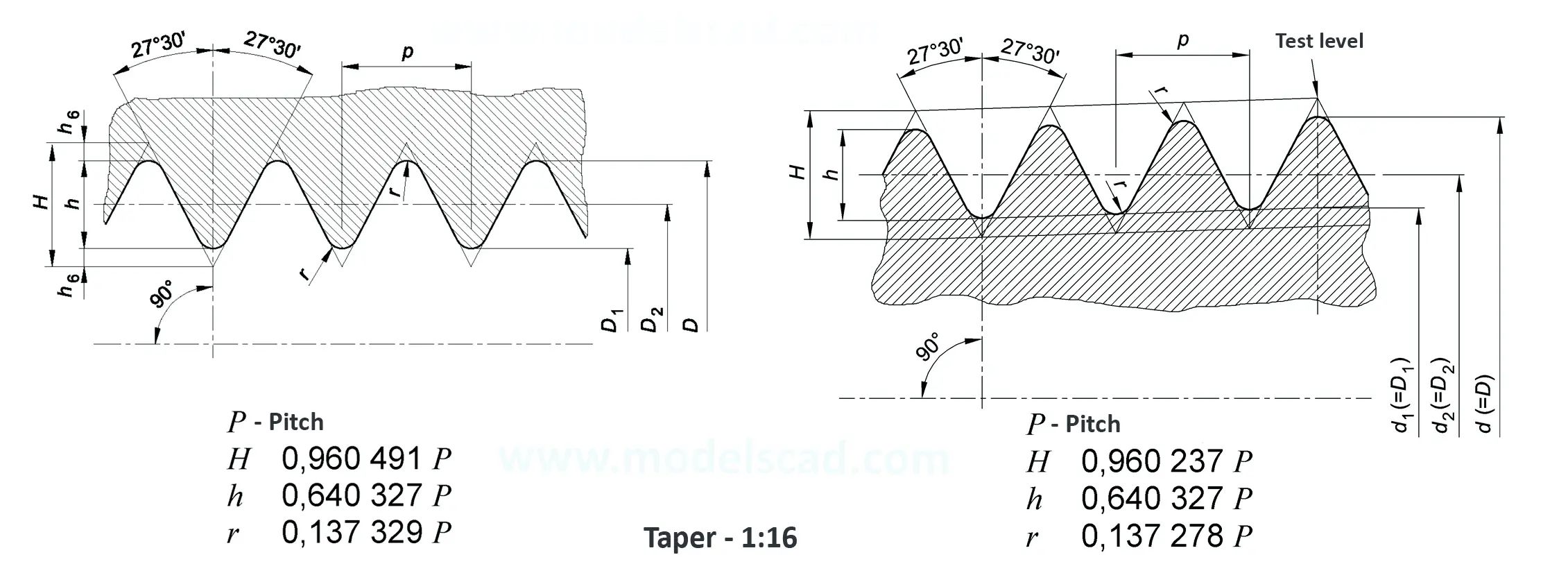
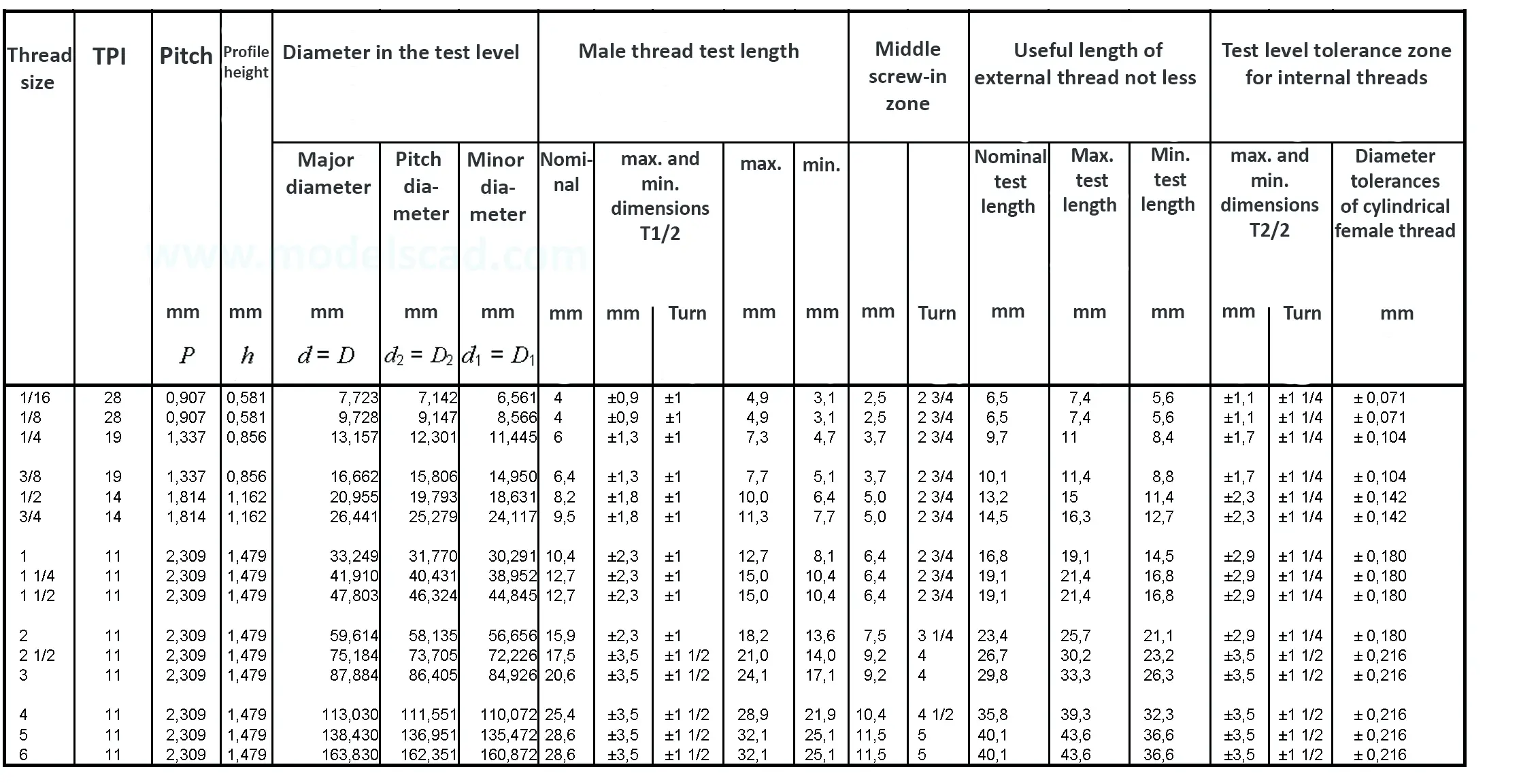
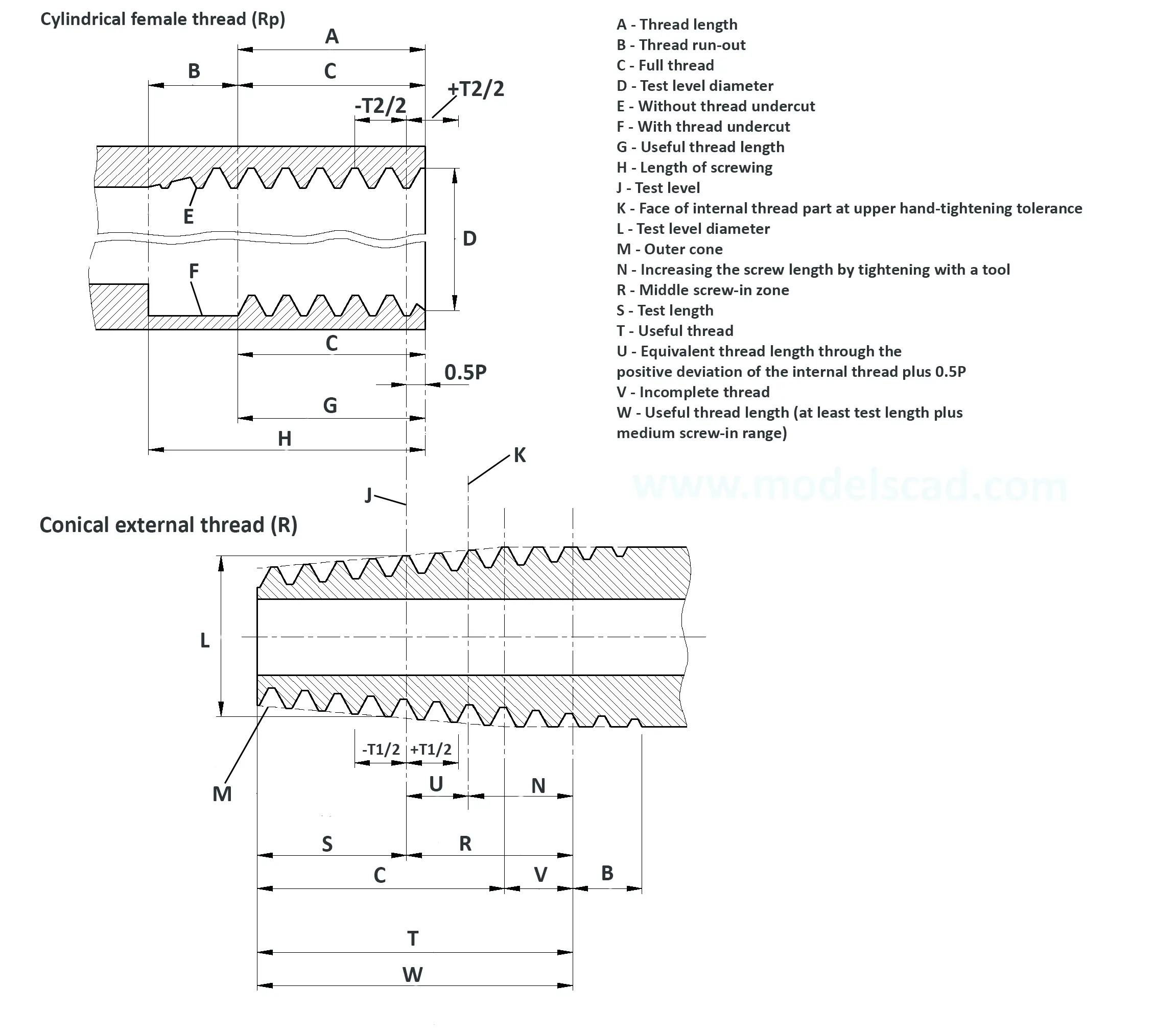
Pipe thread for pipes and fittings. Tapered female thread and tapered male thread. Taper 1:16. The flank angle is 55°.